The turbine is a rather complex device that increases engine power. Its breakdown, unlike many other components of the car, is not critical. But you should understand that the engine will not work normally without it, and oil and fuel leaks will not have a positive effect on the general condition of the vehicle and the car owner’s wallet. How can you understand in time that the turbine is dying? To determine the malfunction, you need to understand the principles of its operation, find out the signs and what could lead to this. However, for a more accurate diagnosis, you will need to contact a car service center or service station.
What is a turbine?
To put it simply, a turbine is a mechanical device in a car that supplies pressurized air into the combustion chamber. The main task performed by turbocharging is to significantly increase engine power without increasing its displacement. Installing a turbine provides a fifty percent, and sometimes more, increase in the power of the power unit when compared with non-turbocharged engines of the same volume. This is due to the turbine forcing air under pressure into the cylinders and increasing the oxygen content in the fuel mixture, and as a result, increasing its efficiency.
Structurally, the turbine consists of a mechanical impeller driven by the movement of vehicle exhaust gases. That is, exhaust energy is used to capture and supply air (and, accordingly, oxygen) into the system to improve the quality of the fuel mixture. From a technological point of view, today this is the most effective device for increasing engine power at the same fuel consumption, which has reduced the emission of toxic gases into the atmosphere.
Such units are widely used in both diesel power plants and gasoline engines. Moreover, in the first case, turbocharged engines turned out to be the most efficient due to the high compression ratio and low crankshaft rotation speed when compared with gasoline cars.
In addition, the limited use of turbocharging on gasoline cars is due to the possible manifestation of detonation, which occurs with a sharp increase in engine speed, as well as due to the high temperature of the exhaust gases, reaching one thousand degrees versus six hundred for diesel engines. Naturally, such temperatures can lead to damage to turbine parts.
Truck turbine cleaning and repair
Once again you need to check the axial play of the turbine. If the compressor is working properly, then the presence of oil in the impeller is explained precisely by the increase in pressure in the crankcase; the turbine needs to be cleaned. There may also be a plug in the oil drain line.
Important
If the diesel engine is too noisy during operation, the high pressure air supply pipes should be checked. And also the impeller rotor. While turning, it should not touch the walls.
The condition of the impeller itself also deserves close attention. If there are nicks or other damage on the blades, this means that the compressor requires immediate repair. If the rotor defects are clearly visible, the turbine must be removed and sent for more accurate diagnostics.
You can check the performance of the turbine as follows. You need to start the engine, find the pipe connecting the turbocharger and the intake manifold, and pinch it by hand. At this time, the invited assistant should sit behind the wheel and accelerate for a few seconds. During normal operation of the turbine, you will clearly feel the pipe inflating. If the impeller does not pump gases, then no special changes will happen. In addition to this, you can check the condition of the pipes. And also look for cracks in the exhaust and intake manifolds of the diesel engine.
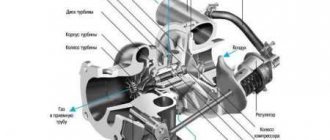
What does a turbine consist of?
Depending on the manufacturer and model, turbines have some differences, but their main structural elements and mechanisms are identical. So, the design of any turbine includes an air intake, immediately behind it an air filter, a throttle valve, a turbocharger, an intercooler and an exhaust manifold are installed. All parts of the unit are connected to each other by tubes and hoses, which are made of reliable wear-resistant materials.
Most people familiar with the design features of the car have noticed several differences between turbocharging and standard intake systems - the presence of an intercooler and turbocharger, as well as some elements for controlling and regulating the boost.
One of the main and most important elements of a turbine is the turbocharger (or turbocharger). It is this that provides increased air pressure on the engine intake lines. In its design, a turbocharger has two wheels - a turbine and a compressor, located on the rotor shaft. Each wheel is mounted in a separate, reliable housing, and the design includes a bearing.
What to check for yourself
Before contacting a service station, in some cases, you can do basic diagnostics of the car yourself.
- If smoke appears, then, regardless of the color, you need to check the air filter and the connections of the pipes. If the seal is lost, then you need to remove and replace the filter.
- How worn out the turbine is can be determined by lightly turning the rotor - there is little play, which means everything is fine, and when, while turning, the rotor even touches the housing a little, then the turbine will need to be taken in for repair.
