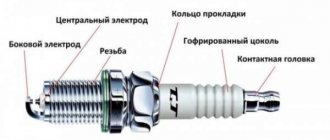
Sooner or later, any driver begins to wonder whether the engine of his “iron horse” is working well. A visit to a service center, where it is possible to diagnose the engine using computer programs, or measure the compression level, can help to understand this situation, but both of these methods, like other technologies in this area, require sophisticated equipment and a good specialist. Naturally, this work is usually quite expensive. In order to avoid unnecessary expenses, you can first try to check the operation of the motor yourself. A careful inspection of the spark plugs will help us with this, namely the carbon deposits on them that have formed during the use of the car.
Causes of carbon deposits on spark plugs.
Soot on spark plugs will help an experienced motorist quite clearly determine what is wrong with the operation of his car. Low-quality fuel, interruptions in carburetor operation, disturbances in the cylinder-piston system, and many other problems will leave their mark on the ignition elements. To notice violations, the car owner will only need to conduct a careful inspection of the engine protection system and assess the state of the engine’s functioning by the color of the soot.
How to correctly assess the condition of spark plugs
Plaque on spark plugs, which forms during operation of a car, can provide fairly accurate information, but the test must be carried out in compliance with a number of rules:
- You can evaluate the plaque only after a run of 150–200 km, always with new or well-cleaned SZ.
- Don’t panic if, during the cold season, you hear slight interruptions in the engine’s operation, and at low speeds the ignition elements become covered with a black coating. This is the result of the fact that at low temperatures the working mixture undergoes mandatory enrichment, which, if the engine is slightly warmed up, will not be able to burn completely. If there are repeated interruptions in the operation of the motor, it is worth paying special attention to the condition of the high-voltage wires.
- When visually diagnosing elements, it is worth remembering that they can self-clean only at high temperatures, which are only possible when the engine is running at high speeds.
What color is considered normal?
The performance of the gasoline power unit is indicated by spark plug electrodes painted in a light brown tint, without oil deposits and soot. A similar picture is observed in completely new engines and engines that have undergone a major overhaul.
If the color of the working part differs from the specified one, it is advisable to carry out further diagnostics and identify the cause of the problem. Moreover, the engine itself is not always the culprit. What color options are there for spark electrodes:
- light gray or white;
- black;
- brick or frankly red tint.
In addition to all sorts of colors, the candle skirt is covered with various deposits - soot, brown soot, or may simply look wet. These phenomena are also considered signs of various malfunctions. It is proposed to consider each situation in more detail.
Soot coloring
During long-term operation, the SZ cannot be perfectly clean, and many people are interested in what the carbon deposits should be like if the car is in good working order, and why this is not always the case. In a situation where the car engine is absolutely in good working order, when you turn out the spark plug, you can see a brownish coating - from light to dark shades of brown. This indicates that the electrode burned out evenly during the operation of the car. If all auto components operate correctly, the service life of ignition elements usually reaches 30,000 km. Modern models of two and three-electrode spark plugs may not need to be changed twice as long. If, upon inspection, the car owner discovers that the spark plugs have carbon deposits of completely different colors, this means that there are obvious irregularities in the operation of the engine. Let's look at the possible types of soot.
White soot
White deposits on spark plugs usually come in several shades, which indicate slightly different problems:
- Grayish tint. This is clear evidence of the use of low-quality fuel. In this case, it is enough to unscrew the SZ and clean it, and they will be ready for further use. An important condition for eliminating the problem will be changing bad gasoline.
- Shiny deposits combined with erosions on the contact electrodes. In this case, you can be firmly sure that the spark plugs are overheating. This situation is often caused by low-quality fuel, incorrectly selected fuel protection, or problems with the cooling system. After eliminating the causes of soot formation, the spark plugs may have to be replaced. In this case, you will need to pay more attention to their thermal characteristics.
- White coating. It should not be confused with carbon deposits. Plaque occurs due to antifreeze entering the engine cylinder. Quite often this process is accompanied by the appearance of white smoke from the exhaust pipe. If you smell the candles, you can feel a pronounced sweetish smell. To eliminate this problem, you will need to eliminate the ingress of antifreeze and only then replace the ignition elements.
Spark Plug Maintenance
If you have driven more than 30-40,000 kilometers on the same spark plugs, then even with a working ignition system, they will begin to act up. Plaque and iron oxide form on the electrodes, preventing the formation of a spark. In addition, when the metal burns out, it increases the distance between the electrodes, which complicates sparking.
Typically, spark plugs are replaced after long-term use, but in some cases their service life can be extended. To do this, just clean the contacts. But if you just clean the carbon deposits, the effect may be negative due to an increase in the gap between the electrodes.
You can restore the nominal gap by bending the upper electrode of the spark plug, monitoring it using a special probe.
Gap gauge
You should also pay attention to the condition of the insulators. If the insulator has cracks or other mechanical damage, the spark plug must be replaced. The presence of oil and dirt on the insulator is unacceptable. This reduces the effectiveness of the insulator, reducing resistance to electrical current. Its surface must be cleaned.
If the surface of the insulator is covered with an oil coating, then it is possible that the spark plugs are not screwed in tightly. They need to be unscrewed, the seats, contacts, insulators must be cleaned and screwed in again using a torque wrench. Table 1 shows torque values depending on the type of spark plugs and head material.
| Flat Fit Spark Plug (with Seal) | Tapered Fit Spark Plug | |||||
| Cylinder head material | Thread diameter | Thread diameter | ||||
| 18 mm | 14 mm | 12 mm | 10 mm | 18 mm | 14 mm | |
| Cast iron head | 35-45 Nm | 25-35 Nm | 15-25 Nm | 10-15 Nm | 20-30 Nm | 15-25 Nm |
| Aluminum head | 35-40 Nm | 25-30 Nm | 15-20 Nm | 10-12 Nm | 20-30 Nm | 10-20 Nm |
Cleaning the ignition elements
Spark plugs do not always require immediate replacement; sometimes they can simply be cleaned and the possible cause of deposits can be eliminated. This procedure can be carried out in two ways:
- Mechanical cleaning method. It consists of using simple sandpaper or a small wire brush. Despite the simplicity of the method, it has a number of disadvantages. With such cleaning, the coating on the SZ electrodes can be damaged, and simple scratches can cause increased accumulation of deposits.
