Published:
26.05.2016
Nowadays, most cars use a spark ignition system. Glow ignition was widely used before the invention of spark ignition. However, on modern cars the mixture can be ignited by heating and this is considered a negative incident.
To understand what the essence of this effect is, why it appears and how it differs from detonation, first let’s look at what the glow ignition process is.
Gas exchange in theory
It’s worth starting with the fact that previously spark plugs were not used to ignite the fuel mixture in the engine cylinders, but there was a special glow tube (head) preheated to a certain temperature. Such a system has long since sunk into oblivion, and today it is used only on low-power diesel engines. Glow ignition was completely replaced by spark ignition, and today it is mistakenly confused with detonation. But the glow type of ignition of the fuel mixture and its detonation are completely different phenomena.
When the detonation process occurs, explosive combustion of the fuel occurs with the inevitable appearance of a shock wave. And glow ignition is accompanied by normal combustion of the mixture, albeit with somewhat early ignition.
Consequences of incorrect ignition timing
Note that there is a certain relationship between the glow type of ignition and detonation, namely: in most cases, the occurrence of detonation, characterized by an increased thermal load on the parts of the power unit, leads to the occurrence of glow ignition, which is characterized by early ignition of the fuel, which leads to a decrease in power and overheating engine. Glow ignition is also dangerous because the engine can continue to operate even after it is turned off. And if this process is not eliminated in time, the engine may simply fail.
Temperature - Exhaust Gas
The exhaust gas temperature in the engine cylinders of two-stroke gas engines and compressors ranges from 350 to 480 C, and in four-stroke gas engines at rated load from 510 to 520 C.
The temperature of the exhaust gases in the exhaust pipe of four-stroke engines depends on the type of engine and is 750 - 850 K for carburetor engines and 600 - 700 K for diesel engines.
The exhaust gas temperature should not be lower than 70 C.
The exhaust gas temperature depends mainly on the same factors as the temperature at the end of the expansion process. Further depletion of the mixture leads to a decrease in the exhaust gas temperature, since, despite the increase in combustion duration, the maximum cycle temperature decreases.
The temperature of the exhaust gases in an internal combustion engine is quite high, so the water vapor contained in them cannot condense and carries away the latent heat of vaporization.
The temperature of the exhaust gases (when exhausted from the cylinder) increases as afterburning on the expansion line increases. Typically, in diesel engines, 10–20% of the total heat introduced with the fuel into the cylinder is released in the afterburning section. The heat obtained during afterburning is less valuable from the point of view of converting it into mechanical work. Afterburning occurs under conditions of reduced oxygen concentration at decreasing pressure and temperature. In modern diesel engines, the average rate of heat release during the combustion process is approximately 150 - 300 kcal / kg deg; during post-burning it decreases from approximately 40–50 kcal/kg deg to zero.
The exhaust gas temperature depends on the crankshaft speed, mixture composition, flame front propagation speed, ignition or injection timing and other factors.
The exhaust gas temperature depends on the load and engine speed. With increasing speed and load, the exhaust gas temperature increases.
The temperature of the exhaust gases is regulated by changing the supply of a portion of fuel by pumps, which is carried out by moving the control rack in one direction or another. When the rack output increases by screwing in the adjusting screw, the fuel supply increases, and when it decreases (the screw is turned out), the fuel supply decreases. Moving the fuel pump rack by one notch changes the temperature of the exhaust gases by approximately 22 - 25 C.
The exhaust gas temperature is controlled by changing the amount of fuel supplied by both pumps of a given cylinder. In this case, you cannot cut down or move the stop installed on the pump rail when determining its flow on the stand.
The temperature of the exhaust gases in the converters is increased by reducing heat loss by insulating the converter body, using special screens, using the heat of the oxidation reaction, and also briefly reducing the ignition timing.
An increase in exhaust gas temperature against the maximum set (430 C) or when the temperature difference between individual cylinders is more than 60 E C can lead to cracks in the head or scuffing of the pistons. Therefore, the temperature of the exhaust gases is checked during all rheostatic tests of a diesel generator set, as a rule, at maximum diesel power and 850 rpm of the crankshaft and the temperature of the diesel outlet water is 70 - 80 C, the oil temperature is 60 - 75 C.
The most accurate determination of exhaust gas temperature can be performed using the calorimetric method. But its application under normal test conditions is quite difficult.