- Inspect the turbocharger. To do this, open the hood, start the engine and clamp the tube that runs from the turbocharger to the intake manifold. An assistant should press the gas for 2-3 seconds and when the tube swells from pressure, then everything is in order, but when it is sluggish, the turbine needs repair.
- The turbine is visible. There should be no oil or other stains on its body. If you disconnect a tube that was previously pinched and oil traces appear, the turbine probably needs to be replaced.
How does a faulty turbine affect the performance of a car engine?
Many people believe that a small unit in the form of a turbine, if it fails, is unlikely to have a strong negative impact on the operation of the engine, but this is not entirely true. A very common cause of turbine failure is low oil pressure or poor oil quality. A drop in pressure is often due to severe contamination of the oil filter or its poor quality, as well as as a result of using the “five-minute flush” method.
Given the high turbine speeds, as well as constant exposure to high temperatures, which are normal operating conditions, even a slight and short-term drop in pressure in the oil system can cause turbine axle bearing failure. When it is severely worn, the radial clearance increases, and this play leads to damage and failure of the seals.
With damaged oil seals, there is no proper tightness, and accordingly, oil easily enters the engine manifold. At the same time, the oil pressure in the bearings of the turbine axle drops even more, which leads to even greater damage to this unit.
The hot exhaust gas passes through the broken elements and enters the internal space of the bearings, where it increases the temperature to such an extent that all lubricants are completely burned out. This leads to complete destruction of the bearing itself. It ceases to perform its function, which leads to the breakdown of the turbine blades, the debris of which remains inside the unit.
The quality of lubrication of turbine elements greatly depends on the engine oil pump. Even a short period of operation of the unit in this mode will leave the car engine without lubricants. And what will happen to the engine when running without oil requires no explanation.
To avoid such unpleasant situations, it is important to remember the main signs of malfunction and failure of a turbocharger. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in time and do not take appropriate measures, then the sound of the characteristic grinding of blades rubbing against the internal housing of the turbine, which leads to even greater problems, will not take long to occur. If any hint of a malfunction appears, it is better to immediately contact a car service specialist or service station.
How Vasya checks the turbine (software)
The inspection methods described above only provide an indirect assessment of the condition of a used turbine. To diagnose it in detail, it is better to use electronic means - a laptop and diagnostic software installed on it. The most common program for this among masters and car owners is “Vasya Diagnostician”. The following is a brief description of the algorithm for checking the pressure in the tested turbine. It is assumed that the car enthusiast knows how to connect to the service connector of the ECU and run the program. All further readings are performed with the machine idling, that is, with the engine and turbine running.
Checking the turbine on the Vasya machine
- In the program, select the section “Selecting a control unit”, then “Engine electronics”.
- Select the “Custom Groups” button. A window for customizable groups opens on the left and a list box opens on the right for selecting groups directly. Here is a description of all the components that affect the performance of the car engine (sensors, executable modules, and so on).
- In the list you need to select the line Absolute intake pressure or “Absolute consumed pressure”. The corresponding pressure will be presented in the left window. The units of measurement in this case are kPa instead of bars.
- When idling, the turbine pressure will be slightly more than 100 kPa (or 1 bar, for example 107 kPa).
- Along with turbine pressure, it will also be useful to include additional functions - the angle of the accelerator pedal, the torque value, the coolant temperature, and so on. This will be useful for understanding the dynamics of the turbine.
- When driving a car, the corresponding turbine pressure will increase and will be about 2...3 bar (200...300 kPa) depending on the type of turbine and driving mode.
It is recommended that before purchasing a used car, you check all its systems, including the turbine, not only visually and tactilely, but also using the described software tools like Vasya Diagnostic.
Signs that the turbine is “dying”
In many cases, turbine failure occurs very quickly, there are several reasons for this: it can be, as already mentioned, a lack of oil, solid particles hitting the compressor wheel and the turbine rotor wheel, and an accident can also lead to breakdown. However, more often the turbocharger becomes unusable gradually, and the car owner has time to pay attention and take the necessary measures to eliminate the causes of the breakdown or contact specialists.
There are several of the most common signs of turbine failure. These include the following:
- the presence of extraneous noise from the turbine during operation of the power plant (whistle or hum);
- the appearance of bluish smoke from the exhaust system;
- oil consumption increases sharply;
- boost pressure drops.
