Often, car owners may notice changes in the operation of the radiator and the car’s cooling system as a whole. What is this connected with? The first thing that comes to mind is to replace the antifreeze. At first glance, it will seem absolutely clean, and you will give up on this idea with a wave of your hand. But is this really so? Installing a filter will help you check this guess.
The method I want to offer you is quite simple and will really help clean the engine cooling system. The time and material costs for its implementation are minimal.
Coolant filter
Air dryers, coolant filters and hydraulic filters
Engines subject to extreme loads, such as trucks and heavy machinery, require efficient cooling, which is what effective coolant filters provide. Reliability and durability of hydraulic and pneumatic systems are ensured by air dryers and hydraulic filters.
Coolant filters
Coolant filters are used in cooling systems for large engines found in trucks and heavy equipment. These engines are subjected to extreme loads in harsh operating conditions, so a highly efficient engine cooling system is very important. Coolant filters function as bypass filters in the engine cooling system, allowing only a small portion of engine coolant to flow through.
This type of filter has a paper or non-woven filter membrane that serves to clean the mechanical coolant from solid contaminants coming from outside and from the internal engine cooling system. They also contain a combination of chemicals that protect the metal surfaces of the cooling system from corrosion and erosion caused by cavitation. These substances, slowly dissolving in the coolant flowing through the filter, stabilize its pH and hardness, thereby maintaining the high thermal conductivity of the cooling medium.
The inside of the filter housing is coated with a layer of epoxy resin that protects against corrosion caused by improper coolant chemicals or improper maintenance procedures. A special compression spring, adapted for Filtron liquid cooling filters, ensures a tight connection of all filter elements with the cover.
Filter cartridges are made from specially developed filter materials designed for currently used coolants. The purpose of these materials is to separate solid impurities from the coolant. A spring strut on the inside of the box protects against damage to the epoxy coating. The cube of the active ingredient inside the filter, releasing, prevents scale formation, corrosion and cavitation processes.
Hydraulic filters Hydraulic
Oil filters are found in many machines and devices that operate under extremely difficult conditions. The reliability of a hydraulic system largely depends on the properties of the oil and the durability of individual components (pumps, valves, seals, actuators, etc.), subject to high pressures, abrasion and erosion caused by the occurrence of cavitation phenomena. To ensure optimal operating conditions for the hydraulic system, filters are used to remove contaminants in the hydraulic oil.
In hydraulic systems, filters are most often used in dismountable housings with replaceable cartridges. Hydraulic systems that require thorough cleaning usually use filter cartridges with a baffle made of special paper or filter fleece, often pleated, together with fine-mesh steel mesh. These filters are characterized by very good filtration properties and high resistance to mechanical stress. Air dryers
Air dryers are filters whose job is to remove moisture from the air injected into pneumatic systems. They also remove particulate matter from the air. Filters made from this gypsum are used in pneumatic installations, both stationary and those mounted on trucks and heavy equipment. Since pneumatic systems use precision-manufactured components, they do not tolerate water, which increases the phenomenon of corrosion.
Filters of this type have a structure similar to spin-on oil filters; instead of a filter membrane, a special granulate with very hygroscopic properties is used. This granulate is primarily designed to capture and bind moisture particles contained in the air stream. Highly hygroscopic granules remove moisture from the air in the system with very high precision.
Regular replacement of dryers is recommended, especially before winter, as this prevents condensation from forming in the system. At low temperatures, freezing of water can cause failure or damage to the pneumatic system.
Cooling system filters
Everyone knows that problems with engines are often associated with overheating. When fuel burns in an engine, up to 10,000 fuel ignitions per minute occur; the temperature during fuel combustion exceeds 2200ºС. The cooling system must dissipate into the atmosphere through the radiator a third of all energy released during fuel combustion to maintain a safe operating temperature of the engine. Therefore, efficient cooling of diesel engines is very important. In heavy equipment cooling systems, the water pump must operate in a closed system at a flow rate of up to 600 l/min to ensure safe engine operating temperatures.
Ineffective operation of the cooling system is influenced by: stone overgrowing of the system, cavitation processes on the water pump impeller, linear pitting or cavitation corrosion on cylinder liners, poor thermostat operation, and the formation of a gel-like mass in the radiator. Heavy-duty diesel engines are typically designed with wet cylinder liners that provide better heat dissipation, but these liners are often subject to pitting corrosion due to cavitation.
We would like to remind you what cavitation leads to in diesel engines. When the engine is running, vibration of the cylinder liners occurs. Vacuum bubbles, under high pressure (15,000 - 20,000 bar), hit the walls of the cylinder liners, “drilling out” the smallest pieces of metal from there. This happens millions of times, as a result of which the walls of the sleeves are destroyed, “shells” are formed in them, which turn into through holes. The engine fails.