For the D100 diesel engine, the exhaust gas temperature and combustion pressure are adjusted by changing the adjustable parameters of both fuel pumps of a given cylinder. After adjusting the load on the cylinders, check the output value of the fuel pump racks. It is considered normal when the difference in gaps between the rack stop and the pump housing for all pumps of the D100 diesel engine does not exceed 0 3 mm, and for the D50 diesel engine – 0 1 mm.
Causes of spontaneous glow ignition
One of its possible causes is considered to be a low heat rating of the spark plugs, which causes them to overheat and the occurrence of this phenomenon. In this case, dealing with such a problem is quite simple: you need to opt for spark plugs recommended by the car manufacturer and having a higher heat rating. The corresponding table, which can be found on the Internet or in automobile reference books, will help you choose them correctly. This table also contains information about the interchangeability of spark plugs and helps to make the right choice for a specific type of engine.
In addition, glow ignition can be caused by overheating of the exhaust valve or piston. Reasons for this:
- low octane fuel;
- incorrect operation of the exhaust valve;
- damage to the piston part;
- low-power engine;
- Incorrect adjustment of the exhaust valve.
Also, the described phenomenon is a consequence of an incorrectly adjusted ignition timing, prolonged operation of the power unit at the maximum permissible load, and a clogged cooling system. Simply put, factors that negatively affect the engine and cause it to overheat lead to such a dangerous phenomenon as glow ignition.
Preventive measures
The following recommendations can be given as additional measures to prevent the occurrence of such a harmful phenomenon:
- The right choice of candles. It would be better if there is a separate set for winter and summer with different heat ratings.
- Constant monitoring of the cooling system, preventive cleaning of the radiator.
- Avoid overheating and keep it clean to ensure the best heat transfer.
- Carry out routine maintenance and timely maintenance.
- Monitor the load on the engine and do not expose it to increased and maximum loads unnecessarily.
Following simple and generally accepted rules and taking preventive measures will help keep the car engine in working condition for as long as possible and will delay its repair as much as possible.
Signs of a problem
Various deposits that appear on the walls of combustion chambers can cause glow ignition to occur. This often happens if the vehicle has an engine with a long working life. To prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to periodically wipe all parts on which plaque forms.
Experienced drivers will be able to identify that very dangerous moment immediately after turning off the ignition. In this case, the engine does not turn off, and the fuel mixture continues to detonate during ignition. At this time, you can observe an excessive amount of idle speed, and the car’s engine is not quite stable, you can even hear strong popping noises under the hood.
How does detonation manifest itself?
The occurrence of detonation in the cylinders is accompanied by a metallic ringing. At the same time, the engine itself vibrates, which is transmitted to the body, as well as a delay in stopping work (after turning off the ignition, the engine still runs for some time). If these symptoms appear, detonation combustion occurs in the engine cylinders.
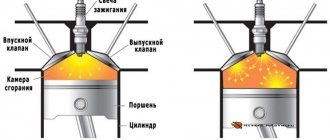
In a gasoline engine, the air-fuel mixture, which is pumped into the cylinders, is pre-compressed by a piston, which ensures mixture formation and an increase in temperature, which affects flammability. The pressurized mixture is ignited by a spark from the spark plug. In this case, a flame front is formed, which spreads throughout the entire volume from the ignition point to the edges. The propagation process is slow - 20-30 meters per second. The combustion of fuel is accompanied by an increase in temperature inside the cylinder and pressure, which acts as energy converted into mechanical action.
Detonation combustion is a process in which an increase in pressure and temperature leads to the appearance of oxidation processes of the components of the mixture, which causes the appearance of an additional source of ignition. As a result, the flame front spreads faster than during normal combustion (flame propagation speed exceeds 1500 m/sec). Instead of one source (from a candle), there are two (the second is spontaneous), while the front of the flame of each of them goes towards each other.
Video: DETONATION VISUALLY
In the cylinder, this process causes an explosion of the mixture, rather than a gradual spread of flame. The collision of two flame fronts leads to an increase in pressure and temperature. And this leads to increased shock loads on the cylinder-piston group and the crank mechanism, and the engine overheats due to temperature.