To identify breakdowns in the early stages, just listen carefully to your car. For example, the car’s power has dropped or it has lost its dynamics, this indicates that the turbine is not creating enough pressure.
Sometimes this is due to increased back pressure due to severe contamination of the catalyst. This can also be caused by malfunctions of the solenoid valve (which controls the turbine vacuum), which also leads to a decrease in engine power.
If these elements are working properly, then it is worth checking the wastegate or variable geometry. Often, with an aggressive driving style, the flow of exhaust gases goes past the valve, or the variable geometry is damaged, clinging to the turbocharger housing and not directing air to the turbine wheel. In this case, the efficiency of the turbine drops significantly. If it was not possible to identify the cause of the breakdown in this way, then the turbocharger will need to be removed from the power plant.
The imminent failure of the turbine and a possible sign of a defect can also be indicated by smoke from the exhaust system.
Main symptoms of a malfunction
If this mechanism begins to malfunction, you will immediately feel it. First of all, a turbine malfunction will be reflected in the driving performance of the car. Thus, the acceleration dynamics will significantly disappear. It will be difficult for the machine to reach the desired speed, especially when going uphill or when loading. The engine will also have a harder time revving up. In fact, it will turn into an ordinary “aspirated” car. And as you know, on turbocharged cars the tachometer needle significantly “comes to life” after a certain rpm range (2 thousand or more, depending on the type of engine). If the compressor is faulty, it will rise as slowly as at the beginning.
Another sign of a malfunction is increased oil consumption. This element requires constant lubrication. In addition, the oil acts as a heat sink. Manufacturers claim that with a working turbine, a car should not lose more than two liters of oil per 10 thousand kilometers. On trucks - up to 10-15 percent of the total volume of the lubricated system. If there is a problem with oil consumption, you will notice a characteristic smell from the engine compartment. The fact is that the lubricant gets onto the hot exhaust pipe and begins to burn.
For more serious malfunctions, a characteristic noise will be heard. It could be a hum, howl or whistle. The latter is the norm for any turbine. But if the turbine whistles excessively, this is a reason to carry out diagnostics. Along with this, there will be problems with speed. The engine will no longer idle normally. The arrow will “float” or even go beyond one thousand. How to check the turbine on an engine? Below we will look at several methods.
Smoke color and exhaust smell
The appearance of smoke in the exhaust system cannot be ignored; you should take a closer look at it. The process is often accompanied by an unpleasant chemical odor, which is clearly audible when moving.
Presence of black smoke
This indicates combustion of the combustible mixture in the turbine. The defect may be caused by a lack of oxygen in the fuel system. You should check:
- all pipes and their connections for leaks;
- electronic control unit;
- air filters;
- quality of operation of the entire fuel system;
- motor.
Particular attention should be paid to filters; the most common cause of lack of air in the fuel system is a dirty filter element.
Blue smoke
This indicates that oil is entering the combustion chamber. The cause may be a leak, which lies in a problem with the turbocharger or engine. In this case, it is necessary to inspect and check all connections.
White smoke
The main reason for this defect is a clogged oil drain line. It needs to be replaced or repaired.
Symptoms and causes of disorders
The smoke that appears in the exhaust pipe soon comes into view. Along with this, a pronounced pungent odor appears, which is felt as you move.
Here are other manifestations and where to look for the root of the breakdown:
- Black smoke. This manifestation is caused by the combustion of fuel in the turbine. The difficulty arises due to a lack of air mixture in the fuel system. It is important to pay attention to: the tightness of all pipes, the ECU, the engine, the air filter (often the malfunction is rooted in it), the functionality of the fuel system;
- Milky whitish color. This often occurs due to a clogged oil drain line;
- Sky gray shade. This is where the oil enters the engine. Most likely, the root of the problem should be found in the leak. It is necessary to inspect all connections, and the reason is a breakdown of the turbine or engine;
- Increased oil consumption, oil leaks. Difficulties with the oil line may be accompanied by a decrease in air flow to the mixture. This also indicates wear and charring of the channels or axle casing;
- Decreased productivity. Appears due to lack of air. It is worth taking a good look at all the parts of the air transmission system.
