Diesel fuel (diesel fuel in colloquial speech), due to its chemical properties, at low temperatures might freeze. As diesel fuel hardens, it can clog fuel lines and filters and jam the fuel injection pump. To prevent this from happening, in winter, at gas stations, they sell varieties of diesel fuel with a high freezing threshold. Depending on the region, the freezing point and fractional properties may differ. It is conventionally divided into summer, interseasonal, winter and arctic.
If you want to find out at what temperature diesel fuel freezes in the tank, depending on the type, at what ambient temperature you should use winter fuel, and when you need to fill in arctic fuel, read the article.
What to do if diesel fuel freezes?
The diesel fuel is frozen, what should I do?
- It is advisable to drive (push) the car into a warm box.
- Pour an additive to prevent diesel freezing into the tank, at a rate of 1.5-2 times more than what is written in the instructions for using the additive.
- Charge the battery.
- Point a hairdryer at the fuel filter and let it work. (
Interesting materials:
How many astronauts have flown into space? How many episodes are there in the series Practice? How many stickers are there in VK? How long does the installation last? How many payments are due upon redundancy? How tall is the submarine? How much energy is released from 1 gram of fat? How much suprax is excreted? How long to beat the charlotte dough? How much does a chef earn in Moldova?
Why does diesel fuel freeze?
The answer to the question why diesel fuel freezes lies in its composition. Diesel fuel is a mixture of heavy oil fractions obtained during its distillation. Among these fractions there are paraffins , which have a relatively high freezing point (+3°C). Their removal is a complex and costly chemical process, so paraffins are not removed from summer diesel fuel, in which they do not interfere. In addition, they create additional lubrication of parts in the fuel system.
So if you use summer fuel in severe frost, then the answer to the question of whether diesel fuel can freeze while driving is yes. Despite the fact that during engine operation, fuel from the tank is constantly pumped into the injection pump, where it is heated and the excess is drained through the return line into the tank, in severe frost this heating is not enough. And if your diesel fuel freezes while driving, then you definitely filled the tank with cheap and not very high-quality fuel, suitable only for summer.
GOST 305-2013, which regulates the quality and composition of diesel fuel in Russia and the Customs Union, does not establish clear standards for the mass fraction of all components. Therefore, there are no clear requirements for paraffin content for seasonal types of diesel fuel. Their number is determined only indirectly, by the kinematic viscosity of the fuel. According to GOST 33-2016 it should be like this:
Paraffin separation in the filter when summer diesel fuel freezes
- for summer fuel – from 3 to 6 mm²/s;
- for off-season – from 3 to 6 mm²/s;
- for winter – from 1.8 to 5 mm²/s;
- for the Arctic - from 1.5 to 4 mm²/s.
The higher the viscosity numbers, the thicker the fuel, and accordingly, the higher the mass fraction of paraffins in it. And since the temperature at which diesel freezes directly depends on paraffins - the thicker it is, the sooner the fuel will begin to crystallize! So if you pour such fuel into the tank in winter, there are often situations when diesel fuel freezes and the engine cannot work without heating, and sometimes even fails.
Someone then may ask - why not drive in winter all the time, and not worry about how many degrees the diesel fuel freezes at ? And all because, in addition to the price component, seasonal fuels, due to different amounts of paraffins, have different flash points (summer and off-season 40-50, and winter 30 degrees) and cetane number (summer 51, and winter 47 ). Plus, the lubricating properties of the winter one will be worse. As a result, all factors together will answer the question: is it possible to drive diesel fuel in winter in the summer and why you have to monitor the weather.
Features of combating frost
The struggle to reduce the freezing point of fuel, allowing the engine to be operated in cold weather, is carried out in various ways. The most expensive is replacing summer fuel with winter fuel. The latter, intended for cold climates, is obtained by dewaxing - removing hydrocarbons with a high melting point at the production stage.
