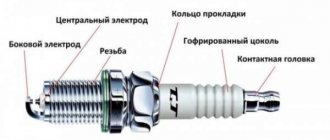
How to measure the spark plug gap in a VAZ 2107 car
The spark plug gap in a VAZ 2107 can be measured with a special probe. It should pass between the spark plug electrodes with barely perceptible resistance. If necessary, it must be adjusted down or up. Although, by and large, candles are relatively inexpensive and it’s easier to carry an additional set of candles with you so that, if anything happens, they can replace the previously installed ones.
A lot depends on the correct spark plug gap. If the gap is larger, fuel consumption will increase. If it is less, the engine will start to jerk or refuse to work at all. As mentioned above, the gap depends on the engine power supply system. For example, in a VAZ 2107 and with a carburetor engine, the spark plug gap with a contact ignition system is 0.5-0.6 mm. If the system is non-contact, then the gap is larger and is 0.7 -0.8 mm. If an injector is installed on the seven, then the gap is already 1 - 1.3 mm.
In general, injection engines always have a larger spark plug gap. Cars with injectors have more powerful coils and better design of high-voltage wires. They maintain a gap of 1 mm. If, for example, you put spark plugs from a carburetor V8 on a Kalina, with a gap of 0.7 -0.8 mm, it will run without problems, although the performance characteristics will deteriorate. But if you put spark plugs from Kalina with a gap of 1.1 on the same “eight”, then most likely it won’t run.
Spark plugs that are recommended to be installed on LADA (VAZ) 2107
VAZ 2107 is a middle class car, produced in Russia for more than 30 years. The five-seater sedan is universal and can be used both on city roads and in rural areas. The car is presented in several modifications, which differ in power plants. The first models were equipped with carburetor engines with 4 and 5-speed gearboxes. Later, engines with fuel injection appeared. The second version is characterized by economical gas consumption.
Stable engine operation is ensured by high-quality spark plugs. They can be of both domestic and foreign production. The factory equipment offers spare parts of the A17 series. Their resource is small, so analogues are often installed. For example, Japanese spark plugs NGK VAZ 2106.
What spark plugs to install in a VAZ 2107
Car ignition system
Spark plug gap, mm.
NGK contact ignition system:
- BP6ES code 7811 (standard)
- BP6ES V-LINE No. 4 code 5637 (with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
- BPR6EIX code 6637 (with resistor and iridium center electrode)
- BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
NGK contactless ignition system:
- BPR6ES code 7822 (standard with resistor)
- BPR6ES V-LINE No. 2 code 2268 (with resistor and v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
- BPR6EIX code 6637 (with resistor and iridium center electrode)
- BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
- NGK BPR6ES-11 code 4824 (standard with resistor)
- NGK BPR6ES-11 V-LINE No. 13 code 5339 (with resistor and v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
- NGK BPR6EIX-11 code 3903 (with resistor and iridium central electrode)
- NGK BUR6ET V-LINE No. 1 code 2876 (with resistor, three-electrode, with a v-shaped cutout on the central electrode)
When to change spark plugs in Lada (VAZ) 2107
If original spark plugs are used, then the replacement schedule is 15-20 thousand kilometers. For others it is different and replacement of spark plugs may be carried out later. In this case, it is necessary to monitor their quality of work. If problems arise with starting the engine or the unit begins to stall, then it is necessary to install new spark plugs.
Spark plug gaps: what should they be and what do they affect?
If the engine begins to run intermittently, jerking is noticeable when accelerating, and problems with idling are observed, many motorists tend to blame the electronic control unit (ECU), carburetor, breaker-distributor, and any other components of the ignition system. Meanwhile, the cause of all these problems can be candles - the simplest-looking devices for igniting the working mixture.
In fully working spark plugs, there is only one variable parameter: the gap between the electrodes. How does a car react if the spark plugs are not adjusted correctly?
The first step is to check the spark plugs
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a complex unit, the stable operation of which depends on the condition of all its components. If it functions intermittently, then an experienced driver will definitely start looking for the reasons by checking and assessing the condition of the spark plugs.
