Wheel balancing is the elimination of imbalance of a car wheel by shifting the center of rotating masses as close as possible to the axis of its rotation. The need for such a procedure arises when the mass of tires and wheels is displaced relative to their axis of rotation. Because the imbalance is transmitted to the car’s suspension elements.
Balancing the wheels on a car prevents excessive vibration of the steering wheel and body while driving, and also helps prevent deterioration in handling and premature wear of wheel bearings, ball joints and suspension silent blocks.
In this article we will talk in detail about when you need to balance wheels, how this procedure is carried out and whether you can do it yourself, as well as answer other frequently asked questions about wheel balancing.
What affects car wheel balancing?
It is almost impossible to ensure an absolutely accurate mass distribution relative to the center of the tire and wheel. Therefore, a slight imbalance is present even in new products. A deviation of a couple of tens of grams already has a negative impact on the behavior of the car during operation, giving rise to such problems as:
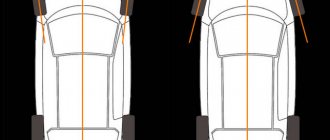
Example of wheel imbalance
- steering wheel beating and body vibration when driving;
- deterioration of controllability, deviation to the side from the correct trajectory;
- premature wear of wheel bearings, ball joints, suspension silent blocks;
- uneven and accelerated tire tread wear.
Eliminating this imbalance and related problems through compensating elements is exactly what wheel balancing does .
The symptoms and consequences of operating a car with unbalanced wheels directly depend on how much and in which direction the mass of the assembled wheel is shifted relative to the center of the rotation axis. Depending on this, three types of imbalance .
When is wheel balancing needed: causes and types of imbalance
| Type of imbalance | What causes | How does the car behave? | How the imbalance is corrected |
| Static (vertical) | Imbalance of the wheel vertically relative to the axis of rotation. | Radial runout of the wheel, slight swaying of the body on a vertical plane on a flat road, intense wear of the tire tread in one area across the entire width. | Static leveling is the installation of a counterweight at a point opposite to the point where the unbalanced mass is located. |
| Dynamic (longitudinal) | Displacement of the center of mass along the axis of rotation of the wheel. | Steering wheel runout at speeds of 40 km/h (tire imbalance on the front axle) or 100 km/h (tire imbalance on the rear axle), accelerated tread wear along the circumference on one side. | Dynamic compensation – placing weights to correct imbalances on the disc. |
| Combined | Imbalance in the vertical and horizontal planes. | Signs of dynamic and static imbalance are combined. | Use of compensating weights. |
a combined imbalance is most often observed , and the installation location of the compensation weights is chosen in such a way as to ensure balance on both axes. You can achieve the best result by changing the position of the tire on the rim. Sometimes this allows you to do without the use of cargo, but it requires significantly more time.
Elimination of wheel imbalance is possible with the help of microbeads - special granules poured inside the tire. However, due to the high cost of the latter and insufficient accuracy on small-diameter wheels, this method is not widely used.
Important Balancing Information
When balancing wheels, certain rules must be followed. If you ignore them, the result will noticeably worsen.
- It is necessary to remove lead weights from the rim of the disc;
- The disk is cleaned of dirt;
- It is checked how well the tire is installed on the rim;
- If there are plastic caps on the wheels, the wheel balancing is disrupted.
You can often hear the opinion from car enthusiasts that balancing does not require special attention, and the quality of car operation does not depend on it in any way. If balancing is incorrect, you may encounter the following problems:
- Tires wear unevenly;
- Individual suspension elements are subject to accelerated wear;
- The vehicle's handling is noticeably reduced;
- You can feel the steering wheel beating;
- When driving, the car may pull to the side;
- The braking distance increases noticeably;
- Road grip is reduced;
- The body begins to vibrate;
- The degree of comfort when using the car is noticeably reduced;
- Car costs increase significantly.
How often should wheels be balanced?