Since this reduces the fuel yield from crude oil by half, the price also increases. The freezing point of such winter diesel fuel is - 45 ºС, it becomes cloudy at -35 ºС, it is recommended to use it at a temperature not lower than -30 ºС.
A simpler way is to obtain winter diesel fuel for temperate climate zones. In summer, depressant additives are added, which prevent paraffin crystals from sticking together. The freezing point of this summer diesel fuel, which has actually become winter-grade, is -35 °C, and the cloud point is -25 °C. It is recommended to use it down to -15 °C.
Every motorist can make summer fuel into winter fuel in this way outside the factory. To do this, when frost sets in, you need to add a depressant additive in accordance with the instructions. It is important that during this operation the fuel temperature is not lower than +5°C, otherwise the effect will be zero.
What methods of lowering the freezing point should we be wary of?
Along with the recognized methods of reducing the pour point, there are many fraudulent methods. Most often, summer diesel fuel is diluted almost half with kerosene or other petroleum products and the resulting composition is passed off as normal winter fuel. It does work at low temperatures, but kerosene sharply reduces the lubricity of the fuel - in just one season, a car engine can fail.
It is impossible to find out what freezing point the purchased diesel fuel has. We recommend not buying fuel from random sellers, but refueling at reliable and proven gas stations.
If you liked our article and we were somehow able to answer your questions, then we will be very grateful for your good review of our site!
Results
Summer diesel fuel is a type of diesel fuel used in the warm season at positive ambient temperatures. In reviews of diesel fuel, car owners note its efficiency, good viscosity and density, which improve the softness and smoothness of the engine. The only nuances are the correct choice of fuel brand - many sellers dilute the fuel, which is why it loses its properties and can lead to fuel system problems. Since the minimum freezing point of summer diesel fuel is -5 o C, it must be used only at positive ambient temperatures.
Is it possible to drive in winter on summer diesel fuel?
In severe frosts, such experiments on your own expensive motor are unacceptable. But in the most extreme cases and at slightly negative temperatures, you can add special compounds to the tank that lower the temperature threshold.
Such antigels allow it to change by a few degrees, but no more. You must first study the specific characteristics and procedure for use according to the manufacturer. And remember that this is only a temporary measure.
It is now unacceptable to dilute fuel with kerosene and especially gasoline, as old drivers did with outdated engines. The motor will not last long on such mixtures; its specific characteristics are too high; everything there already works close to the strength limit.
Diesel fuel is summer, and frost is just around the corner. What to do to avoid problems?
“Frosts are coming, but gas stations are still selling only summer diesel fuel. How scary is it if it ends up in the tank in sub-zero temperatures?” – the reader is interested. Well, let's figure it out.
We discussed this topic in some detail just a year ago, on the eve of the winter season. So now we will voice only the main points and give advice on the essence of the issue.
On the one hand, the alarm seems premature: frosts are not yet predicted, and if the temperature briefly drops “slightly below zero” at night, then this is not scary - even summer diesel fuel will retain its filterability qualities. However, there is a nuance: when moving, the incoming air cools the fuel lines located outside (under the bottom), which can also lead to fuel solidification. Plus, it’s only a matter of time before the temperature drops to critical values for summer diesel fuel. And this raises a question consonant with what the reader asked: what to do?
The ideal comprehensive solution for a diesel car is a timely transition to winter diesel fuel, replacement of the fuel filter, and for an old car, also flushing the tank. But we are realists: the last point for the majority becomes relevant only when problems arise with the fuel system; winter diesel fuel will begin to be filled when it appears at the gas station, and summer fuel will be “rolled out” from the tank.
What to do now, when summer diesel fuel is both in the tank and at the gas station? The most obvious advice is to use anti-gel additives during this transition period. Let us remind you that they must be filled in a timely manner, at the time of refueling. If diesel fuel has frozen, additives will no longer help.