Stone and overgrowing of the cooling system leads to deterioration of heat removal from the engine. One way to avoid engine failure due to overheating and cavitation is to maintain the cooling system in good condition. Most modern engines use filters to protect the cooling system. They are called Water filters - water filters.
Compared to passenger car engines, heavy-duty cooling systems are exposed to environments that are five to ten times more severe in terms of cooling system dynamics such as heat dissipation, flow rate, flow rate, and engine load factor:
| Application | Heat removal through the cooling system (kcal/hour) | Engine load factor (%) | Consumption rate (km/year) | Engine life (km) |
| Cars | 35000 | 25 | 25000 | 300000 |
| Heavy equipment | 136000 | 70 | 25000 | 1500000 |
The table shows that coolant that is intended for use in passenger cars cannot be used for heavy-duty engines. This coolant complies with ASTM D3306 - Ethylene Glycol Coolant for Passenger Cars and Vans. For heavy-duty applications, a coolant that complies with ASTM D6210 is used - defines the characteristics for ready-to-use ethylene glycol-based coolant for heavy-duty diesel engines. Cummins Filtration offers ES Compleat, the ideal heavy-duty coolant because it contains the optimally balanced key ingredients of nitrite and molybdate to protect against liner pitting corrosion.
ES Compleat antifreeze is available as a concentrate and ready-to-use liquid. Available in containers of 20, 208 and 1000 liters. The freezing point of ready-to-use antifreeze corresponds to a minimum of -37ºС. When using ES Compleat, there is excellent protection of aluminum engine parts and radiator joints. ES Compleat has no problems when topping up or mixing with coolants from other manufacturers. ES Compleat complies with ASTM D 6210.
Many manufacturers produce antifreeze that meets ASTM D 4985: a low silicate ethylene glycol based coolant for heavy-duty diesel engines. This coolant is not fully formed and requires additional additives before use.
Coolant filtration is a proven means of reducing wear and preserving all cooling system components. Additionally, water filters can provide a convenient and reliable way to add additional coolant additives to the cooling system to improve system performance and extend the life of the coolant.
Cummins Filtration is a leader in cooling system protection. One in four cooling system filters used worldwide are manufactured in Cummins Filtration plants.
What function does this filter perform? It carries out mechanical and chemical filtration.
Mechanical filtration. Any cooling system contains a certain amount of substances that impair heat transfer. These are mineral stone, rust, particles of the cooling system sealant, residues of anti-corrosion oils, and molding sand. Capturing these contaminants in the filter will ensure long-term diesel operation.
Chemical filtration (protection). This is protection against the formation of corrosion, scale, and the effects of cavitation. The filter contains the chemical substance DCA-4 (Diesel Coolant Additiv) in the form of granules, which, when dissolved in the coolant, forms a film on the walls of the cooling jacket that protects against cavitation. Under the influence of cavitation, it is not the metal that is destroyed, but this chemical film, which is constantly restored due to the presence of DCA-4 in antifreeze. DCA-4 maintains system pH levels between 7.5 and 11, which prevents scaling, corrosion and electrocorrosion.
Cummins Filtration produces a variety of water filters with different service intervals:
Long life water filters:
- Easy maintenance every 12 months, 250,000 km or 4000 operating hours
- Patented slow release mechanism replenishes chemicals produced during use
- StrataPore™ multi-layer filter media offers exceptional service life, efficiency and performance
Standard Life Cooling Filters
- With a service life of up to 500 hours or 40,000 km
- Immediate release SCA additive for use with any coolant at standard service intervals
- High quality filtration to effectively remove harmful contaminants
Chemical-free filters
- With a service life of up to 500 hours or 25,000 miles (40,000 km)
- High quality filtration to effectively remove harmful contaminants
To check the freezing point and concentration level of DCA-4, Cummins Filtration produces monitoring indicators (test strips) for the condition of the coolant - COOLANT TEST KIT. After the test, it becomes clear what condition the cooling system is in: it is necessary to add DCA-4 in liquid form, or replace the cooling system filter. If the test shows normal DCA-4 concentration levels and normal freezing temperatures, the system will be serviced at the next service.
It is convenient to use a professional refractometer manufactured by Cummins Filtration at service stations. The refractometer is designed to determine the freezing point of coolants. This is a more accurate method than dipsticks or float hydrometers. Comes with a durable storage case.
If your cooling system does struggle, Cummins Filtration offers two types of cleaning products to keep your cooling system in top condition. Both Restore™ and Restore Plus™ remove contaminants without damaging metal surfaces, cuffs, hoses or plastic parts. They are also approved by Cummins as the preferred product for cleaning contaminated cooling systems during warranty service.
Customers are provided with the best possible warranty coverage - this is an ongoing commitment from Cummins Filtration as we strive to become our customers' go-to filtration supplier. Cummins Filtration is the only filtration system manufacturer that offers a warranty on its products, regardless of the age of the equipment.
