What are the differences between spark plugs?
In addition to the obvious parameters, there are also those that are invisible at first glance. But they can cause difficult starting, interruptions, or even quickly lead to failure of the internal combustion engine. What differences should you pay attention to?
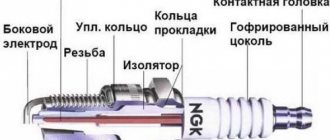
- Thread diameter and pitch - with inappropriate characteristics you will not be able to screw it into the cylinder head.
- The height of the threaded part - if a short 12 mm spark plug does not cause harm with a short mileage (until the free turns of the threads in the cylinder head become overgrown with soot), then a long one (19 mm) can “kill” the engine when it meets the piston.
- Heating number is one of the main parameters. Characterizes the thermal operating mode. Excessively “cold” spark plugs will not be cleaned and will become covered with soot, due to which the engine will become unstable. Hot ones will provoke detonation, up to glow ignition. Visually, you can distinguish by the thickness and length of the ceramic cone of the central electrode.
- The seal is a crushable ring or a conical fit (depending on the design of the internal combustion engine).
- Hexagon size - turnkey products are available from 13 to 25.4 mm. By installing larger ones, there is a chance that a “candlestick” with a larger diameter will not fit in the well.
- The connection of the high-voltage wire is a thread for a nut (obsolete type) or a tip of the SAE standard. If you have an old motorcycle, don't worry. For most products, the adapter is unscrewed.
- The number and material of electrodes - there are both classic ones with one side, and various modifications - with bifurcated, two, three, and even four dischargers.
“Multi-spark” candles received their popular name from the visual effect when, at a high frequency of sparking, we notice many flashes between all electrodes. In fact, there is only one discharge, and it occurs along the shortest path. But due to the fact that the distance is almost the same, it alternately jumps between different contacts, creating the appearance of simultaneous sparks in all directions.
What is heat number
The heat number is a numerical value that expresses the period of time after which the spark plug is able to achieve glow ignition, which determines the level of compliance between the spark plug and the engine of a particular model. A large value of the heat number indicates the ability of the candle to heat up less, and a small value of the heat number indicates the opposite. Accordingly, the first type of heat rating designates a “cold” candle, the second - a “hot” one.
“Hot” or “cold” candles - which are better?
The right choice is those that comply with the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations. Conscious deviation in one direction or another is acceptable when the user clearly knows for what purpose this is being done.
For example, the car idles mostly in traffic jams or does not have time to warm up during short trips - the standard version will quickly become covered with soot, because will not self-clean. Therefore, we need “hotter” ones.
If the engine is operated under maximum load (auto racing, drifting, towing a heavy trailer), then in order to avoid local overheating and detonation, it is permissible to install a “cooler” kit.
The optimal temperature in the arrester area is 400-850 degrees Celsius. The more heavily loaded the internal combustion engine, the colder the spark plugs are needed. Recommendations for the same power unit in different versions (industrial, marine, automotive, racing) may differ.
Correct selection
Standard spark plug geometry: 14-19-16. 14 mm is the diameter of the threaded part, 19 mm is its length, and 16 is the size of the upper nut for which the spark plug wrench is selected. There are also less common versions of spark plugs with other geometric dimensions - it all depends on the seat in the engine head provided by the engineers. It is important that the spark plugs exactly match the calculated geometry. Installing the first spark plug you come across may result in damage to the engine piston and a major overhaul.
But it is impossible to select spark plugs only by thread size, because many more characteristics need to be taken into account: spark gap, heat rating, electrode material and their number... Therefore, spark plugs are selected according to special catalogs of manufacturers: Denso, NGK, Bosch. Or by the OEM number of the original spark plugs: to do this, you need to find the spark plug (spark plug) on the car component diagrams.
Whose recommendations should you follow: the car manufacturer or the spark plugs? Ideally, they should coincide, but sometimes there are discrepancies. Perhaps, priority should be given to candle brands - they know the features of their products better and regularly release new models that might not have yet existed when the production of your car began.