Another option to solve the problem is to install a fuel heater. Depending on the design features of the fuel system, you can install a bandage or flow-through heater (or even two at once), and this will also be a fairly effective solution.
But, as in the case of anti-gel additives, this reduces the risks during the transition period, when temperatures are winter and the fuel in the tank is still summer. Only high-quality winter grade fuel with a serviceable vehicle fuel system can guarantee that problems are eliminated.
Clean and bright. Fuel filters in the Automotive Business ad database
Source
Fuel composition
The main substance is oil. It consists of 85% carbon and 15% hydrogen.
It produces various types of fuel:
- petrol;
- diesel;
- kerosene.
Gasoline is the most volatile of them. It is toxic and has the ability to evaporate.
Diesel fuel comes in two types: summer and winter. They are distinguished by the amount of paraffin additives (less in winter).
Calculation of specific gravity for 20 C
- Measure the density and average temperature of diesel fuel.
- Calculate the difference between the actual temperature and 20 ◦C.
- Multiply the temperature difference by the correction factor.
- If the actual temperature is less than 20 ◦C, then subtract the result of the calculation of the third point from the density value at a given temperature. If the liquid is warmer than +20 ◦C, then these values need to be added.
For example, the density of fuel at a temperature of 0 ◦C is 0.997 g/cm3. The difference between the actual temperature and 20 ◦C is 20. Then 20 × 0.0007 = 0.014 g/cm. Since at 20 ◦C the density of the fuel will be less than at 0 ◦C, it is necessary to subtract the correction value from the density at 0 ◦C - 0.997-0.14 = 0.857 g/cm3. To convert the result from grams per cubic centimeter to kilograms per cubic meter, you need to multiply the value expressed in grams per cubic centimeter by 1000. That is, the specific gravity of our diesel fuel at 20 ◦C will be equal to 857 kg/m3. This allows us to make the assumption that, judging by the calculation results, it is more likely to be summer than winter. It is impossible to make an exact conclusion about what season the fuel is intended for based on its density.
Relationship between fuel density and diesel efficiency
Since the combustion of diesel fuel, which has a high specific gravity, is accompanied by the release of more energy than the combustion of less dense fuel, it is obvious that the use of summer fuel is more economical. However, its use to increase diesel efficiency in the cold season is not possible. This is explained by the fact that in addition to kerosene-gas oil hydrocarbons, which contain the main energy reserve of the fuel, its composition also includes paraffins dissolved in them. The latter, even with a slight decrease in fuel temperature, harden, thickening the fuel and worsening the permeability of the fine fuel filter. As a result, the ability of fuel to be pumped through the power system and sprayed into the engine cylinders deteriorates. Therefore, winter diesel fuels contain additives that slow down the hardening of paraffins and the thickening of diesel fuel to a gel state.
These additives, while reducing the concentration temperature of the fuel, have no effect on its density at all. It is logical to assume that if you add an antigel additive to summer diesel fuel, the result will be economical winter fuel. But this is far from true. Because the additive will only lower the freezing point of paraffins dissolved in the fuel.
The diesel fuel itself will not become less dense, which means that as the temperature drops, it will thicken significantly, which will make it difficult to spray it in the combustion chambers and move along the fuel line. In addition, it is a mistake to believe that by pouring an additive into frozen diesel fuel, we will ensure that the paraffins in it melt and it will regain its fluidity.
To summarize the above, it should be noted that density is very important for winter fuel. For summer, such parameters as sulfur content and cetane number are more important. The fact that diesel is less economical in winter than in summer is, of course, largely due to diesel fuel being less dense than in summer, but not only that. Snow on the roads also does not contribute to efficiency.
Diesel fuel express testing method
In everyday life, the owner of a diesel engine rarely needs to check the quality of the fuel. Since he usually refuels his car at the same gas stations, the quality of the fuel at which has been tested during the operation of the car, and most likely suits the car owner. If you are in an unfamiliar place in winter, express analysis of winter diesel fuel in frosty weather can be carried out using the simple method described below.