The recommended frequency of wheel balancing is every 10–15 thousand kilometers . It is advisable to carry it out every time you change wheels seasonally. However, sometimes additional procedures may be required.
When do you need to balance your wheels more often?
How often should you do balancing: video
- After tire fitting . A prerequisite is to balance the wheel after each installation of a tire on a rim (including after repair) due to changes in their relative position.
- After falling into a hole or hitting an obstacle at high speed . Even if there is no visible damage to the tire or wheel, the balance of the wheel may be affected.
- During frequent braking with wheel locking on a car without ABS . Sharp braking leads to uneven tread wear, resulting in changes in mass distribution.
- With an aggressive driving style . Sharp acceleration and braking, and cornering, accelerate tire wear, thereby disturbing the balance of the wheels.
- When driving on bad roads . On roads with damaged or gravel surfaces, as well as off-road, tires also wear out faster.
- If vibrations occur in the steering wheel . Vibrations and beating of the steering wheel are one of the signs of imbalance.
- After the car has been idle for a long time . If the car has been sitting motionless for six months or more, then deformation of the rubber is inevitable.
How often to balance wheels also depends on the characteristics of the tires and wheels:
- Low profile tires need to be balanced more often as they are lighter and more susceptible to damage.
- The wider the tire relative to the diameter of the disc, the more susceptible it is to dynamic imbalance.
- Summer tires need balancing less often than winter tires. Winter tires are softer, so after warming up they wear out faster when braking and on bad roads.
- Studded tires must be additionally balanced if the studs are partially lost.
Is it possible not to balance the wheels when changing them?
Drivers often have a question: is it necessary to do balancing when replacing wheels and tires seasonally? If you have one set of wheels, the answer is clear: balancing is required every time the tires are reinstalled. If the second set of tires is on separate discs, then it all depends on the storage conditions of the rubber. Wheels may not be balanced if the following factors are met:
- Since the previous balancing, the tires have traveled less than 10 thousand km;
- before the last change of these wheels there were no vibrations or beating in the steering wheel;
- the wheels were stored in compliance with the rules: in a suspended state, maintaining pressure and without sudden temperature changes.
All stages of the process
At service stations and tire fitting stations, technicians eliminate defects of unevenly divided mass using compensating weights in certain places. The process is performed on special equipment.
The equipment automatically determines the place where the weight needs to be installed. The wheel dimensions are entered into the computer. The equipment will then select the optimal point for additional cargo. This is static balancing.
What type of weight to use depends on the disk and its parameters. This can be zinc or lead weight. They differ in weight - usually the weight ranges from 5 to 100 grams.
There is also dynamic balancing, however, this service is not provided everywhere. The problem is the equipment - in most cases it is very old. The wider the wheel, the greater the chance that dynamic imbalance will appear.
Final balancing is performed after static and, if possible, after dynamic. When the car is suspended, special equipment is installed under the wheels, the wheels are spun to high speeds, the system takes measurements and marks the places where the load should be installed. The system also calculates the weight of the load itself.
This process requires serious equipment, available only in professional wheel centers.
There is also automatic balancing, but it is not for cars, but for trucks. The master pours a special granule, beads, and sand into the wheel. During movement, due to centrifugal force, the material is attracted to the tire inside. The result is self-balancing. It is a pity that the technology is not available for passenger cars.
Equipment
There are different types of equipment – stationary and mobile. Stationary machines can determine the amount of imbalance of only the dismantled wheel. These machines can be electrically or manually driven.
On the first models, the disk rotates due to an electric motor. In the second case, you need to turn it manually
It doesn't matter what makes the disk spin - it doesn't affect the accuracy one bit
Simple models of machines work with steel disks and several types of cast ones. More complex equipment can work with disks of any design without problems. The program itself is capable of placing a weight at any point.
The electronic part of serious stands is capable of performing a lot of useful functions. For example, it can divide large loads into many small ones and distribute them to different points. This mode is effective if the imbalance is huge.