But the automaker's key requirements cannot be ignored. For example, if the instructions for the car indicate only iridium or platinum spark plugs, you cannot install ordinary nickel spark plugs, even if they are suitable in terms of geometric parameters. After all, the coils and the entire ignition system are not designed for the higher voltage required by spark plugs with a thick electrode, and such savings will sooner or later backfire. The same goes for the number of electrodes. If the engineers provided multi-electrode spark plugs, then there was a reason for this - these are the spark plugs that you need to buy. Choose your spark plugs wisely, and you won’t have to put a spark plug in for the health of your engine.
Spark plug markings
There is no single standard - the designation does not match between different manufacturers. In general, the number characterizes the time before glow (spontaneous) ignition occurs. The higher the value, the colder it is. The letter R (or Russian "Р") denotes built-in resistance to reduce radio interference.
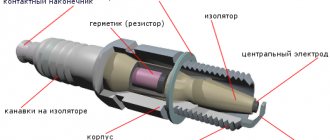
The inscription on the insulator or housing encrypts the following data:
- thread diameter and length, key size and seal type;
- heat rating and heat cone protrusion;
- material of the central electrode and the presence of a resistor;
- dimensions, scope and design features;
- interelectrode gap, type and number of electrodes.
Within the framework of this article, it is not possible to give an exhaustive description of the labeling of various manufacturing companies; for this, an entire book would have to be written. But Topdetal consultants have the necessary information and will help you choose spark plugs for your car, offering several brands to choose from in different price categories.
When to use
It must be borne in mind that the operating conditions of the car engine are different - they depend on traffic on the roads, average speed, increased load, and seasons.
If you often get stuck in traffic jams, then install hotter spark plugs, and if you drive at high speeds, install colder ones. For long distances and high speeds, “cold” spark plugs are suitable, and for short distances, at low average speeds, “hot” spark plugs are suitable. The choice is influenced by the size of the engine; the larger its volume, the “colder” the spark plug. The same spark plug can be “cold” for one engine and “hot” for another. How much it will heat up during operation, and how it will give off heat, depends on the insulator material and the length of the thermal cone.
Which candle manufacturer should I choose?
Preferences depend on budget, knowledge and requirements.
- If you don’t want to delve into the intricacies of design and applicability, take the “original”. It was made by one of the “grandees” of the industry, and will definitely fit your car. This is the simplest, but most expensive option.
- You trust only “top” manufacturers - Bosch, NGK, Champion, Denso are at your service. These companies supply original spare parts to the assembly lines of car factories.
- Want to save money? A properly adjusted “civilian” engine will work no worse with Brisk, domestic ZAZS, inexpensive Finwhale or Lecar.
Is it worth overpaying for iridium and platinum?
If a specific core material (platinum, iridium, copper) is recommended for your car, you will have to accept it (or shorten the replacement period). Whether it is necessary to engage in tuning, changing ordinary ones to “fashionable ones” - everyone decides for himself. A serviceable engine works great even on stock ones.
Trying to revive a problematic engine that is “eating” oil and overflowing fuel is applicable as a temporary measure. It is possible that one of the several side electrodes will have less deposits, but the thin central one will still produce a flash. And the faulty internal combustion engine will start.
Marking and service life
Each part is marked on the ceramic insulator, allowing you to determine whether it will fit a given motor or not.
Here is an example of one of the options: A – U 17 D B R M 10
| Labeling position | Symbol meaning | Description |
| 1 | Thread type | A – thread M14x1.25 M – thread M18x1.5 T – thread M10x1 |
| 2 | Support surface | K – conical washer – – flat washer with gasket |
| 3 | Design | M – small spark plug U – reduced hexagon |
| 4 | Heat number | 2 – the “hottest” 31 – the “coldest” |
| 5 | Length of threaded part (mm.) | N – 11 D – 19 – – 12 |
| 6 | Features of the heat cone | B – protrudes from the body – – recessed into the body |
| 7 | Availability of glass sealant | P – with resistor – – without resistor |
| 8 | Core material | M – copper – – steel |
| 9 | Serial number of modernization |
Each manufacturer sets its own timing for replacing spark plugs. For example, a standard single-electrode spark plug needs to be changed after a mileage of no more than 30,000 km. This factor also depends on the engine hours (how they are calculated is described using the example of changing car oil). More expensive ones (platinum and iridium) need to be changed at least every 90,000 km.