Signs of diesel fuel freezing
If the car does not start in cold weather and there is a suspicion that the diesel fuel in the tank or fuel pump has frozen, you can check this using several signs.
The first signs of frozen diesel fuel in the tank are its cloudiness and gel-like appearance . Sometimes you can check whether the diesel fuel is frozen by quickly unscrewing the fuel filter flask. You can look at it to see if there are any paraffin flakes there. When diesel fuel freezes, its consistency changes as the temperature decreases as follows:
Stages of diesel fuel freezing
- Cloudiness appears
. As the limiting freezing temperature approaches, diesel fuel loses its transparency, but the motor still works normally on it. - Small clots, sediment, and crystals are formed
. When the lowest temperature at which the use of a given grade of fuel is permissible is reached, thick and solid inclusions become larger and more noticeable. The engine can still work on such diesel fuel, but instability is possible. - The diesel fuel acquires a mushy consistency
. If the temperature outside is lower than the maximum filterability temperature of the selected type of diesel fuel, it becomes thick. It is unrealistic to start the engine on such fuel and drive; you will most likely drain the battery. Frozen diesel fuel in the filter with such a consistency can tear its paper and dirt will go into the nozzles. - Large clots appear
. When the temperature is significantly (10 degrees or more) below the filterability limit, diesel fuel becomes cloudy and hardens, and large pieces of crystallized fractions appear in it. If the diesel in the fuel injection pump is frozen, then attempts to start the engine using such fuel can lead to its breakdown.
The most typical symptoms of frozen diesel fuel are given in the table. Along with them you will find information about what frozen diesel fuel looks like, at what frost it freezes and whether it is possible to start a car with such fuel, about the temperature threshold for their appearance and the possibility of use.
Signs of diesel fuel freezing in a car: table
| Sign | Causes | Development temperature | Possibility of use |
| Cloudiness | Natural chemical processes | When temperature changes, for example, +10 during the day and -10 at night | If initial symptoms of diesel fuel freezing appear, but it is not cold outside, you can drive it without risk |
| Appearance of sediment | Oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel | A short decrease in temperature to the filterability threshold (-5 -15 depending on the type of fuel) | CO2 emissions increase, especially in cars without catalysts; short-term use is allowed |
| Thickening | Beginning of paraffin crystallization, freezing of water (condensate in diesel fuel) | Below 0 degrees, depending on the seasonality of the fuel | Possible problems with starting and unstable idle speed before warming up, risk of freezing while driving with further cold weather |
| Crystallization | Freezing of paraffin in diesel fuel | From -10 and below, depending on the seasonality of diesel fuel | Difficult to start, may not start and stall, high risk of freezing while driving |
| Delamination | Chemical decomposition into fractions of diesel fuel components. | It depends not on temperature, but on the duration of storage without movement, but at the same time, being in a frozen state for a long time catalyzes this degenerative process | Unusable |
Environmental Standards
They are as follows:
- Euro-3. A currently obsolete standard that was relevant until 2005. The fuel was discontinued after new requirements were developed that it did not meet.
- Euro-4. Replaced Euro-3, which was no longer in use, and began to be used after 2005. All vehicles imported into Russia must comply with this standard since 2013. The exception is cars manufactured before 2012 - the previous Euro 3 class applies to them.
- Euro-5. A relatively new fuel quality standard, compliance with which in EU countries is mandatory for passenger cars manufactured since 2009, and for trucks manufactured since 2008. In Russia, this standard is also valid and applies to vehicles imported into the country.
- Biodiesel is worth mentioning separately. The peculiarity of this type of fuel is the vegetable and animal fats included in its composition. Diesel fuel is the result of processing various plants, including rapeseed and soybeans. The peculiarity of this type of fuel is the ability to use it as an independent fuel and as a special additive to other types of diesel fuel. Biodiesel is marked with the letter B in the United States, after which the percentage of the composition in the total mass of fuel is indicated. For such fuel, the cetane number is in the range of 50–51 units.