In this case, the stand shows several points. Another useful feature is optimization. The electronics analyze the imbalance of the tire and wheel, then find the optimal position relative to each other, thereby ensuring maximum balance. Using this function, you can reduce the amount of weight on the disk.
Mobile equipment is rolling stands for cars. They can be used for balancing without removing the wheels. The advantages are that the stand also takes into account other rotating masses - these could be hubs, brake discs or drums. Most often, such stands are used for finishing work after a stationary stand.
How to do balancing correctly
The wheel is thoroughly cleaned and then installed on the machine. Next, the equipment calculates the weight of the weights and the mounting points.
The mechanic installs the weight and checks the balance. If all indicators are normal, then the wheel is installed on the car. If there is no balance, then the process continues further.
Errors
There are a number of rules that must be followed:
- The disk must be thoroughly cleaned. There is usually a lot of dirt on the outside and on the inside. Automation calculates the weight of the weights. If you work with a dirty disk, you can lose your balance already on the first bump, when large dirt falls off the disk;
- Be sure to remove all old weights;
- It often happens that the tire simply does not fit into place. This is not visible from the outside, but it affects the balancing process;
- Hubcaps and other accessories can add imbalance.
These mistakes are often made at tire shops, because they work not on quality, but on volume and speed.
How to understand that wheel balancing is needed
An experienced driver can easily identify a significant imbalance of wheels, as it directly affects the behavior of the car.
Typical symptoms of imbalance:
Signs of imbalance in movement: video
- Vibrations and shaking of the steering wheel, progressing with speed.
- Deterioration in controllability, deviation from the correct trajectory.
- Uneven wheel noise when driving on a flat road.
- Vibrations in the rear of the car (imbalance of the rear axle wheels).
- The tire tread pattern has uneven wear and there are “bald spots” on it.
Similar symptoms can occur with steering and suspension faults. Therefore, if balancing does not help eliminate the problems, then these components should be diagnosed.
The need for balancing is indicated by the presence of defects in tires and wheels that were not previously present during a visual inspection.
General balancing rules
The wheel must be absolutely clean.
Balancing
Moreover, you need to wash it not with a hose, but in a special washing machine. If the service center does not have this, it is better to leave there immediately. Other rules:
- The technician must first balance the disc separately, and then the wheel assembly.
- The total weight of weights per wheel should not exceed 60 grams.
- A good result can often be achieved by moving the tire relative to the wheel, placing the heaviest points of the wheel and tire on opposite sides.
It is mandatory to use special lubricants when beading.
The principle of balancing wheels on a car
The general principle of wheel balancing is to detect deviations from the uniform distribution of mass relative to the center of the wheel and eliminate them by moving the tire and wheel and/or adding weights. If there are disc deformations, they are first corrected, and only then the balance is restored. Before performing the procedure, it is necessary to wash the surface of the wheel and remove small stones and other objects from the tread that may affect the weight distribution.
To perform vertical balancing, you need to find the lightest points on the circumference of the wheel and weigh them down. For longitudinal balancing, it is necessary to detect points that cause a displacement of the vectors of inertia forces, and similarly balance them by hanging weights. Tire offset helps less in this case, because it is usually the tire, and not the disk, that is more involved in causing the imbalance.
How to do wheel balancing
There are 4 main ways to balance car wheels, depending on the equipment:
Balancing wheels on professional equipment: video
- Static (manual) balancing . The wheel is mounted on an axle that allows free rotation and allows detection of mass displacement. To search for statistical imbalance, the wheel rotates in the vertical plane, while dynamic and combined imbalances rotate in the horizontal plane. If there is an imbalance, the wheel will constantly fall towards the point of overweight. The technology is simple and accessible, but has low accuracy ; the quality highly depends on the qualifications and experience of the master. Today, such a service is not provided by professional service stations, but can be found in garage workshops.
- Dynamic balancing on a stand . The wheel is fixed to the axis of the balancing stand, after which it is rotated, during which sensors detect and measure the imbalance. Next, the operator independently or based on the stand’s prompts (if this function is available) selects their installation locations. The procedure ends after the imbalance is zero.