DO YOU THINK ALL FILTERS ARE THE SAME?
BE REALISTIC.™
For over 50 years, Fleetguard filters have been recognized throughout the industry for helping engines run longer, stronger and cleaner. Fleetguard filters win where it matters most - in REAL life. Expert knowledge of engines and integrated systems provides real quality you can rely on.
So, be REALIST.
Take Fleetguard - a filter for REAL life.
Technical terms
Antifreeze: An ethylene glycol or propylene glycol based composition that contains supplemental coolant additives (SCAs) and/or organic acids to prevent corrosion, foaming and other damage to cooling system components. It must be mixed with water before use! The most typical mixture is 50% for each component.
ASTM: American Society for Testing of Materials = The American Society for Testing and Materials (www.astm.org), the world's most important standard-setting organization, publishes the most frequently cited specifications, ASTM D-3306 for Passenger Automotive and ASTM D -6210 (new) and ASTM D-4985 (old) for trucks.
Borate: A pH buffer solution used in some antifreezes and SCAs (supplemental coolant additives) to maintain the pH value of the coolant as it ages.
Hybrid Coolant: A coolant prepared using a chemical additive package that contains a combination of organic acids and traditional corrosion inhibitors.
Deionized (DI) water: Water that has been purified by removing ions. It is chemically pure and does not contain calcium, magnesium, chlorides or sulfates, as is the case with almost any tap water. It is recommended for coolant preparation, especially for long-life coolants.
Alkalinity Reserve: The ability of a coolant to resist aging, as expressed by the amount of hydrochloric acid required to lower the pH value to 5.5 in the ASTM test.
Carboxylates: Organic acids that have the chemical moiety COOH in the molecule. In orange-colored coolants such as GM DEXCOOLR, some of the anti-corrosion inhibitors come from this chemical group.
System Amount: To fill or prefill heavy-duty coolant, add 3% SCA to a 50% low-silicon (ASTM 4985 specification) antifreeze and 50% water solution. In water, 6% SCA is usually the pre-filled dose.
Molybdate: An ingredient in Fleetguard DCA-4, an SCA additive and coolant technology to prevent cylinder liner cavitation and protect hard and soft metals from corrosion.
Nitrate: A general anti-corrosion additive that is particularly effective in protecting aluminum and solder.
Nitrite: An additive found in all quality SCA additives and fully formulated antifreezes (ASTM Specification D-6210) that is the most important additive for preventing cylinder liner cavitation. Total hardness: Calculation of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate – indication of scale deposits. ASTM, TMC and OEM specifications are based on overall hardness.
Total Dissolved Solids: A measure of the total amount of additives, added water minerals, and contaminants in the coolant.
Organic Acid: A large group of chemicals commonly used in the antifreeze field for carboxylate inhibitors (see Carboxylates).
Coolant: A liquid chemical compound in the cooling system, usually half antifreeze and half water.
Fully Formulated: This term describes new heavy-duty coolants that contain all the chemicals needed to protect the diesel engine as well as automotive cooling systems. The ASTM specification for complete coolant, ASTM D-6210, requires simultaneous compatibility with all previous automotive and heavy-duty specifications. Therefore, it is a true universal specification for antifreeze and can be applied to any system.
Propylene Glycol: An alternative, slightly more expensive liquid antifreeze base that is more environmentally friendly than ethylene glycol due to its lower toxicity. Provides excellent corrosion protection.
pH: A scale that indicates the acidity or alkalinity of a liquid or solution. This scale extends from 0 to 14 units, with pH values below 7 being acidic and pH values above 7 being alkaline. Antifreeze, coolant and SCA solutions operate in the alkaline to slightly alkaline range with pH values from 7.5 to 11.0. The coolant or SCA solution becomes unstable if the pH value drops too much during operation. The minimum permissible pH value depends on the type of coolant. Rapid degradation/precipitation of the additive and corrosion is likely if the pH value of the coolant drops below the limit value. Pre-Added: A term to describe antifreeze that contains an SCA additive. This term is now obsolete and the preferred term is “completely ready”.
Silicate: The best protection against corrosion of aluminum. However, silicate has limited solubility in coolant and is often associated with radiator plugging with poorly formulated coolants or SCA additives. High-quality coolants contain silicate stabilizers.
Silicate Stabilizer: A chemical used in the best coolants and SCA additives to prevent silicate precipitation that can cause problems.
Esters: A chemical group found in some reused antifreezes. These chemicals quickly destroy the inhibitor package, oxidize the coolant, and cause catastrophic cooling system failure in astonishingly short periods of time.
Freezing Point: The temperature at which ice crystals begin to form in the coolant, as specified in ASTM Practice D 1177.
Electrical Conductivity: The ability of a coolant to resist the passage of electric current between dissimilar metals. Excess levels may result from improper source water, extensive metal corrosion, or overtreatment with SCA additives.