The fuel supply is frozen, what to do?
What to do if diesel fuel is frozen
Now let's move on to our everyday life and questions from readers, why is gasoline not supplied to the injector or carburetor from the tank? What's frozen? Of course not! All the fault here is as fuel, sometimes the owners themselves.
SO
: I won’t criticize all gas stations now, but now there are more or less conscientious ones. However, in many, especially “unnamed” gasoline, they are mercilessly “fueled” - sometimes with diesel, sometimes with water, but who knows what, you can even find fuel oil and oil.
What's happening? In summer and warm weather, water and other “bad stuff” float at the bottom of the tank, sometimes falling on the filter mesh, but it does not let them through. This way they remain “filtered” and your engine runs clean without problems.
But with the onset of frost the situation changes dramatically. Water freezes already at 0 degrees, diesel, if it is not “winter”, also begins to thicken, and other petrochemical products too. Thus, a dense film forms on the mesh of your fuel filter, which does not allow fuel to flow through the line, it seems that it is working, but no fuel is flowing! This happens all the time, no one is immune from it.
I also pointed out that sometimes the drivers themselves are to blame - why? It’s also simple - water can get into the tank when refueling a car in rainy or snowy weather, or when pouring gasoline from a canister through a regular funnel, and who knows what’s in that canister at the bottom! So when pouring gasoline into the tank from a canister, use a funnel with a mesh, there will be fewer problems in winter.
Now let's watch the video version.
Gasoline is used as fuel for most passenger cars. It is a mixture of hydrocarbons having a boiling point between 30 and 205 degrees Celsius. In addition to hydrocarbons, gasoline contains impurities containing nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen.
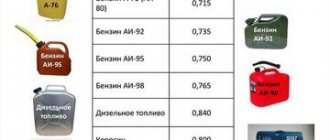
Depending on the amount of certain compounds, motor gasoline is divided into different grades, which have slightly different performance properties:
- AI-92;
- AI-95;
- AI-98.
With the tightening of environmental requirements, gasolines with a lower octane number, such as A-76 or AI-80, and, therefore, a “dirtier” chemical composition, are currently not produced.
Features of summer diesel fuel
Literally a few degrees below zero will turn summer diesel fuel into a viscous substance, from which paraffins will begin to fall out.
In theory, if the fuel meets the standards, it should pass through the filter down to -8 degrees. But in practice it will be almost unusable and will begin to clog its pores already at -5. This is normal for summer trains, but it is detrimental to engine performance.
The filter will be the first to suffer. This alone is enough to stop the engine. But similar deposits will be throughout the line, in the tank, pipes, pumps and injectors.
Even just warming up the system to revive the engine and replace diesel fuel will be very difficult. For cold weather, regardless of the climatic characteristics of the region, winter diesel fuel should be used. The problem will arise without warning, so you need to take care of the motor in advance.
Freezing point of diesel fuel
At what temperature diesel fuel freezes in a car directly depends on its type. Four seasonal grades are produced and sold in Russia : summer, interseasonal, winter and arctic. Each of them has its own freezing temperature of diesel fuel, which directly depends on the maximum filterability temperature (PTF). PTF is the temperature at which fuel tested according to standards stops flowing through a standardized filter.
Since the air temperature for summer diesel fuel must be higher, it stops flowing through the filter with less cooling.