- Chemical method. It is more preferable, especially for removing black deposits. The car enthusiast will need to prepare simple cleaning products, a toothbrush and a rag. The elements need to be soaked for about half an hour and then rinsed well. After drying, the candles can be used again.
Repair recommendations
Regarding repairs, we will consider each case individually, since individual faults and types of soot indicate the need for different types of repair work.
Oily black soot
The appearance of oil deposits indicates the penetration of oil into the combustion chamber. Accordingly, it is necessary to thoroughly study the condition of all components that could cause such a defect, and, if necessary, replace them. These components are:
Guide bushing wear
Wear of valve stem seals
The problem relates strictly to the wear of components of the cylinder-piston system. Accordingly, they must be replaced.
conclusions
Analysis of this problem and the experience of motorists suggest that visual diagnosis of spark plugs covered with soot is an excellent method not to miss the onset of problems with the car’s fuel system. You need to not be lazy and inspect these parts from time to time. In addition, do not forget that protective gear has its own service life, and when plaque appears, this is the first thing to check. If necessary, the spark plugs must be replaced and only then proceed with initial engine diagnostics.
Brown deposits on candles
Some drivers of cars using gasoline fuel conscientiously approach the choice of the “base” to be filled. It’s no secret that the first generations of the fuel series are not “clean”, and very often contain large amounts of impurities and deposits that are invisible to the naked eye. Nevertheless, they have an impact both on the spark plugs and on the entire movable component of the car.
Low quality fuel is quite often the culprit of additive clogging. In practice, this effect is manifested by brown soot on the spark plug insulator. The car's injector, due to clogging, is unable to cope with its duties, and gasoline begins to completely fill the spark plug. The electrode of a standard spark plug is not able to burn out all the gasoline that surrounds it, and some of it settles on the walls of the ignition device itself.
In fact, constant exposure to wet conditions leads to spark plug failure. The gasoline previously deposited on the walls dries out, and the generated spark exposes the ignition system itself to even greater thermal effects. The brown soot that forms on the spark plug insulator is a product of the reuse of gasoline.
Very often, drivers who are faced with a similar problem complain that the engine begins to “trouble.” It is possible that no problems with operation will arise, and the driver of the car will learn about such an incident only during the next maintenance.
The working part is covered with black soot
Black spark plugs are a symptom indicating that the fuel mixture is too rich (the proportion of gasoline is increased above normal). Therefore, the fuel does not burn completely and forms a layer of soot on the chamber walls and spark plug electrodes.
An additional sign of this problem is black or dark gray smoke from the exhaust. When over-gassing, small flakes of soot may fly out of the pipe.
There are quite a few reasons for the enrichment of the air-fuel mixture, the most common ones look like this:
- One of the key sensors has become unusable - air flow, temperature, throttle position or oxygen content in the exhaust (lambda probe). The controller activates the emergency program and prepares the mixture according to other indications.
- Carburetor malfunctions (clogged air jets, worn throttle valves, etc.).
- Failure of the pressure regulator in the fuel line.
- Wear of nozzles - nozzles “overflow” and leak when the power unit is not working.
- Problems with sparking - the power of the electrical pulse is not enough to ignite the combustible mixture normally.
Important! If during the diagnostic process you find black spark plugs, the fault should be found immediately. Increased gasoline consumption is only part of the consequences of excessive enrichment.
There are others, not so harmless:
- some of the unburned fuel penetrates the crankcase and dilutes the oil, accelerating the wear of engine parts;
- the other part gets into the exhaust manifold, which is why shots are periodically heard in it;
- soot clogs the expensive catalytic converter - it has to be cleaned or replaced with a new one;
- The service life of the spark plugs is sharply reduced.
When running on a rich fuel mixture, the engine “chokes”, unstable idling and skipped cycles are observed. When a certain amount of soot heated to a high temperature accumulates in the chambers, a “pseudo-diesel” effect occurs - after turning off the ignition, the engine does not want to stall and makes 2-10 crankshaft revolutions. The reason is hot soot, igniting the combustible mixture without a spark.
Light electrodes
White or light gray spark plugs in all cylinders are a sign of a lean air-fuel mixture supplied by the injector or carburetor. Moreover, the skirt, area near the electrodes and the threaded part are absolutely dry, without traces of oil.
Why is the fuel mixture supplied lean?
- lambda - the probe incorrectly informs the control unit about the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, the reason is sensor wear;
- faulty or clogged nozzles;
- incorrect carburetor settings or clogged fuel jets;
- insufficient pressure in the injector fuel rail;
- problems with the idle air control;
- air leakage under the manifold or in another place;
- unsuccessful chip tuning of the controller made by the owner of the car.
A lean mixture does not pose any particular danger to a running engine, but it does cause discomfort to the driver. The car accelerates slowly, pulls poorly and jerks - there is a lack of fuel. Oddly enough, the phenomenon causes increased gasoline consumption - a car enthusiast who wants to achieve better performance indicators presses the accelerator pedal harder and more often.
Note. Often the light shade of the working electrodes is explained by the type of fuel used. If the car is operated on methane or liquefied gas (propane-butane mixture), this color is considered normal.