Signs of turbocharger failure
As mentioned above, a bluish-gray exhaust indicates the combustion of oil in the engine cylinders, which got there from the turbocharger or engine. Black indicates air leaks, and white indicates a blockage in the oil line. The appearance of a whistle may indicate an air leak at the junction of the compressor and the engine. A grinding sound indicates abnormal friction of parts and structural elements.
In case of periodic shutdown or complete failure of the turbine, all its parts and components should be checked. The bulk of all turbocharger breakdowns are due to three reasons. About them below.
Insufficient oil pressure
It can occur due to a leak or when the oil hose is pinched, or due to improper connection to the turbine. Leads to rapid wear of the rings, shaft journal, poor lubrication and a sharp increase in temperature on the radial bearings of the turbocharger. They will need to be replaced with new ones.
Contaminated oil
It can occur due to untimely replacement of lubricant or oil filters, when water or fuel gets into the oil, as well as when using low-quality lubricants. Leads to premature wear of bearings, clogging of oil pipeline channels, and damage to the axle.
Failed elements must be replaced with new ones.
Foreign object inside turbocharger
May damage or break compressor wheel blades, resulting in reduced air pressure; turbine wheel blades; rotor. In this case, the compressor will need to replace the filter and check the intake tract for leaks. On the turbine side, the shaft needs to be replaced and the intake manifold checked.
Is it possible to repair the turbine yourself?
The design of the turbocharger seems simple and straightforward. And all you need to repair a turbine is to know the turbine model, engine number, as well as the manufacturer and have spare parts or a factory repair kit for turbines on hand.
You can independently carry out visual diagnostics of the turbocharger, dismantle it, disassemble and replace defective turbine elements, and install them in place. Inspect the air, fuel, cooling and oil systems with which the turbine closely interacts, check their operation.
Visual inspection
At the very beginning of the diagnosis, the level and quality of the engine oil is checked. It is also very important that no foreign objects get inside the turbocharger.
Then you can begin to analyze the exhaust gas. A decrease in power and overall dynamics, as well as a black exhaust, indicates an over-enrichment of the fuel mixture. This may be caused by insufficient oxygen supplied to the cylinders due to malfunctions in the intake system. Sometimes power drops due to exhaust leaks.
To check, you will need to start the engine and listen for any extraneous noise when the turbocharger is operating. There should be no whistling or creaking sounds, noise of air escaping at the joints, etc. The pipes through which air is supplied to the motor are checked for leaks. Any leaks or damage are unacceptable. It is important to check the condition of the air filter - contamination reduces its throughput, which leads to insufficient air in the cylinders.
The appearance of white or bluish smoke can be caused by a malfunction of the compressor itself or other engine components. A sharply increased oil consumption may also indicate this problem.
Under such circumstances, the air filter and turbine rotor should be rechecked. A clogged filter does not allow enough air to pass through, and this leads to a pressure difference between the housing and the cartridge with bearings, and oil begins to flow from it and enter the compressor housing. If everything is in order here, then you should inspect the oil drain line for kinks, damage, etc.
Unnatural sounds
First you need to open the hood slightly and recognize where the sound may be coming from. When noises are heard from the turbine, then it is necessary to inspect the axial rotor for chips and free rotation.
The scratching effect means distortion and cracking. A whistling sound indicates air leaks.
- Sometimes this happens when the flow capacity of the oil pipeline decreases or when foreign objects get stuck.
- The first step in diagnostics is to check the oil lines, ECU, air transmission system, and axle with rotor.
- Turbine breakdowns sometimes occur due to improper disassembly and assembly.
To determine the performance of the turbine, you do not need to remove it; service station technicians do not do this; they carry out the procedure only as needed.
What is the difference between checking on a gasoline engine?
On gasoline cars, the imminent failure of the turbine can be determined by the same signs. Here the exhaust turns blue or white when the car accelerates. If there are air leaks in the injection channels or if the fuel system malfunctions, black smoke appears. A white exhaust with the smell of burnt oil will indicate a lubricant leak into the exhaust system. May be caused by increased end play, circlips not holding oil pressure. If oil gets into the exhaust system, soot will form on the hot turbine wheel, which will subsequently lead to an imbalance of the unit with subsequent destruction of the bearing housing.