When diesel fuel freezes according to GOSTs: table (GOST 305-2013 and 55475-2013)
| Variety | Type | Density at +15, no more | Filterability threshold (PTF), not higher than degrees Celsius | Freezing temperature (TZ), not higher |
| L | summer | 863.4 g/l | -5 | Not regulated |
| E | off-season | 863.4 g/l | -15 | Not regulated |
| Z | winter | 843.4 g/l | -25 -32 for Z-32⚹ -38 for Z-38⚹ | -35 Not regulated⚹ |
| A | arctic | 833.5 g/l | Not regulated -44 for A-44⚹ -48 for A-48⚹ -52 for A-52⚹ | -45 Not regulated⚹ |
⚹ — requirements of GOST 55475-2013 for dewaxed winter and arctic varieties
The table above shows the regulatory requirements for different types of diesel fuel, but it is impossible to say with absolute certainty at how many degrees diesel fuel freezes. The fact is that it is technically unrealistic to achieve constancy of its fractional composition at a refinery (and this is not necessary: it is not the exact composition that is important, but the working properties of the flammable liquid) due to the different compositions of oil, and the components (fractions) contained in the fuel have different temperatures crystallization.
Even when pieces of ice float in the tank, some of the fuel remains liquid. That is why PTF was chosen as the determining criterion for standardization, which shows at what temperature normal pumping of diesel fuel through the filter becomes impossible.
As you can see in the table, for regular summer and off-season diesel fuel, GOST regulates only PTF . For winter grades of diesel fuel, the specification is also indicated, at which the bulk of the fuel turns into ice. For ordinary Arctic diesel fuel there are no standards for filterability limits, but it is strictly indicated at what temperature diesel fuel of this type freezes. Filterability limits are indicated only for special dewaxed winter varieties in accordance with GOST 55475-2013.
Due to the fact that diesel fuel at gas stations is stored in underground tanks, where the temperature almost never drops below 0, summer fuel does not freeze there even in severe frosts. Therefore, you won’t be able to tell right away what kind of diesel fuel was filled for you by eye.
To quickly check on your own at what temperature the diesel fuel freezes in the tank, without placing it in the freezer, you can use a hydrometer for petroleum products with an operating range of about 800-900 g/l.
This inexpensive device (from 300-500 rubles) will allow you to almost immediately understand what was poured at the gas station. To do this you need:
Samples of different types of fuel at sub-zero temperatures
- At the end of refueling, pour 100-300 ml of fuel into the container.
- Warm the vessel to approximately +15 degrees.
- After heating the diesel fuel, measure its density with a hydrometer.
If the density is above 845-850 g/l , it means that the fuel contains a lot of heavy fractions (including paraffins) and it is not advisable to drive it in winter. If the density does not exceed 840-845 g/l , this is winter diesel fuel, which can be used in severe frost. And if the obtained figures are below 830 g/l , this is a frost-resistant fuel from the “arctic” category.
When does summer diesel freeze?
At what temperature summer diesel fuel freezes depends on its fractional composition. Fuels with a high content of heavy components, having a density of about 880 g/l , can quickly “set” even in slight frost. GOST sets the filterability threshold at -5 degrees , but there are no clear criteria specifically for freezing.
That is, the document does not indicate at what degrees summer diesel fuel freezes, but at the same time guarantees its suitability for use only at temperatures not lower than -5. And at what frost the diesel fuel freezes depends on the composition. But in any case, as soon as the temperature outside is stably below zero, driving on summer fuel is undesirable. Diesel fuel can thicken at -5, and already at -10 form lumps of paraffin and ice.
When does demi-season fuel freeze?
How antigel, gasoline and kerosene work when added to diesel fuel at a temperature of -20: video
At what temperature does off-season diesel fuel freeze - similarly depends on the fractions in its composition. According to GOST, grade E fuel should have performance characteristics no worse than summer grades (grade L), but usually manufacturers label fuel that is slightly more frost-resistant and can withstand up to -20 degrees . When diesel fuel freezes for the off-season of a particular company, you can find out in its passport, which gas station workers must present upon request.
Since the properties of diesel fuel of grades E and L are very similar, the answer to the question of whether it is possible to mix summer and winter diesel fuel is positive: it is possible. Please keep in mind that the properties of such a mixture will most likely be closer to summer fuel than to off-season fuel.
When does winter diesel freeze?