- Automatic powder balancing . The wheels are filled with a special powder (also known as granules and beads), which, under the influence of centrifugal forces, is distributed over the inner surface of the tire and balances the wheel. Under the influence of a static electric charge generated by friction, the powder adheres to the wheel and is held at the desired points. The method allows you to quickly balance the wheels of heavy equipment, it is relatively simple, but the granules themselves are expensive, their correct dosage is required depending on the size of the wheel and the magnitude of the imbalance.
- Final balancing on the car . The car wheel is jacked up and a balancing device equipped with a roller and sensors is attached to it. The roller spins the wheel to speeds of about 90–100 km/h, and sensors record the magnitude of the vibrations that occur and calculate the load attachment points and their mass. Since the hub, the brake drum or disc, and the drive axle shaft rotate together with the wheel, this balancing technology makes it possible to balance all arising inertial forces as accurately as possible and eliminate runout. The advantage of the method is high accuracy, the disadvantages are low prevalence and high price.
The table below presents a comparison of wheel balancing methods, which will help you weigh their pros and cons and find out which balancing of passenger car wheels will be the best choice, and what is the best way to balance truck wheels.
How wheels are balanced: description and comparison of technologies
| Balancing method | Advantages | Flaws | Peculiarities | Average price for the season* 21–22, rub. |
| Installing balance weights manually |
|
| Due to its low accuracy, the method is suitable for balancing small passenger wheels on cars moving at a speed of no higher than 100 km/h. | Free (only costs for weights) if done independently. Almost never found in professional services. |
| Adding balancing powder to the tire |
|
| Suitable only for vehicles with wheels with a diameter of 15 inches or more due to low accuracy. |
|
| Dynamic balancing of a car on a stand |
| Weights get lost when driving on bad roads and during washing, spoiling the aesthetic appearance of the wheel | The most common balancing method. Optimal for cars of all classes. |
|
| Final wheel balancing directly on the car |
|
| Recommended for fast sports cars, not available for heavy equipment (trucks, buses). |
|
*Average prices are indicated for two balancing of 4 wheels per year, when switching from summer tires to winter tires and vice versa.
**Before final balancing, a “rough” dynamic balancing may also be required to eliminate the most pronounced imbalance.
Some tips for improving wheel balancing
To check the accuracy of the tire mounting procedure, after it has been carried out, you can remove the wheel from the balancing stand and then put it back on. Repeated diagnostics will certainly show the presence of an imbalance. For wheels made using light alloy casting technology, a discrepancy of 3 grams per side is acceptable. In the case of steel stamping, the plus or minus can reach five grams.
Some tire centers have special installations that help with “finishing” balancing. It is in no way an alternative to the procedure carried out on classic stands, but serves as an important addition with which you can determine the static imbalance of not only the wheel, but also the entire assembly consisting of wheels, hub and brake disc. The maximum weight of weights used during “finishing” balancing should not exceed 15 grams.
How to balance a set of tires at home?
DIY balancing device
If a tire service is unavailable or if you want to save money, you can balance the wheels yourself using a machine that can be assembled in a garage. The simplest garage balancing stand consists of a hub securely mounted on a rigid support with a flat base.
Balancing must be done in the following order:
- Fasten the wheel, cleaned of dirt, to the hub and spin it by hand.
- During rotation, observe the beating of the rubber, the “figure eight” of the disk.
If there are strong pronounced deformations and runout, balancing is unlikely to help. - Wait until the wheel stops and is balanced, put a chalk mark at the top point.
- Turn the wheel 90 degrees (a quarter turn) in both directions several times, waiting for it to stop after each turn.
- If the wheel is in a different position each time, there is no pronounced static imbalance, it is “conditionally balanced.”
- If the mark is always at the top, the main point of imbalance has been identified, you can begin to eliminate it.