Preventing turbine breakdowns
To extend the life of your turbocharger, follow these simple rules:
- Change air filters promptly.
- Fill with original oil and high-quality fuel.
- Completely change the oil in the turbocharging system after every 7 thousand km .
- Monitor the boost pressure.
- Be sure to warm up a car with a diesel engine and turbocharger.
- After a long drive, allow the hot engine to cool down by idling for at least 3 minutes before turning it off. There will be no carbon residue that harms the bearings.
- Carry out regular diagnostics and ensure professional maintenance.
Diesel engine selection
Before coming to the dealership, you need to understand the basic characteristics that the engine of the car you are buying would have. There are no universal diesel engines, so desires must be linked together. An engine cannot be powerful and not actively consume oil, reliable and relatively cheap to maintain.
Powerful motors have a long service life and are reliable, but are not as economical as low-power engines, which are less reliable and have a shorter service life.
Engines without turbines are more reliable, but turbocharged diesel engines have better power characteristics with lower efficiency.
Having chosen an engine that suits the buyer in terms of its performance, you should understand the methodology for testing a diesel engine. The engine ultimately determines the fate of the car you buy.
Loss of power during acceleration, description of problems, removal of logs, diagnostics
FAQ VW Audi Skoda Seat
To carry out the work, we need VAG-Com or another VAG diagnostic cable, for example VCDS.
For an initial assessment of engine operation, we take the log in blocks 3, 10, 11 at an engine temperature of at least 75 degrees, car acceleration
in 3rd gear up to 3000 rpm minimum.
As necessary, you can make and post logs of other blocks necessary for analysis.
Convenient program for graphical log processing DIESELPOWER LOG VIEW
You can download it here:
Below you can read a brief description of problems in engine operation, what you should first pay attention to, what can be checked before performing diagnostics. And finally, a step-by-step description of diagnostics with a description and interpretation of the readings of some important channels.
For this information we thank a colleague from the forum under the nickname - moiPASSATtdi
. He offered his assistance in technical translation of information from Dutch:
If problems arise related to loss of power during acceleration, both constant and variable loss of traction while driving. Loss of traction in the “Slipper to the floor” mode or the engine goes into emergency mode (it drives, but does not pull or pulls weakly).
Read the entire text carefully, 9 out of 10 this will help you establish the exact cause of the problem.
1.
Pay attention to: A. Check the presence of the chip (Powerbox). If there is one, then disable it. B. Install a new air filter. B. Check the condition of the inlet air duct from the filter to the turbine, from the turbine to the intercooler (radiator-cooler for the air mass flowing under pressure from the turbine to the inlet manifold) for contamination or blockage. D. Also check the condition of the output manifold, except for the catalyst. * the catalyst may also be clogged with combustion products, and it is not surprising that there is a problem with loss of power. * the catalyst has a honeycomb system inside (meaning like bees) and their destruction leads to blockage and a problem associated with loss of power. D. High pressure fuel pump (HFP). Check that the injection angle is set correctly. If required, install correctly and drive. This angle check is carried out with VagCom at an engine temperature of 85 degrees. E. Injector. You also need to check the timing of the response in accordance with the position of the engine camshaft (Sensor G40 value). If you need to fix it, go to normal mode and drive.
2.
Connect VagCom to the car and diagnose. Erase existing errors, because they may already be outdated and do not require attention.
3.
Drive for a couple of days. Check the motor in different modes. It is also advisable to use the “sneaker to the floor” mode (full throttle). Have your car diagnosed again. Review the errors and save them to a file (print or rewrite). See if errors that were erased earlier still appear.
4.
Connect VagCom to your car. Go to Address 01 (Motor) and click on Measuring units 08. Take a log on channels 03 and 11. * Preferably channel 03 and 11 in one log. Because they influence each other. If you have VagCom registered and with one of the latest versions (from 704 and higher), then use the “TURBO” button for a more accurate measurement. * Remove logs two to three times to eliminate errors during recording. * Make graphs of log files.
5.
We will consider the logs for these two channels separately. First, turbine pressure. Then the readings from the mass air flow sensor (MAF). Because the turbine pressure will show us whether the engine ECU is in emergency mode (or there are other reasons). Attention: In emergency mode, the MAF readings are also underestimated. Therefore, some services mistakenly replace a completely serviceable sensor.