The service life of SZ depends on the characteristics of the material from which they are made, as well as on operating conditions. For example, carbon deposits on the electrodes may indicate a malfunction in the fuel system (supply of an overly rich mixture), and a white deposit indicates a mismatch in the glow rating of the spark plug or early ignition.
The need to check spark plugs may arise in the following cases:
- when you press the accelerator pedal sharply, the engine reacts with a noticeable delay;
- Difficulty starting the engine (for example, to do this you need to turn the starter for a long time);
- reduction in engine power;
- significant increase in fuel consumption;
- The check engine light comes on on the dashboard;
- complicated engine starting in cold weather;
- Unstable operation at idle (motor “troits”).
It is worth noting that these factors indicate not only faulty spark plugs. Before you start replacing them, you should look at their condition. The photo shows which component in the engine requires attention in each individual case.
How to change spark plugs and what to do when a spark plug thread is torn off
Maintenance comes down to a visual inspection (checking with a spark probe and gap with a feeler gauge) or preventive replacement according to the instructions for the car (in Soviet times there were also collapsible spark plugs) with a mileage of 20-60 thousand km.
Leaded gasoline, malfunctions of the cylinder-piston group and difficult conditions (congestion, increased loads) can reduce the life of the kit. At the same time, there are known cases of operation for more than 100,000 kilometers.
Some practical recommendations.
- Replace only on a cold engine - tightened ones “from the heart” on a warm one will subsequently be difficult to unscrew.
- You should not exceed the recommended tightening force - the threads are thin, and the block head is usually aluminum. For precise dosing of torque, a torque wrench is useful.
- To make it easier to change next time, run a pencil along the threaded part - the graphite will not allow it to “stick” during operation.
If you overdo it and damage the thread, use a thread restoration kit with a “spring” or a screwdriver. If you have experience, you can do without removing the cylinder head - the repair will take less than an hour.
Number of electrodes for a spark plug
Today you can find single- and multi-electrode hot and cold spark plugs on sale.
Each of these varieties has certain advantages. Today, single-electrode spark plugs are used mainly with older engines, due to their short service life and instability in operation. Modern powerful high-performance engines use multi-electrode spark plugs, which can have up to four side electrodes. They are characterized by durability and stability in operation. We note a significant reduction in exhaust toxicity and reduction in fuel consumption when using such multi-electron spark plugs. Their only drawback is their high price, which leads to a significant increase in the cost of car maintenance and repair, especially when it is necessary to replace them with a set on a six or eight-cylinder engine.
Engine diagnostics based on spark plug condition
In addition to its direct function (sparking), it is an accurate diagnostic tool. By the nature of the deposit one can judge the quality of the air-fuel mixture and the state of the CPG:
- sandy shade, uniform - normal appearance;
- soot velvety - a rich mixture. Absent (white color) - depleted;
- tracks on the cone - “breakdown”, indication for replacement;
- black oily flakes - oil entering the combustion chamber;
- erosion, melting, chipped ceramic parts are signs of detonation.
Timely monitoring of spark plugs will ensure reliable engine starting, stable power characteristics and fuel economy. Spend a few minutes on the ignition during maintenance - and the engine will delight you with trouble-free operation.
Ilya Ilmarin
Causes of glow ignition and detonation
Glow ignition occurs when the insulator and electrode overheat, as a result of which the electrodes melt. Most often, the cause of overheating is incorrectly selected spark plugs, or rather, selected “hotter” ones than required. If the “correct” spark plugs are selected, then the reason must be sought in the power system; perhaps the reason lies there. For example, the mixture may be too lean due to an incorrect carburetor setting or malfunction of one of the sensors (on an internal combustion engine with gasoline injection), most often the mass air flow sensor. It would be a good idea to make sure that no foreign air is sucked into the intake manifold, and also check the valves and, if necessary, make adjustments, since an incorrectly set ignition timing can cause constant overheating of the spark plugs.
Detonation occurs due to a violation of the gap between the electrodes, when using gasoline with a low octane number, as well as in the case of early ignition. All of this can lead to cracking and chipping of the heat cone. For a piston group, detonation is much more dangerous and often causes pistons to burn out. Detonation manifests itself in the form of strong engine vibration, as well as regular “shots” from the exhaust pipe.