The faster the wheel returns to the top position, the more weight is needed. Its exact value can only be predicted experimentally. Without experience, you can start with a load weighing 20–30 grams. - To eliminate the imbalance, you need to hang (without fixing it securely) a weight opposite the mark and repeat step 4.
- If, after hanging the weight, the mark still appears at the top, its mass must be increased; if it now goes down, it must be reduced.
- It is necessary to adjust the weight of the weights until the wheel, after spinning 90 degrees, stops in any position. When the optimal set of weights has been selected, they can be fixed.
For a more uniform distribution of masses, you can use several weights: for example, instead of one for 40 grams on the outer side, attach 20 gram weights on the outer and inner sides opposite the mark.
The described method is a static balancing designed to shift the center of mass of the wheel as close as possible to the axis of its rotation. It allows you to eliminate very large imbalances with an accuracy acceptable for cars that do not drive fast, but is not suitable for fine adjustments of balance. This is acceptable wheel balancing for VAZ classics and other similar models.
More accurate balancing of car wheels at home is possible using a “spinning top” shaped device. The tool can be made on a lathe from a solid steel blank (moreover, steel is harder than the common ST-3) with a diameter of about 150 mm, so that the structure is monolithic and balanced.
Aluminum and other soft metals are not suitable because the ends of the spindle axle must be rigid and not deform or become dull under the weight of the wheel!
The tool should have a slight taper on one side that turns into a thread. The conical shape is needed so that the wheel self-centers when the nut is tightened.
The balancing process is carried out as follows:
Balancing a wheel at home: video
- Place the “top” in the central hole of the disk and tighten it with a nut.
- Place the wheel with the tip of the “top” on a flat, hard surface or in a stand with a recess.
- Move the wheel and release it, controlling the position in space. A balanced wheel should independently occupy a horizontal position and return to it after rocking. If there is an imbalance, it will not stay “in the horizon”.
- If an imbalance is detected, you need to take a weight and place it at the highest point of the wheel, and then repeat step 3. If the same section still rises with the load, its mass must be increased; if it begins to fall, decrease it.
- The weight of the weights is selected until the wheel on the spoke begins to take a horizontal position and returns to it after each rocking. The static balancing of the wheel is completed, and if high accuracy is not required, then it can be placed on the car. If you also need to eliminate dynamic imbalance, then you need a rigid tripod (for example, a laboratory one) with chalk and the following further actions:
- The wheel is manually spun on the top to the maximum possible speed.
- With the help of a small wooden block, lightly pressed against the upper edge of the top, the vibrations introduced during spinning are dampened.
- The tripod arm with the chalk attached is smoothly brought to the wheel rim until it makes the first contact.
- After several revolutions of the wheel (and touching the chalk), you need to stop it and see at what point the chalk touches the disk.
- At the point where the chalk touches, a weight should be secured (the weight is selected experimentally), and a second weight of the same weight should be secured on the diametrically and diagonally opposite side of the rim. This is necessary to prevent static imbalance.
- Experiment with the weights until the beating of the wheel goes away and it stops touching the chalk with one point.
Self-balancing in a garage cannot fully replace the procedure on modern equipment due to low accuracy. Therefore, if possible, it is better to visit a service station and eliminate the imbalance completely. This is more reliable, and taking into account the considerable labor required to balance large wheels, it is also much easier.
Static balancing
The simplest type of balancing, it is done at any tire shop. This balancing eliminates static imbalance of the wheel, that is, when one point of the wheel is heavier than the rest. To do this, the wheel is spun several times on a special machine, then waiting for it to stop after completion of rotation by inertia.
The master marks the bottom point and then repeats the procedure. If the points lie scattered, everything is in order with the wheel. If some area of the wheel is always at the bottom, the imbalance needs to be eliminated.
To do this, the master places weights at the top point of the wheel, achieving uniform rotation.
Basic mistakes when balancing wheels
Mistakes made when balancing wheels can result in the imbalance not being completely corrected. As a result, while driving the car, the same symptoms may occur as before the procedure.