Coolant Filter: A filter through which coolant flows and which is widely used as a supply device for SCA chemicals. Care is required to ensure proper application using the proper chemical dosage. Nowadays, filters with long life and slow release of chemicals are used along with the use of coolants with long life.
Phosphate: A pH buffer solution used in many coolants. Detroit DieselR does not recommend phosphated coolants.
Ethylene glycol: The most well-known base for antifreeze. At 50% water content, ethylene glycol antifreeze provides freeze protection down to -34ºF. Ethylene glycol may be harmful if swallowed.
SCA: Abbreviation for supplemental coolant additive, which is a chemical compound added to a coolant either as a liquid or powder, or as a cartridge of granules inside a filter to enhance the anti-corrosion and other desirable properties of the coolant. SCA additives that meet the ASTM SCA specification are highly recommended for maximum protection.
Filters for trucks, refrigerators, road, construction, agricultural machinery, industrial equipment, hydraulics.
Contact our specialists!
How to properly dilute antifreeze concentrate?
To dilute antifreeze concentrate, use only distilled water. Typically, instructions for diluting antifreeze concentrate are on the back of the canister. The car owner should select the required temperature range in which the car will be used and mix the antifreeze concentrate with water in the required proportions. As a rule, the proportions for diluting antifreeze with distilled water are as follows:
1:2 - up to -17..-20 degrees; 1:1 - up to -36 degrees; 1.2:0.8 - up to -40 degrees; 2:1 - up to -65 degrees.
Yes. I confirm. Nylon stocking. I have been using this filter for about 15 years. At first, once a week I raked out a handful of dirt. Then, after about a month, this handful was collected over the course of a month. Then in six months. Now, during the period from change to coolant change (2 years and something like 25-30 thousand km), there is a pinch of dirt there.
By the way, in these 15 years I have never had to climb into the radiator with cleaning rods. But in fairness, I must note that about 3 years ago, I had to switch to a spare radiator, due to the complete failure of the original patched radiator (it worked on the car for at least 25 years, of which 15 on the water and was washed at least 5-6 times then) .
Almost. I do this. I cut a piece from a stocking that replicates a man's sock. As a last resort (if I have already cut off a sock from this stocking, I cut off a 15 cm pipe and tie one end with a knot). The open end fits onto the radiator hose. Moreover, it is very advisable to first wrap at least one layer of fabric tape around the pipe. It is clear that the stocking is larger in diameter and there is no talk of any tension. Therefore, boldly folding the edges, we cover the pipe with a stocking. We wrap cloth tape over it again. Add a little bit of LITOL on top of the electrical tape (so that the hose slides when pulling and removing). The stocking hanging out looks like a net. Using your finger, we tuck it inside the pipe and pull the hose onto the pipe and secure it with a clamp. If cleaning is necessary, drain the coolant from the system until the upper ends of the tubes are exposed. We pull off the hose. Usually, thanks to LITOL, the hose is removed, and the net with ribbons remains in place. To turn the stocking inside out, blow into the neck with your mouth - the stocking spits out and the dirt spills out. We assess his condition. If the stocking is damaged (rarely but happens after 3-4 years), we replace it.
How to choose antifreeze
Before replacing antifreeze, you must first buy it. Oddly enough, this can also cause problems. After all, it comes in different brands, as well as different characteristics, and not every car owner knows which ones are suitable.
Here are the important points to pay attention to when choosing a coolant:
- Marking. First, let's look at the conventions. Any antifreeze is marked with a letter and a number. There can be two letters: “A” - ready to be poured into the cooling system, “K” - means a concentrate that requires dilution before use. After the listed letters, the freezing temperature is placed on the Celsius scale - 40, 65 degrees, etc. After this, at the end, there may be the letter “M”, which indicates the presence of additional impurities and additives. Sometimes the label just shows a name and a number.
Antifreeze markings
There is also some “unofficial” but common marking introduced by Volkswagen. In accordance with it, antifreeze is divided into groups G11, G12 (G12+, G12++) and G13.
G11 - mainly green antifreezes, which contain organic and chemical additives;
Antifreeze G11
- G12, G12+, G12++ are red antifreezes of various shades, they are almost completely organic;
Antifreeze G12, G12+, G12++
- G13 - basically purple or yellow antifreeze, more modern and safer.
Antifreeze G13
Not all antifreezes of different markings can be mixed with each other. In any case, the seller will tell you about the product you are buying, so there will be no problems with this.
Mixing antifreeze of different markings
Manufacturer
You also need to pay attention to this, since you may get a defect that will ruin your engine. To prevent this from happening, you need to buy antifreeze from trusted or at least well-known companies
For example: Liqui Moly, Lukoil, Hepu, Motul, Mobil.