5a.
Channel 11 shows us the following about the turbine pressure status: If the incoming amount of air pressure (G71 Intake Air Pressure Sensor - DPVVG) is different than the requested pressure (More or Less), then this is very likely the cause of the problem. Attention: Low or high pressure can also be the reason the engine ECU goes into emergency mode. Also, unfortunately, it is impossible to determine in this log what the cause is (Air ducts, Valve No. 75, turbine, vacuum hoses.)
Carry out the check in the following order (in ascending order of cost):
1.
Check the condition of all hoses and air ducts between the turbine and the engine, pay attention to the presence of cracks, kinks and other damage. Also, connections must be sealed. It is advisable to rinse everything.
2.
Check the readings of DDVVG (G71) in the measurement blocks (Although it is strange, a damaged or defective sensor does not show an operating error). * Erase errors even if there is no longer an emergency mode, * Remove the log of groups 3 and 11 in different engine speed modes (but this time without “sneaker to the floor”, otherwise an emergency mode may occur again). * View the readings of the required (requested) amount of air pressure and the actual (actual) amount of air pressure (DDVVG (G71) prescribed readings and DDVVG (G71) actual readings). If the readings are in the normal range, then everything is fine. If constant, constantly low or high, then DDVVG (G71) is defective or broken.
3.
Valve No. 75: * View the readings of the operating cycle of Valve No. 75 in the recorded log (or log graph). The readings should be between 45% and 90%. If they are too high and more than 95%, then there is probably a problem with the turbine. * Test Valve No. 75 as follows: Connect the VagCom to the vehicle. Start the engine. Go to 01 – Engine, then 04 – Basic settings and open channel 11. The engine slightly raises idle speed. If everything is in order, then you will notice that the readings will change in a couple of seconds from 0% to 92%. Let the motor run for a while and see if the valve operates. You can help it work a little with your hands. In a good case, you will see that with each actuation, the turbocharger pressure value increases, which ultimately means positive operation. Check for vacuum in the tubes (in Basic settings - 04 channel 10). The engine must be started, otherwise there will be no vacuum. Follow the tubing to valve #75 and check the valve again. Check the vacuum (should be about 800 mbar) on the other tube of valve No. 75. One of the tubes has a constant vacuum, the other does not. The tube without vacuum goes to the air filter. If there is no vacuum in the tube going to the turbine, then valve No. 75 is faulty. For turbines with a bypass valve, the main culprit is valve No. 75 (The bypass valve is the pressure relief valve in the engine exhaust manifold). * Replace valve No. 75, it may not work stably and create problems only when the gas pedal is fully pressed. This is a normal valve that may not be fully open or closed. It seems to work, but not properly. The cost of replacing a valve is much lower than replacing a turbine. So start there.
4.
If you have a variable geometry turbine, then most likely the reason is soot deposits in the turbine.
Those. too much (errors 16618; 17965) or insufficient (errors 16619; 16683) incoming pressure from the turbine. Attention:
* Even if the rod moves to change the position of the turbine blades, the blades may be so dirty that they do not create enough pressure. * And also the shoulder blades can be locked in one position, thus creating a constantly high or constantly low pressure. Check the movement of the turbine blades as follows: Connect the VagCom to the car, start the engine. Go to 01-engine, then to 04-Basic settings and to channel 011. The idle speed will rise (essentially the procedure is the same as when checking valve No. 75). The blade movement regulator (a metal round boss on the turbine, with a vacuum hose suitable for it) will come under control. The rod on the regulator should move +/- 1.5 cm downward from the adjusting screw. If nothing happens, then try using a screwdriver or some thin rod to gently push the rod. It didn’t help and the rod remains standing in place or is jammed, then apparently the problem is related to the turbine. If the rod moves, then you should check the control tubes (in other words, the presence of vacuum using a vacuum gauge or using a finger). A. Clean the turbine and moving blades yourself. Run the test again. B. Take the turbine to a specialist for inspection. C. Replace the turbine (which will be a good blow to your wallet).
5.
The cause may also be poor performance of the turbocharger sensor G31.
Then you will find errors 16619; 16620; 16621; 16622. 5b.