The main signs of improper wheel balancing and how to eliminate them are presented in the table.
Poor wheel balancing: signs
| Balancer error | Why is this happening | How to determine | How to fix |
| Balancing when there is dirt on the wheel or moisture inside the wheel | Adhered dirt, foreign objects lodged in the tread, and water inside the tire create inconsistent imbalances. | The wheel is not brought to zero on the machine, the imbalance is not completely eliminated | Wash the wheel thoroughly, remove foreign objects from the tread |
| Balancing a wheel with a broken tire or wheel geometry | The tire is deformed due to abnormal loads or violation of storage conditions |
| Replace a defective tire or wheel |
| The disc is deformed, its core is displaced relative to the rim, a “figure eight” appears | |||
| Incorrect torque of the hub bolt on the balancing machine | Deformation of the central center of the disk |
| Correctly fix the wheel on the machine hub and recheck the balance |
| Weak disk tightening on the machine hub | |||
| Incorrect selection of centering cone | |||
| Violation of technology for installing a tire on a disk | Misalignment of mark and nipple | Many tires have a colored manufacturer's mark at the point of lightest weight, which should be located near the valve. | Orient the tire on the rim so that the mark is near the valve |
| Poor quality side lubrication | The technician did not apply a special compound to the tire beads, which is why their fit is noticeably poor. There may be some beating noticeable to the naked eye. | Coat the beads with a sealing compound and inflate the wheel to maximum operating pressure. | |
| Insufficient pumping | The tire did not press tightly against the rim due to lack of pressure. | ||
| Misalignment when installing a wheel on the vehicle axle | Tightening bolts or nuts in a circle | The wheel on the machine shows normal balance (“to zero” or an imbalance of less than 5 grams), but after balancing the wheels there is still vibration. | Unscrew the wheel and re-tighten it to the hub, tightening the bolts or nuts crosswise diagonally, observing the torque specified by the car manufacturer |
| Uneven tightening of bolts or nuts around | |||
| Failure to secure the machine | Unreliable fixation of the machine on the ground (on a concrete base, using anchors) | In the process of spinning the wheel, the machine itself begins to vibrate, and the floor in the workshop hums. | Balance the wheel on a machine fixed in accordance with the rules for its installation and operation |
| Poor fixation of weights | The master did not fasten the weights securely enough, without pressing them to the side or without treating the surface of the disk for gluing | Soon after balancing, vibration arose again, there are no weights on the wheel, traces of fallen weights are visible (on the alloy wheels). | Re-balance the wheel and securely secure the loads. For stamped disks - check the clamping of the weights; for cast disks - clean the surface before installing the weight on an adhesive base |
| Inaccurate balancing | The master did not set the imbalance indicators to zero, leaving a slight runout | Small vibrations still appear at speed. The balancing stand shows an imbalance on one side of more than 5 grams. | Rebalance the wheel. |
| Excessive amount of cargo | The imbalance measurements were made inaccurately, which is why the number of weights and their mass were selected in excess. The tire is not aligned relative to the rim. | The total weight (for a passenger wheel) is more than 70 grams on each side. | By moving the tire relative to the disk, select their optimal position, in which less weight is needed. Have the wheel balanced on a more accurate machine and/or by a more experienced technician. |
| The tire or disk has critical deformations | Replace a defective tire or wheel |
How to carry out balancing
This operation is not particularly difficult, but to perform it you need a specialized balancing machine with a special fastening cone that automatically centers the wheel. The wheel is spun on a machine and, with the help of lead weights attached to the disk, its position is achieved as randomly as possible when stopping. This is called rough balancing.
For accurate balancing, you need an electronic machine into which the wheel parameters are loaded. With the help of such a stand, balance is automatically measured in different positions of the wheel, and information is displayed on the screen about the places where the weights should be installed and their weight.
Weights are made of lead and can be padded or adhesive. The latter are glued inside the wheel rim, they are not visible to the eye, they do not spoil the appearance of the wheels.