It is recommended to buy antifreeze only from proven brands
Detection of counterfeits. It often happens that recently purchased antifreeze very quickly became unusable or, more simply put, you came across a fake. But how to choose a good product? Easily! There are basic parameters that are common to all coolants. First of all, this is the color: it must match the markings (the standard color is blue) and be transparent, but only slightly. In addition, the consistency of the substance should be slippery and resemble vegetable oil. You also need to pay close attention to the label. At factories they glue it evenly and indicate GOST and markings on it. By the way, all domestic manufacturers comply with these requirements. The brand must be in line with GOST. In other cases, you will most likely buy a defect.
Original antifreeze (left) and fake (right)
Another important point worth mentioning is the name. The coolant container may be labeled “Tosol” or “Antifreeze”. What is the difference between them? Nothing! Simply, the word “antifreeze” can be used to describe any substance that is capable of removing heat, and antifreeze is produced exclusively for cars and, in particular, for internal combustion engines, since it has anti-corrosion properties, thanks to which the block and cooling system are not damaged.
Why the cooling system gets dirty: the main reasons
The main reason for rapid contamination of the cooling system is the use of ordinary running water, since water in the cooling system causes abundant formation of scale and rust. Also, plain water contains a large amount of salts, which, under high temperatures, settle on the internal surfaces of the cooling system. As for distilled water, there is less scale as a result of its use, but it is still not able to provide adequate protection against corrosion.
Article on the topic: Which car color is the most practical and safe?
Filling the cooling system with high-quality antifreeze or antifreeze does not lead to scale formation and slows down corrosion processes. At the same time, after a certain time, antifreeze loses its protective properties, and the additives in its composition stop working. As a result, sediment may form and decomposition products accumulate on the walls of the pipes and on the internal surfaces of the cooling system elements. The overall efficiency of the system is reduced, and in some cases blockage of the lines may occur.
Which antifreeze to choose?
As a result, the use of antifreeze as a coolant becomes more effective. However, antifreezes themselves differ in composition and characteristics. Therefore, with proper planning, the question is no less important: “Which antifreeze is best for the heating system?”
Today there are only two options for antifreeze: based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol.
Despite the similarity of names, the technical characteristics of the liquid vary greatly:
- Propylene glycol coolant has a wide range of positive qualities, including: environmental safety, thermal conductivity, protective properties, and greater resistance to low temperatures. Antifreeze based on propylene glycol delivers heat faster than other coolants even to the most remote areas of the heating system.
- Ethylene glycol coolant has good thermophysical properties and is in the average price range. But when working with it you need to be extremely careful, as this substance is more toxic. And it can only be used in well-insulated systems.
Modifications of FMO filters
Automatic filters FMO...ROT-A
The FMO...ROT-A filter is an automatic filter with a filter element regeneration system using a reverse flow of washing liquid and a built-in hydroacoustic emitter. The automatic regeneration system allows you to clean a clogged filter element without disassembling the filter housing. The use of a hydroacoustic emitter allows the use of corrugated filter elements rather than “smooth” ones (with the same filtration area, the volume of the filter housing is reduced several times), and also reduces the washing time. Thanks to this, the consumption of washing liquid, which determines operating costs, is reduced by 10 to 100 times compared to known regenerable filters.
How to replace antifreeze
The question of whether it is necessary to flush the cooling system when replacing antifreeze has been resolved. Now let's proceed to the actual procedure itself.
First, we drain the used composition. It is worth remembering that everything must be done on a cooled engine, because otherwise the temperature of the antifreeze can reach almost a hundred degrees Celsius. There is nothing complicated here, just remove the radiator cap and then unscrew the drain plug (don’t forget to place a large bucket underneath).
Next, it is important to check the cooling system hoses for damage. If cracks or other defects are found, the element should be replaced
As already mentioned, we flush the system to eliminate corrosion and various contaminants. If necessary, you should use special cleaning chemicals. Fill the system to the brim, then turn on the engine until it warms up to its normal operating temperature. Then turn off the engine. Again, we wait for the engine to cool down, and then drain the water.
Again, pour water into the system, close the lids, and turn on the engine for 15 minutes. When everything has cooled down, drain the liquid. Only when everything is completed do we begin pouring the new composition.
When the purchased antifreeze is in the system, turn on the engine and heater to the maximum level. This allows the coolant to be evenly distributed and also eliminates air bubbles from the system. But it doesn't end there either
After a couple of days, it is important to look at the antifreeze level. If necessary, it is worth adding the composition
Remember that before starting such procedures, it is advisable to read the recommendations of the manufacturer. Sometimes it happens that during use the composition changes its shade, and this is quite normal - everything depends on the characteristics of a particular brand.
Tuning the VAZ 2106 cooling system
Some VAZ 2106 owners are attempting to modify the cooling system by making changes to the standard design. So, if the car is equipped with a mechanical fan, during long periods of idle time in city traffic jams the coolant begins to boil. This problem is typical for cars equipped with a conventional mechanical fan. The problem can be solved by installing an impeller with a large number of blades or replacing the fan with an electric one.