Why does it occur
The reason for the occurrence of “incorrect” ignition is a reduced glow number of spark plugs. Car enthusiasts call this phenomenon “hot spark plugs”. During engine operation, they heat up to high temperatures. If they heat up to 400 degrees, this is normal, but stronger heating will lead to self-ignition of the fuel.
Manufacturers regulate the values characterizing the heat rating. This is done by changing the parameters of the spark plug insulator and its skirt. To avoid problems, you must strictly follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the operation of the vehicle.
Large loads are more easily tolerated by “cold” spark plugs, while moderate use is more favorable for “hot” spark plugs.
There are spark plug compatibility tables for different types of engines. They are used to select parts whose characteristics are optimal for a specific car model. Owners of cars with an outdated design can be advised to improve the car - for example, install a contactless system.
Another reason is severe overheating of the valves. Occurs due to:
- reduced octane number of fuel;
- incorrect setting of valve system clearances;
- defect of one of the pistons.
The cause of glow ignition may be a malfunction of the propulsion system. If the ignition timing is set incorrectly, the engine will begin to overheat due to heavy loads. Hence the unstable work.
More about detonation factors
Towing cable: which one is better to buy, how to tie it correctly
There are several most common and probable reasons why the engine begins to detonate.
- Fuel quality. Sometimes, out of desperation or in order to save money, drivers stop at questionable gas stations, not knowing what quality of fuel they offer. Often, gas stations artificially increase the octane number by adding methane or propane. This causes detonation because the gas evaporates faster than pure gasoline. As a result, carbon deposits form on the walls, which then provokes the so-called glow ignition. This mixture ignites due to heated electrodes and carbon deposits on the inner walls. As a result, the ignition is turned off, but the engine is still running;
- Octane number. There are other situations when a driver deliberately saves on fuel by buying fuel with a lower octane number. Therefore, do not be surprised when, instead of the recommended 95, you pour 92 and even more so 80 gasoline, detonation appears;
- Spark plug. Often, motorists simply do not know how to choose them correctly, buying the cheapest ones or those recommended by the seller. Therefore, spark plugs are chosen strictly in accordance with the automaker’s recommendations for a specific engine;
- Design features. These include the pressure in the chambers, the structure of the piston bottom, the design of the combustion chamber, the location of the spark plugs, etc. Practice shows that with greater pressure created in the cylinders, the risk of detonation increases.
If you yourself cannot determine the cause, then you should not waste time and wait for everything to suddenly go away on its own. Go to a car service center, carry out diagnostics and solve the problem as quickly as possible.
Signs of glow ignition
The combustion of fuel during glow ignition occurs as usual, but even before the spark is formed. This affects the operation of the propulsion system: unpleasant noises are heard in the area of the motor, reminiscent of pops, and the speed “floats”. All this happens against a background of strong vibration.
“Incorrect” ignition is very harmful to the engine. It indicates its wear and the appearance of soot deposits in the combustion chamber and cylinders. The engine temperature rises, heat dissipation deteriorates. If the cylinder head overheats, expensive repairs cannot be avoided.
Consequences
This kind of engine operation is extremely harmful to it. If the spark plugs are selected correctly according to their characteristics, then glow ignition indicates significant engine wear or the accumulation of a significant layer of soot and deposits on the walls of the combustion chamber and valves. They contribute to worse heat dissipation and an increase in the overall temperature of the engine. It should be remembered that this can lead to overheating of the cylinder head and its warping. Unfortunately, in this case, you will have to undergo labor-intensive and expensive engine repairs, including complete disassembly and cleaning of the combustion chambers and valves.
Why does glow ignition appear?
And all this happens because soot impairs heat transfer inside the combustion chamber, which is why the elements inside it heat up so much that they can ignite the working mixture. Due to this, the engine continues to operate even after the ignition is turned off, when the spark on the candles no longer occurs. Before taking action, it is necessary to establish the reasons for the appearance of glow ignition. Very often this effect appears due to incorrectly selected spark plugs according to the heat number. Incorrectly set timing of sparking can also give this result. But if everything is in order with the ignition system and its components, then carbon deposits are to blame.
What is Low Speed Pre Ignition (LSPI)?
Researchers have found that the modern motorist has a much more dangerous enemy, which can very quickly destroy the engine of a car.