But for winter it is better to use padded weights. The thing is that in winter, due to increased temperature fluctuations, the linear dimensions of the disks change. And such fluctuations do not have the best effect on the properties of the adhesive tape that secures the balancers. It will be easy to knock off such a “played up” weight with a stream of water at the sink. But, there are disks on which it is not possible to put weights; their balancing is carried out only with adhesive balancers.
To perform high-quality work on wheel balancing, it is necessary not only to correctly configure the machine itself, but also to have a certain skill. These two factors together influence the final result.
And, if you can also evaluate the work of a tire fitter visually, then here is the accuracy of the equipment settings, the date of its last calibration, etc. you won't determine. It is for this reason that balancing should only be done in a trusted place that you trust.
Equipment
It is important to prepare the wheels for the balancing procedure, namely, thoroughly clean the tread and disk from sand and dirt. If this rule is neglected, the operation may be performed inaccurately and will have to be repeated. If the car has already been balanced, the technician must remove the balancing weights before starting.
It is very important to check the tire pressure: the tires should not be flat. Before balancing the wheels, the center of gravity is determined, which is monitored by balancing machines. Devices can range from ordinary computers to huge systems with laser sensors and measurement mechanisms. Once determined, the machine automatically installs the balancing weight.
To carry out the procedure, a balancing machine is used, which aligns the position of the wheel along the center of the rotation axis during the procedure.
The type of balancing weight depends on the type of discs. Weights with fastening brackets are installed on steel disks, and with landing on the inside - on cast disks. They are mainly made from zinc, lead or steel.
Weight also depends on the level of imbalance. The weight of the balancing weight with bracket fasteners varies from 5 to 100 g. The weight of the weight for alloy wheels is from 5 to 60 g.
The complexity of the procedure also depends on the mass. The larger the weight, the more likely it is that the wheel needs to be checked for its external qualities: tread condition and general geometric qualities such as symmetry.
In the cold season, due to temperature fluctuations, adhesive weights may come off, which cannot happen with padded ones.
There are special types of weights for stamped wheels. They are stuffed between the disk and the tire, installed on the edge of the disk. Padded weights are not suitable for low-fusible discs. For this type, there are Velcro - self-adhesive weighting agents with an adhesive base. They are practically invisible, because they practically do not stand out from the general appearance. However, they are used only on a perfectly flat surface.
The process of balancing car wheels
The procedure for balancing a car starts with removing the discs, regardless of the characteristics of the model. Balancing occurs according to the following method: remove the wheel, balance it, put it back, then move on to the next one. This completes the procedure for all wheels.
The result depends mostly on the artist, and only a small part is due to the equipment. If the device is modern, then the specialist can only monitor the condition of the rubber and the progress of the procedure.
After cleaning the tread from stones and dirt, a plate is selected, depending on the number of holes in the disc. The specialist places the plate on the disk, tightening the nuts well. After that, he goes to the machine to balance the wheel.
Before balancing, remove any dirt or stones from the tire tread.
After identifying the problem area, the process of installing weights begins. Upon completion, the master returns to the equipment and re-checks the geometric condition of the wheel. If the procedure is successful, the wheel is installed in its place and the next one is taken. Otherwise, the procedure is repeated.
What errors can occur during balancing?
- The imbalance cannot be determined unless the tire is cleared of stones and dirt.
- Installing new weights without removing old ones.
How to check wheel balance
You can check it yourself. If you feel that on a flat road, when you release the steering wheel, the car immediately throws to the side, or you feel that the steering wheel vibrates with a certain frequency, then this is a sign of imbalance.
Place the car on a jack. Draw a transverse line on the rubber with chalk. Spin the suspended wheel. A bent wheel, a figure eight, you can see right away.
Video
Training video for those who want to purchase a machine and engage in this business. How to learn how to balance wheels.
One of the options for a balancing machine.
Boarding and balancing.
FAQ
Why is wheel balancing done?