There are only four types of probable cases of spark plug malfunction (not counting possible mechanical defects), namely:
- Electrical breakdown of a ceramic insulator.
- Open circuit due to destruction of the central electrode.
- Insufficient or too large gap between electrodes.
- The presence of slag deposits that impede the passage of a spark.
For example, when one of the spark plugs completely fails, the four-cylinder engine suffers. Almost any motorist can recognize such a problem by ear. If the problem is somewhat different - unsystematic in nature, then determining the cause is more difficult. However, the first step in engine diagnostics should be to check the size of the gaps between the spark plug electrodes. The reasons for this may be:
- Noticeable loss of power.
- The car moves jerkily when accelerating.
- Interruptions are heard when the engine is running.
- It floats and the idle speed is not adjustable.
To check the size of the gap between the electrodes, a simple tool is used - a portable set of measuring probes. Such a device should be in the toolkit of every car owner.
What is the normal gap size
The distance between the spark plug electrodes influences the formation and passage of a spark that ignites the working mixture prepared by the engine power supply system. The dependence of the quality of the spark on the size of the gaps in the spark plugs arises from the fact that the passage of the discharge is the result of an electrical breakdown of the air layer located between the electrodes.
If the electrodes are too close, a smaller potential difference is needed to form a spark. If the gap is too large, breakdown of the dielectric (air) may not occur at all. The standard limits that must be adhered to when adjusting spark plugs depend on the type of engine and the design of the ignition system:
- For carburetor engines with a distributor-distributor: 0.5-0.6 mm.
- Carburetor with electronic ignition control: 0.7-0.8 mm.
- Engines with injection injection: 1.0-1.3 mm.
Any deviations from the specified norm are considered insufficient or excessive distances between the electrodes. The greater this discrepancy, the more problems will arise in the operation of the engine.
Types of motors affected by incorrectly set gap
The most critical consequences of insufficient or excessively large distances between the electrodes of the spark plugs appear on carburetor engines. In contrast to electronic ignition systems, which are capable of reacting to some extent to the operation of spark plugs and compensating for problems that arise by changing the quality of the working mixture. The carburetor practically does not have such capabilities.
What is the difference between spark plugs for contact and contactless ignition systems?
On classic cars VAZ 2101, 2102, 2103, 2104, 2105, 2106, 2107, two ignition systems are used: contact and non-contact.
In contact, current interruption occurs due to the opening of contacts in the distributor; in non-contact, due to a pulse from the Hall sensor. For each ignition system of these VAZ vehicles, spark plugs of different design and characteristics are required. The reason for this is different ignition coils with different characteristics used in contact and contactless systems.
For example, the B-117-A ignition coil is used in the contact ignition system of VAZ cars and has a spark discharge energy of 18-20 mJ, and in the contactless ignition system of the same cars, an ignition coil 27.3705 is installed with a much higher spark discharge energy of 40-50 mJ. Therefore, the use of spark plugs for a contact system in a non-contact system can lead to destruction of the spark plug electrodes due to a more powerful spark.
Differences between spark plugs for contact and non-contact systems
Contact ignition system
Spark plugs without an interference suppression resistor with a gap between the electrodes of 0.5 - 0.6 mm.
Examples of spark plugs for the contact system of VAZ 2101-2106, 2105, 2107 cars: A17DV, A17DV-10.
spark plug A17DV for contact ignition system
Contactless ignition system
Spark plugs with an interference suppression resistor and a gap between the spark plug electrodes of 0.7 - 0.8 mm (see photo at the beginning of the article). Designed for higher voltage and current than spark plugs for KSJ.
An interference suppression resistor is necessary to suppress radio interference that appears during operation of the ignition system, thereby reducing its negative impact on the operation of the vehicle’s electronic devices (switchboard, car radio).
Examples of spark plugs for a non-contact ignition system: A17DVRM, where the letter “P” indicates the presence of a resistor in the design of the spark plug.
Notes and additions