To increase the efficiency of the cooling system on the VAZ 2106, an additional electric pump is installed
Another option for increasing the efficiency of the VAZ 2106 cooling system is to install a radiator from the VAZ 2121 with a larger heat exchange area. In addition, you can speed up the coolant circulation in the system by installing an additional electric pump. This will have a positive effect not only on heating the interior in winter, but also on cooling antifreeze on hot summer days.
Thus, the cooling system of the VAZ 2106 is quite simple. Any malfunctions can lead to sad consequences for the owner, including major engine repairs. However, even a novice car enthusiast can perform most of the work on diagnosing, repairing and servicing the cooling system.
Is it possible to add water to antifreeze?
There are many disputes and opinions regarding the possibility of adding water to antifreeze. Let us take the liberty of saying that it is possible to add water to the coolant, but there are a couple of important points.
Antifreeze crystallization temperature
Firstly, the water must be distilled or at least well purified using filters. This is necessary so that the elements present in the liquid do not clog the engine cooling system and do not enter into a chemical reaction with the additives and additives present in the antifreeze.
Secondly, you can add very little water - 100.200 ml. Otherwise, it will greatly dilute the coolant, and the latter will lose its performance properties (critical in winter). Therefore, you can use water as a top-up liquid only in extreme cases, when the level in the system has dropped to a critical level, and you do not have similar antifreeze on hand.
Now let's look in more detail at the arguments that suggest that water can still be mixed with antifreeze:
- Water added to antifreeze will not impair its performance. Unlike coolants belonging to other classes listed above. This statement can be made on the basis that the properties of antifreeze largely depend on the volumetric ratios of the additives included in its composition. If they are violated (which happens when mixing “coolants” of different types), then the mentioned properties are reduced to “no”. Water proportionally reduces their volumetric quantity, that is, their ratio remains the same.
- Contrary to popular belief, adding water to antifreeze will lower the freezing point of the coolant. This statement can be made on the basis that the reduction in the volume of coolant in the system occurs mainly due to the evaporation of water. This process occurs when the safety valve on the expansion tank opens. Water evaporates first, and only then ethylene glycol. Accordingly, if you add water, the freezing temperature will be restored.
The rationale for adding water also stems from the fact that most antifreezes themselves are about 70% water. This is largely responsible for the evaporation of liquid in the summer. But remember that in winter it is not recommended to dilute antifreeze too much.
When and why you need to change antifreeze
Let's start with the fact that water in the cooling system is practically not used today, giving way to antifreeze or antifreeze. One of the properties of such a working fluid in the system, regardless of the type (antifreeze or antifreeze), is its tendency to gradually boil away.
In other words, the level in the expansion tank gradually drops. In this case, most car enthusiasts add regular distilled water, since the coolant itself is a concentrate, which is diluted in a certain proportion with distilled water. Let us add that such a liquid (provided the concentrate itself and distilled water are of good quality) performs two functions at once:
- The main task is to remove heat from the engine and transfer the heat to the radiator, where subsequent cooling of the circulating coolant occurs;
- An additional function is to protect, clean and partially lubricate the internal surfaces and elements of the cooling system;
Due to significant heating and boiling of the coolant, which requires periodic dilution with water, as well as for a number of other reasons, a gradual loss of the properties of the coolant occurs. Consequently, the service life of such a working fluid is limited. The result is the need to replace it. There is also the fact of the formation of scale and dirt in the cooling system. For this reason, a noticeable change in the color (darkening) and odor of the antifreeze occurs, which indicates the end of the coolant life and/or contamination of the cooling system.
Taking into account the above, it is necessary not only to periodically change the fluid in the cooling system, but also to flush the engine cooling system before replacing the coolant. Ignoring this rule leads to the fact that fresh antifreeze or antifreeze darkens or even turns black after several tens of kilometers, as it is poured into a dirty cooling system. Let us add that a contaminated system cannot function normally even when taking into account the replacement of the coolant.
When to replace
First of all, it is important to understand when to perform such a procedure. Most auto mechanics advise replacing antifreeze at least every 24 months.
This especially applies to vehicles with a cylinder head and radiator made of aluminum. In addition, the technical documentation indicates the maximum period for the operation of the coolant.
For example, on Ford cars the manufacturer sets 240 thousand km. mileage, on Mercedes - five years, etc. In domestic models, this period is usually 2-3 times less. Long antifreeze service life is achieved through the use of innovative coolants with an improved formula.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out such a procedure if the liquid changes color, becomes cloudy, or a precipitate begins to form. You also need to change the antifreeze after repairing the power unit and adding fresh material there (this prevents its corrosion).
At the same time, it is advisable to use the original composition, so when choosing a product, follow the manufacturers’ instructions.