The phenomenon is called cylinder pre-ignition (LSPI), and it is serious and destructive. Scared? Experts like Scott Lindholm, Global Product Application Specialist for Shell Lubricants, don't yet fully understand what exactly causes this, but they can provide some early advice on engine protection rules.
“Classical detonation and LSPI are two different events caused by two different phenomena,” explains Lindholm. – Typical detonation can be controlled by fuel octane rating and spark calculation and is very predictable. LSPI (in-cylinder pre-ignition) is still not well understood and can occur spontaneously.”
Both LSPI and typical knock occur because the gasoline in the cylinders ignites at the wrong time, although the conditions leading to each phenomenon are different.
Detonation occurs at higher speeds and under higher loads when the engine is hot and the flywheel is persistently turning. But LSPI can happen at very low rpm and under much lighter load. The second phenomenon also occurred in the operating range, where modern engines have the best fuel efficiency. Unlike detonation, LSPI is very unpredictable.
Ways to deal with soot
There are several ways to remove carbon deposits. The first, and simplest of them, is to burn deposits towards the combustion chamber. To do this, you just need to drive for a long time at high speed. That is, we drive out onto a good long highway and “press the gas pedal to the floor.” The result of this will be the burnout of carbon deposits and its removal through the exhaust system. By the way, this method can be used as prevention. That is, it is enough to periodically “drive” the car so that a layer of soot does not form inside the combustion chambers.
If the first method does not give results and glow ignition appears, you can try to “soften” the carbon so that it peels off on its own. For this, a special solution is used, consisting of one part motor oil and four parts kerosene.
The engine will require 80-120 g. such a solution. After the trip, while the engine is still hot, you need to pour 20-30 grams into each cylinder. prepared mixture. After this, the car is left for a day so that the solution can take effect. Next, you need to start the power plant and let it run for half an hour. After using the mixture, the oil filter and the lubricant itself must be changed.
If the second method does not help , then you will have to remove the carbon deposits mechanically. That is, you will have to remove the cylinder head from the car and clean off the existing layers using a metal brush and scrapers, after soaking everything in kerosene. Carbon deposits need to be removed not only from the surface of the combustion chamber, but also from the pistons and valves. This method is the most labor-intensive, but after it you will be completely sure that everything inside the cylinders is clean.
Combustion of the air-fuel mixture
The fact is that during detonation, improper combustion of the air-fuel mixture occurs. With a short circuit, only the arson of the mixture is not standard, but its combustion occurs as usual.
During detonation, the mixture is ignited at a speed exceeding the speed of sound. Roughly speaking, a small explosion occurs in the cylinder. During a short circuit, the mixture ignites at the same speed as it would ignite from an electric spark.
Consequences
Detonation is considered a more dangerous phenomenon.
During detonation, the oil film is destroyed, which contributes to accelerated wear of parts due to dry friction. An explosion during detonation can cause mechanical damage to parts. Due to detonation, the engine may overheat. Prolonged driving with detonation conditions may lead to the need for major repairs or engine replacement.
The consequences of glow ignition are not so global, but they also promise trouble.
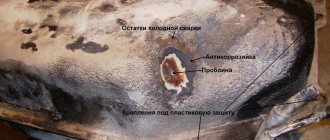
During a short circuit, the spark plugs and their insulators will deteriorate. Scores may form on the cylinder bore and piston. Also, the bottom of the piston may burn out. The piston parts may simply jam.
Correcting the parasitic effect
It is not difficult to cure such a car ailment. It is better to do this before the unpleasant consequences of the negative effect appear. To do this, it may be enough to replace the spark plugs along with the insulators.
Also contact specialists. Let them check whether your mixture ignition and gas exhaust mechanisms are configured correctly. Perhaps these are the reasons for the glow rather than spark ignition of the mixture.
If you have to use the car at high speeds, give it a little rest.
We do not allow a parasitic effect
To ensure that the mixture in your car ignites only from an electric spark, regularly check the spark plugs for the presence of carbon deposits, as they can become as hot as the insulator.
Carefully adjust the mixture ignition mechanism (if you do it yourself), do not allow it to shift to an earlier phase. And it’s better not to adjust the gas exhaust mechanism yourself, but contact a specialist. And of course, the car must have spark plugs with the correct heat rating.
What is a knock sensor used for?