Channel 03 shows us the functioning of the mass air flow sensor (mass air flow sensor). When the gas pedal is fully pressed, the required amount of air (MAP) is most often about 850 mGy/rev. And the amount delivered (starting at 2000 rpm) is somewhere between 1000 and 1200 mGy/rev. (On 1Z engines the standard readings are much lower). If the incoming quantity (which is obvious) lags behind the required one, then there may be no problems with the turbocharging and valve No. 75, and the culprit of the whole problem is most likely the mass air flow sensor. Replace it. It’s better to take PIERBURG rather than Bosch (but for 130 hp and 150 hp engines, use the original Bosch). The mass air flow sensor always works together with the turbocharging. Because the turbine regulates the air flow flowing through the mass air flow sensor.
Note: On chipped engines, air consumption is much higher than the mass air flow sensor can measure. Well, if it cannot measure accurately, then installing a new mass air flow sensor will help increase the potential of the engine, while the readings of the old one are more than 850 mGy/rev. This difference is noticeable but not sensitive. Measuring blocks in group 8 are a very convenient tool to use. In short: You can always see low MAF readings in the context of the turbine pressure at the moment. Therefore, measurements in groups 3 and 11 must be taken together.
Various graphs for examples: https://www.gerritspeek.nl/vag-com_logs.html#cordoba_asv-a
Addition from [email protected] :
It is very IMPORTANT that all logs are taken the same way. Dynamic logs should be recorded like this:
We enter the measuring blocks (8) Select channel 3,10,11 Press the “log” button We drive in 3rd gear at a speed of 20 km/h Press the “start log” button After a couple of seconds, we set the gas to the floor in one sharp movement.
We accelerate to 3500 engine rpm. Let's take our foot off the gas pedal. Let's roll in gear until the revs drop to XX. Depress the clutch. After a couple of seconds, press the stop button. We save the log.
Based on the logs taken in this way, one can unequivocally judge the operation of the supercharger, the USR, and the condition of all sensors of the INTAKE SYSTEM. I think it is more convenient to post logs in SCV format, to eliminate errors in files that will prevent the DIESELPOWER program from opening the log correctly.
The log start speed of 20 km/h is not a dogma. Let her be different. The purpose of the dynamic log is to record the acceleration mechanical characteristics of the engine under maximum load. I’ll try to formulate it this way: the speed should be the minimum stable speed of the engine in 3rd gear. For different engines, the speed will apparently be different.
It is advisable to write logs in turbo mode, then there will be more reports and details will be clearly visible
Continuation of the topic, tips and all discussions of your logs here!
Thanks: ten70
How can I find the information I need here?
Decoding the factory equipment of the car (English) Decoding the factory equipment of VAG in Russian! Diagnostics of
Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, Seat, error codes.
If you have not found information on your car, look at the cars built on the platform of your car. Most likely, the information on repair and maintenance will be suitable for your car.
Checking the turbocharger
Turbine diagnostics are carried out in two ways:
- Superficial (visual-tactile);
- Instrumental.
Instrumental analysis is more accurate. It is used primarily at service stations. The only drawback is the high cost of the service.
Conclusions can be drawn from a superficial examination . To do this, you need to know the design features of the device.
Unit design
Diesel turbine elements
Principle of operation
The unit operates on a running motor and starts only with its efforts.
How does this happen:
- the exhaust manifold emits a flow of exhaust gases into the receiving nozzle of a snail-shaped fan;
- gas presses on the turbine wheel blades;
- the fan starts spinning;
- the turbine shaft (rotor) and the multi-bladed compressor wheel mounted on it rotate together with it;
- negative pressure in the cochlea of the latter activates the absorption of air from the atmosphere;
- additional charge air enters the cylinders (combustion chambers), mixes there with diesel fuel and sharply increases the engine efficiency,
- The constantly warming up turbocharger is cooled using an intercooler (analogous to a radiator).
Turbine diagnostics by specialists
provides services for turbine diagnostics and subsequent repairs. Our specialists will help you accurately identify faults in the turbine and select components for repair.
Having experience, components for repairs in their own warehouse, a database with factory standards and high-precision equipment, the specialists will quickly and efficiently carry out work on restoring the turbocharger, and will also give recommendations on the operation of the turbine after repair. Call and get advice on diagnostics and repair of a turbocharger.