Topping up antifreeze
Before adding or replacing antifreeze, you need to carry out a little diagnostics. To do this, you can go to a service center or put your car on a dry horizontal surface and inspect it for leaks. If no problems are found in the system, but it is simply time to replace the fluid, then you need to proceed as follows.
Let's look at the process using the same Hyundai Solaris as an example. The procedure for cars of other brands is approximately the same. Differences may lie, for example, in the expansion tank itself. The first thing that car owners are usually interested in is when to pour antifreeze: on a cold or hot engine. There is only one answer: only when it’s cold. Even if something goes wrong on the road, you need to let the system cool completely. This is dictated by basic safety rules, because otherwise there is a high risk of getting burned.
In Hyundai Solaris cars, the expansion tank is located to the right of the engine. Let's look at how to fill in antifreeze using the algorithm:
- The car needs to be parked on a slight slope, so that the front is slightly higher than the rear. This way the air will come out better. If you need to add a small amount of antifreeze, the machine can be installed in any convenient position;
- Next you need to open the lid of the plastic tank. You need to be extremely careful during the process, as there may be slight pressure in the system. You can use a clean rag to protect your hands;
- Add antifreeze to the reservoir in a thin stream. This will gradually remove air from the system. As a result, there should be no air bubbles on the surface of the liquid. If you ignore this recommendation, you may subsequently encounter a number of problems due to the formation of an air lock;
- Coolant must be added to approximately 75% of the container volume. It is recommended to focus on the maximum mark on the tank;
- After all the manipulations, you need to start the engine and let it run for 5 minutes at idle. This way, the antifreeze will be distributed throughout the system, and you will notice that its level has decreased slightly;
- If the coolant level has dropped significantly, the procedure must be repeated. You need to add a small amount of antifreeze in a thin stream;
- After completing all actions, remove any remaining liquid from the surface of the tank with a cloth and close the cap.
Even if you have used all the liquid, do not rush to throw away the canister. It contains information about the brand of antifreeze and its features. When you need to buy new fluid, you can easily check the brand compliance.
What causes pollution?
Sediment appears as a result of contact of liquid with the surface of metal parts. It settles in the pipes and radiator, often in the form of fairly large “flakes”. Such particles can soon tightly clog the channels of the cooling system, seriously interfering with its normal operation. This can lead to serious problems with the functioning of the engine.
The filter catches sediment, preventing it from circulating freely throughout the system. This is especially true in cars that use inexpensive antifreeze for maintenance, as well as sealant to eliminate leaks. Important point: You cannot drive with the filter all the time, as it will interfere with the normal circulation of coolant. In addition, high levels of temperature and pressure will not allow it to function for long. To achieve an acceptable result, it is enough to drive a car with the filter installed for no more than 300 km.
How did antifreeze come about?
Initially, vehicle cooling systems were air-based. However, people quickly realized the unreliability and low effectiveness of this method. This is how liquid cooling systems appeared. For quite a long time, ordinary water was poured into it, but this also suited few people.
Therefore, scientists have developed antifreeze - a special coolant that has a much larger temperature range than water, does not expand when frozen, and has other useful functions. Anti-corrosion, anti-foam and other additives are added to modern coolants, which also protect the cooling system.
FILTRATION STATION
I. Silaev, Vladikavkaz
The cooling system contains wear and corrosion products, especially if the car is old. These particles clog the radiator tubes and lead to accelerated wear of the pump seal. Therefore, for many years now I have been using a cooling system filter: a fuel filter with a metal casing from Kalina was inserted into a cut in the steam exhaust hose of the expansion tank. With it, the antifreeze is always clean and transparent, and there are no deposits in the expansion tank. The first filter becomes clogged very quickly and may require replacement. The reason will be a significant weakening of the stream of liquid, which is visible through the transparent wall of the tank. The filter should be secured so that when rocking, the fitting does not break off from the radiator or expansion tank.
The prize for the author of the advice is a 5400 mAh AkkuEnergy PowerBank mobile charging station from Heyner
Which filter is suitable for installation on the cooling system?
The first and most suitable option is to install a thread-based fuel filter. It is equipped with a special settling tank for polluting particles. The second, less preferable option is to install a paper filter. It is used only in case of emergency, as it clogs very quickly. The paper will not last long, collapsing under the influence of hot antifreeze. Quite rarely, such a filter survives in good condition until the car has driven the required 300 km for inspection.
Choosing antifreeze to replace
Before adding antifreeze, you need to decide on its type. Remember that, ideally, you should always only use the coolant recommended by your vehicle's manufacturer. You will find detailed information in the manual or reference literature. In most cases, the use of coolants of different classes and brands is allowed. And when topping up, use only the one that was filled in earlier. Failure to comply with this rule may result in a malfunction of the cooling system.