To monitor dangerous detonation, a modern car is equipped with a sensor. It is located on the power unit block. What is the influence of the sensor on engine operation? Its task is to convert the energy of mechanical vibrations into electrical signals. The housing contains a piezoelectric plate. It produces a voltage proportional to the amplitude of the oscillations.
Knock sensor readings allow you to adjust the composition of the combustible mixture and ignition phase angles
The sensor is an accelerometer that constantly sends pulses to the electronic engine control unit (ECU). After processing the signals, the unit gives commands to change the composition of the air-fuel mixture or shift the ignition phase angles.
If the sensor fails, the ECU is unable to fully control the operation of the engine and deliberately sets the ignition late. This solution allows you to switch the power unit to a gentle mode, but fuel consumption increases by 1.5–2 times, and power drops sharply.
Glow ignition protection
It is difficult to say unambiguously when exactly glow ignition . But preventive measures always come down to the following list:
- Candles must meet performance specifications;
- The heat number is taken into account;
- Fuel quality;
- Periodic diagnostics.
Matching the spark plugs is the main condition that can prevent overfiring. It is important to consider the heat rating, which is different for each engine.
If the spark plug works normally, then the temperature of its insulator is within 600 degrees, but if it is higher or lower, then undesirable consequences can be expected very soon. Soot can form on cold spark plugs, which disrupts the functioning of the spark plug, and then glow ignition .
Bosch
Bosch spark plugs are marked according to a similar principle. For example, the WR7DC marking stands for:
- W - standard thread 14;
- R - anti-interference resistor;
- 7 - heat number;
- D - the size of the threaded part, equal to 19 millimeters;
- C - the electrode is made of copper alloy (O - standard alloy, S - silver, P - platinum).
Bosch spark plugs marked WR7DC, in fact, can replace domestic spark plugs A17DVR, which are installed in the engines of VAZ cars of various models.
Correctly running engine
In a properly functioning engine, during the first stroke, a fuel-air mixture enters the combustion chamber, after which the piston begins to move upward, pressure rises in the combustion chamber, the spark plug gives a spark, gasoline ignites, the mixture explodes and expands, sharply pushing the piston down. However, for a number of reasons, various types of malfunctions may occur, which leads to improper combustion of the fuel-air mixture, detonation and other serious engine damage.
What is detonation
Detonation is a disruption of the combustion process of the fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, when combustion does not occur smoothly, but explosively. At the same time, the speed of propagation of the blast wave increases from standard 30...45 m/s to supersonic 2000 m/s (exceeding the speed of sound by the blast wave is also the cause of the pop). In this case, the air-fuel mixture explodes not from a spark coming from a spark plug, but spontaneously, from high pressure in the combustion chamber.
Naturally, a powerful blast wave is very harmful to the cylinder walls, which overheat, the pistons, and the cylinder head gasket. The latter suffers the most and during the detonation process the explosion and high pressure simply burn it out (in slang it is called “blowing out”).
Detonation is typical for engines running on gasoline (carburetor and injection), including those equipped with gas-cylinder equipment (LPG), that is, running on methane or propane. However, most often it occurs in carburetor cars. Diesel engines operate according to a different scheme, and there are other reasons for this phenomenon.
Preventing the appearance of glow ignition
In each specific case, it can be difficult to predict when such glow ignition will appear and what causes its occurrence. The car owner needs to take a comprehensive approach to preventing engine breakdowns and protecting against such glow ignition, which will avoid serious problems with the car.
The following measures will be required:
1) perform diagnostics of the power unit on a regular basis;
2) use exclusively high-quality fuel with a correctly selected octane number;
3) the heat rating of the engine and spark plugs is taken into account;
4) candles must fully comply with all manufacturer’s requirements and performance characteristics.
Most often, it is the incorrect selection of spark plugs or their malfunctions that lead to the formation of such glow ignition. Each engine has its own heat rating, which depends on various parameters, including the compression ratio, boost rate and a number of other characteristics.
Correctly functioning spark plugs have an insulator temperature of about 600 degrees. However, if for some reason this parameter decreases or increases, problems arise with the ignition of the fuel mixture, namely, glow ignition is formed. Soot deposits often appear on cold spark plugs, which significantly impairs the quality of the spark. Engine power decreases, and fuel may not completely burn in the chambers, which leads to a significant increase in gasoline consumption.