In winter diesel fuel, the freezing temperature according to GOST is set at -35 degrees . Therefore, you don’t have to worry about the question of whether winter diesel fuel can freeze until such severe frosts occur. This type of fuel should not “set” down to -35 °C , and be in a gel state down to -50 °C. True, such a threshold depends on whether this fuel complies with GOST or not. The upper limit at what temperature winter diesel fuel freezes in reality depends on its composition. At some gas stations it can be even lower - from -25 to -32 degrees.
Popular antigel additives for diesel fuel
The filterability threshold for regular winter fuel is set at -25 degrees . So if you buy diesel fuel not in the northern region, then even in such frost, normal pumping of fuel through the filter is not guaranteed. And the situation when winter diesel fuel freezes in extreme cold is not at all uncommon.
Therefore, when refueling before very severe frosts, it does not hurt to add an antigel additive to the diesel fuel, either in the proportion of kerosene (or gasoline). Diesel with antigel can freeze in only two cases - a low concentration of the additive or it is added to summer fuel, to which you cannot add a lot of such an additive.
When winter diesel fuel appears at gas stations depends on the region. In the north it is usually the beginning of October, in the middle zone it is November, and in the south it is the end of November or even December. It is at the same ambient temperature as in these months that winter fuel should be used. When winter diesel fuel is delivered to a gas station, a banner often appears. In mid-latitudes, very often in this case they write winter down to -20...-22, but this is nothing more than a marketing ploy, because they will sell off-season diesel fuel, and not real winter fuel.
Can Arctic diesel fuel freeze?
Arctic fuel at a gas station
According to general GOST 305-2013, ordinary Arctic diesel fuel , the freezing point of which should not be higher than -45 degrees . However, there are varieties whose properties are regulated by GOST 55475-2013. For them, the filterability limit is already indicated, but it is not regulated at what temperature “Arctic” diesel fuel freezes.
The main difference between winter diesel fuel and arctic diesel fuel that meets this standard is dewaxing. Refineries are not required to dewax ordinary winter diesel fuel, but they are required to comply with GOST 55475-2013.
Despite the absence of a standard indicating at what degrees diesel fuel freezes, fuel of Arctic grades A-44, A-48 and A-52 should not thicken earlier than at 44, 48 and 52 degrees below zero , respectively. That is, Arctic diesel fuel can look like a gel even below -55 degrees.
Arctic diesel fuel, which complies with GOST 55475-2013, is a good fuel for modern diesel engines. The standard limits its sulfur content, which is harmful to new engines, to 0.001%. Thanks to the presence of lubricating additives (compensating for the lack of sulfur), you can drive it all year round. But, due to additional technological operations, it is more expensive than winter, and is sold mainly in the northern regions. Gas stations in the middle zone sell it only during severe frosts. Therefore, it will not be possible to drive on such fuel all year round.
What to do to prevent diesel fuel from freezing or how to defrost it
Knowing when different types of diesel fuel freezes, monitor the forecast and always have either 10-20 liters of winter fuel or one of the additives in stock. To prevent the diesel fuel from freezing in the tank, use gasoline (added in proportion), kerosene or anti-gel. If it’s frozen, then a special defroster is poured into both the tank and the filter.
Density of summer diesel fuel
The functionality and efficiency of a vehicle's filtration and fuel equipment depends on the density of the diesel fuel used. The density depends on the temperature of the diesel fuel: the lower it is, the higher the temperature of the diesel fuel.
The heavier fractional composition of diesel fuel occurs at an increased density, which can lead to a deterioration in the processes of atomization and evaporation of diesel fuel. The consequence of this is the accumulation of deposits in the vehicle’s fuel system, which impair fuel circulation and form carbon deposits on the engine valves.
Summer diesel fuel has a density ranging from 840 to 860 kg/m3. The density of winter diesel fuel is 2 units lower. This parameter is measured using a hydrometer.