Wheel balancing prevents wheel runout, which negatively affects handling and ride comfort, and also shortens the life of tires and suspension parts.
How often should wheels be balanced?
The average wheel balancing interval is 10,000–15,000 km. Wheels also need to be balanced when reinstalling a tire on a rim or after a severe impact to the wheel as a result of falling into a hole or hitting an obstacle.
What happens if you don't balance your wheels?
Wheel imbalance leads to increased vibrations when accelerating, deviation from the correct trajectory, accelerated wear of the tread, hub bearings, ball joints, silent blocks and other parts in the suspension.
How to check wheel balancing?
To balance wheels, it is best to use a professional stand, which will accurately detect points of imbalance and determine its magnitude.
How to recognize unbalanced wheels?
Unbalanced wheels cause vibrations and beating in the steering wheel, increase tire noise, and can cause the car to sway vertically on a flat road.
What are the dangers of wheel imbalance?
With the help of balancing, you can evenly distribute the weight of all wheel parts relative to the axis of rotation. After balancing, the center should be located on the axis of rotation. This operation must be done in order to obtain minimal vibrations of the wheel axis when it rotates.
The wheels must have equal mass in different directions of the axis of rotation. Wheel vibration can occur when there is an imbalance in the weight distribution that does not coincide with the direction of the axle. As a result of this, vibration can cause a number of consequences that will negatively affect the operation of the vehicle:
1. Deterioration of tire adhesion to the road due to transmitted vibration from the wheel. As a result, the driver may experience deterioration in vehicle controllability, as well as an increase in braking distance.
2. Rapid destruction of bearings in hubs due to increased loads on the vehicle’s suspension mechanisms. If the bearings break, the chance of losing a wheel increases, and as a result, the risk of getting into a traffic accident and further evacuation of the car with the help of a tow truck in Kolpino, which works around the clock, increases.
3. Frequent replacement of tires due to rapid wear of the tread, which occurs due to the deterioration of its technical characteristics caused by vibrational mechanical load.
4. Rapid fatigue of the motorist and increased loads when turning the steering wheel, caused by vibration transmitted from the wheels to the steering wheel.
How often should balancing be done?
To understand when your car's wheels need balancing, you should know the main reasons for contacting a tire shop to carry out this type of work.
For example, balancing weights can move out of place after a wheel falls into a hole. When you pressure wash your car, there is a chance that the glued weights will fall off. Collisions with speed bumps, curbs, manholes in yards, as well as impacts on the wheel with sudden movements disrupt the design of the wheels, and this in turn upsets the balance of forces affecting the wheel.
When driving aggressively and sportily on roads, balancing must be done after every 6-7 thousand km. According to manufacturers' recommendations, tire balancing should be carried out every 15 thousand km, but, as a rule, this occurs later than the annual tire replacement. If the driver uses an all-season vehicle, it is recommended to perform balancing once a year.
If the driver begins to notice that the steering wheel of the car has begun to vibrate even at low speeds, this may also be a reason to contact a tire repair shop. The reason for this phenomenon may be incompatibility of the wheel rims and the characteristics of the hubs. This can be identified through the wheel balancing procedure.
See further:
- How to properly tow a car using a flexible hitch (cable)
- How drivers are deceived at gas stations
- Current special equipment for big cities
- Do traffic police fines expire after a year?
- Advantages of GAZelle tow truck. Let's consider the used option
- How to replace a driver's license?
Final balancing
Final balancing is done infrequently, since the procedure requires rare and expensive equipment, which only large service centers have. Usually it is used by owners of fast sports cars.
The essence of final balancing is that the wheel rotation parameters are measured directly on the machine.
That is, the car is installed on a platform, the wheel is spun using rollers up to 90-100 km/h, and the automation takes the appropriate measurements. The wheels are also balanced with weights, but, in addition, the computer gives recommendations on the relative position of the wheels: it is better to put the front right one in place of the rear left one, etc. This is done so that the residual wheel defects compensate each other.