Start of feed (blocking channel) and start of injection
The term "start of flow" refers to the actual start of flow of the high pressure pump. Together with the feed start (FB), the actual injection start (SB) is also of great importance for optimal engine performance. Since the start of supply (blocking of the channel) can be determined more simply than the actual start of injection for the engine when it is stopped, the installation (adjustment) of the high pressure fuel pump (HPF) is carried out when the fuel supply begins. This is possible because There is a certain relationship between the start of feed and the start of injection (4). The start of injection is determined by the angle of rotation of the crankshaft (5) in the area of the top dead center (TDC) of the piston, at which the injector opens and fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The start of fuel injection into the combustion chamber has a significant impact on the start of combustion of the fuel-air mixture. The maximum final compression temperature occurs at TDC. If combustion begins before TDC, the combustion pressure increases sharply and inhibits the upward movement of the piston, thereby reducing the engine's effective power. A sharp increase in combustion pressure also leads to “hard” engine operation. Combustion, however, must be completed before the exhaust valve opens. There is also a decrease in fuel consumption if combustion begins in the TDC region.
If the start of combustion is advanced (2), the temperature in the combustion chamber increases, which also leads to an increase in NOx emissions (1). If the start of injection is too late (3), this may result in incomplete combustion and the release of incompletely burned hydrocarbons.
The instantaneous position of the piston affects the movement of air in the combustion chamber, its density and temperature. Accordingly, the speed of movement and the quality of mixing of the fuel-air mixture depend on the start of injection. Thus, the start of injection also affects the emissions of soot and products of incomplete combustion. This mutual dependence of specific fuel consumption and hydrocarbon emissions on the one hand and black smoke and NO emissions on the other hand requires the minimum possible tolerances for the start of injection in order to achieve optimal values (a - optimal start of injection).
Reasons for glow ignition on a gasoline engine
The main reason for the glow effect is the ignition of the mixture due to overheating of the spark plug electrode or engine elements. A malfunction may occur due to an incorrectly selected heat value. The cause may also be overheating of the piston or exhaust valve, which may be the result of errors when adjusting the timing belt. A failure of the gas distribution mechanism results in the valve not completely closing the hole in the cylinder head. Then, the glowing effect is achieved at high speeds. As a result, the mixture continues to ignite after the ignition is turned off. Ignition stops only after the end of the gasoline supply.
When the mixture becomes rich
Deviations in mixture preparation appear as a result of certain failures of vehicle systems. The injector is responsible for the process of creating fuel. It prepares mixtures with a certain percentage of oxygen. It is this ability of the presented engine element that allows the engine to operate in different modes.
If necessary, the driver can, thanks to such a device, increase speed, cope with inclines, overtake, etc.
The rich mixture at the injector is determined by a mathematical formula. The normal ratio is 14.7 kg of oxygen per 1 kg of liquid fuel. If for some reason the amount of oxygen in this formula increases, this composition is called poor. If the amount of fuel in the mixture rises, the mixture acquires the status of rich.
The car owner can independently adjust the level of oxygen supply to the fuel mixture. Errors made in this process lead to breakdowns and improper operation of the vehicle.
A candle with the correct heat rating
The correct heat rating means that the candle will only heat up to the temperature required to clean it. However, the release of such an amount of heat will not be enough to heat the soot or insulator, so the mixture will not ignite.
We will analyze which heat numbers (Russian markings) are suitable for cars. Note that the numbers in the markings indicate the time during which the spark plug warms up to a temperature that threatens the appearance of a short circuit.
- Number from 20 to 26. Used on forced engines designed to operate at high speeds. These are the so-called cold candles.
- Number from 17 to 19. Spark plugs that are suitable for use in engines that do not require boost. The heating time of such a candle is considered average.
- Number from 11 to 14. Suitable for use in unboosted engines with low power. Such candles are called “hot”.
The fact that the glow type of ignition of the mixture was previously used on different cars (the same “Zaporozhets”), and then was replaced by the spark type, misleads some car enthusiasts. They believe that this is just a different type of burning the mixture, in which there is nothing wrong.
However, we should not forget that in technology any deviation from the norm can lead to dire consequences. Therefore, even a car ailment that seems insignificant needs to be paid attention to and measures taken to eliminate it.
Don't let your cars get sick, and good luck on the roads.
If any of our readers have already encountered a parasitic effect or were even able to eliminate it on their own, we will be happy to read about this experience in the comments.
Sources
- https://autolirika.ru/teoriya/prichiny-kalilnogo-zazhiganiya.html
- https://carprice-info.ru/kalilnogo-zazhiganiya/
- https://mashinapro.ru/1796-kalilnoe-zazhiganie.html
- https://remont-avtovaz.ru/kak-ustranit-kalilnoe-zazhiganie/
- https://CarExtra.ru/obzory/kalilnoe-zazhiganie.html
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5db80b6a98fe7900ad127d7a/kalilnoe-zajiganie-pochemu-ono-voznikaet-6-rasprostranennyh-prichin-5f4d19ee361595696bfaf6df
- https://avtopulsar.ru/chto-takoe-kalilnoe-zazhiganie-chetyre-sposoba-kak-izbavitsya-ot-kalilnogo-zazhiganiya/
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/cartechnic.ru/kak-reshit-problemu-poiavleniia-kalilnogo-zajiganiia-5cdfff87baeb6600affc59dc
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5cdecb2f4f68ae00b21fd0cd/chem-grozit-kalilnoe-zajiganie-5ce275e2b3217a00b3887941
Where to look and how to check the knock sensor
In order to check it, you also need to know where the VAZ-2110 knock sensor is located. Everything is simple here; so that it can effectively capture vibrations, it is placed on the cylinder block. Its location largely depends on the design features of the motor itself.
On 8-valve engines it is usually located in the line of sight and is usually easy to get to. Therefore, it is not difficult to determine where the knock sensor is located on a VAZ-2107 (injector). It is installed on the exhaust manifold side and consists of a massive washer with wiring going to it and secured to the engine with a bolt.
But on 16-valve engines, the installation location is slightly different than the location of the knock sensor on the VAZ-2107 (injector). Due to the fact that the block head is much more massive, the sensor is located lower - under the exhaust manifold, so access to it is limited, and often it can only be reached from under the car on an overpass or inspection hole.
And although the location of the motor may differ slightly due to the design of the motor, its connection is always identical. Thus, the connection diagram for the VAZ-2109 knock sensor with an injection engine is the same as on the 2114 model.
Checking the VAZ-2110 knock sensor can be done in two ways.
The first of them implies the presence of a tester switched to measuring resistance (measurement level - up to 2 kOhm).
Checking the knock sensor with a tester
To check, you just need to disconnect the wiring block from the sensor and connect a tester to the sensor contacts. Then you should apply light blows with a wrench to the DD fastening bolt and monitor the readings on the tester display.
After connection, the display will show a certain resistance value of the sensor. At the moment of impact on the bolt, the resistance will increase sharply, but then return to the old value. If this does not happen (the resistance does not rise or does not return), the sensor is faulty and requires replacement.
The second method does not require any equipment and is more effective. To carry it out, you need to start the engine and set the speed to 2000 rpm. Then take an open-end wrench, you can use a small hammer with a metal attachment (if access to the DD is limited) and strike the fastening bolt. If the DD is in good working order, after the impact, the engine speed should drop, since such an impact will be regarded by the sensor as detonation and the ECU, based on its signals, will reduce the ignition angle. After the impact on the bolt stops, the speed should be restored. If this does not happen, the DD is faulty.
Summary
As can be seen from the above examples, proper operation is affected by any characteristic, especially when it comes to the overall dimensions of parts. In any case, the problem of why the car does not shut down when the power supply to the power unit is turned off requires prompt intervention and prompt elimination. An attentive attitude towards it will help you understand the reasons why the car continues to operate when you turn off the power key. Having realized after what previously carried out work this breakdown appeared, the car owner will be able to identify and eliminate it, which can significantly extend the trouble-free life of the vehicle. It is better to entrust repairs and selection of spare parts to professionals who will do everything correctly.
A modern internal combustion engine is a system of many parts and mechanisms, the operation of which requires complex adjustments and settings. It is not surprising that a deviation in one direction or another can throw the installation out of balance and fundamentally affect its performance and technical condition.
One of the most common problems that requires an integrated approach to solve is potassium ignition. The average user observes it when the engine is turned off, when it continues to work for some time, being disconnected from the ignition. This problem is fraught with serious damage later and requires an early solution. In order to understand why this happens, it is necessary to understand its essence, which is what we will try to do.