As for the Hyundai Solaris car, the following types of antifreeze can be used for it:
- G-11. Such compositions belong to the hybrid group - hybrid, hybrid coolants, HOAT (Hybrid Organic Acid Technology);
- G-12 and G-12+. They belong to carboxylate compounds - Carboxylate coolants, OAT (Organic Acid Technology);
- G-12++ and G-13. These are the most modern and technologically advanced liquids that belong to the Lobrid type antifreezes.
Accordingly, only hybrids can be mixed with hybrids, carboxylates with carboxylates, and lobrides with lobrides. Mixing antifreeze of different classes is strictly prohibited. The only exception is G12+ class antifreezes, which can be added to G11 and G12 fluids. Also, you cannot add domestic “Antifreeze” to antifreeze, since their chemical compositions are very different.
Remember that antifreeze is sold in stores in two formulations - completely ready for pouring into the cooling system and as a concentrate
Pay attention to this, since pure concentrate cannot be added to the existing coolant in the car system. Even if they belong to the same class
Therefore, if you bought concentrated antifreeze, dilute it in accordance with the instructions on the package. The choice of solution composition is usually dictated by the freezing point.
Differences between antifreeze and antifreeze in terms of performance
Antifreeze differs in its performance characteristics from antifreeze: it is worth remembering that the old Soviet refrigerant was made according to an outdated recipe and quickly loses its characteristics when the engine reaches high temperatures. Also, the Soviet refrigerant is not able to serve as a full replacement for antifreeze and is not able to protect the car engine when it reaches a temperature of 100 degrees.
Antifreeze in its general consistency is slightly runny in comparison with the same antifreeze and therefore resembles water. How to distinguish one refrigerant from the other? To be able to more accurately find out what you purchased for the car and protect your engine from counterfeiting and possible breakdowns during the operation of the car, try to pay attention to the size of the container in which the mixture in the form of refrigerant is actually stored. For example, many companies with a certain reputation try to value it and put a certain type of designation on the canisters with pressed letters and a multi-stage label.
To preserve the cooling system mechanism longer, do not mix antifreezes with each other. Even if they are the same color (colors were discussed above in the article). However, if you really want to, you can check the refrigerants yourself. In a separate basin or bucket, mix refrigerants of different series and look at the result
If a certain flocculent sediment appears, then the compositions should definitely not be used. Additives in antifreeze can protect the engine from damage and save it from freezing, in addition, multiple tests have proven all this in practice. Working over a huge temperature range, cooling antifreezes are perfect for a wide range of car brands, which makes them more versatile. Before replacing, it is important to consider that antifreeze has a weak freezing threshold and a sufficient boiling threshold, in comparison with the same Soviet refrigerant. From this we can draw a logical conclusion that antifreeze can reliably maintain its characteristics within the limits of up to +50. Other advantages of antifreeze include its anti-corrosion qualities. This makes it possible to maintain a suitable temperature range for motor operation.
All the main nuances have been discussed. Next, we’ll try to figure out how to change antifreeze on our own.
To replace the refrigerant, you should find the cap in the radiator and remove it, then find the drain plug for the radiator and open it, insert a basin or small bucket under it in advance. This is where you should pour out all the old coolant mixture from the radiator compartment. Next, we remove the refrigerant and check the internal system for any damage or failure. If there are faults in the cooling system, it is worth repairing it if necessary.
- Before you can add antifreeze to the car, the entire system should be cleaned and washed with a rag. This is done in order to remove rust and dirt residues that ordinary water cannot cope with.
- To flush the inside of the cooling system, special products from a car store are usually used. It is necessary to add these products (although much depends on the type of product) to distilled or filtered water and pour into the tank. In this case, you close all open necks.
- What do we do next? The next step is to turn on the engine and wait a certain time while it is idling. We are waiting for the engine to heat up to a certain value.
- After all the above steps, you should “turn off” the engine and wait until it cools down, and finally pour out the dirty liquid.
- Let your engine cool down and drain all the water before adding new coolant. After all the steps mentioned above, you should calmly fill in new antifreeze. Then you should “turn on” the engine and turn on the internal heating inside the car to the highest setting.
- After a week of driving, look under the hood and see what level the antifreeze is and, if necessary, you can add the required amount there to the designation.
- To carry out a planned replacement of the working refrigerant in your car, it is ideal to replace the old refrigerant with the highest quality and most expensive one - it is better to replace the antifreeze with the original one that was used at the factory.
But a reasonable question arises - how can you understand this for sure and where can you find such antifreeze in the store?
Follow the tips and tricks of the manufacturer, which was indicated in the instructions for the car.
How to flush and clean the engine cooling system yourself
Let's start with the fact that cleaning the cooling system involves dividing it into two stages. The first includes external cleaning of the radiator honeycombs and the cooling system fan itself from dust, lint, dirt and other debris. To clean it, it will be enough to use any damp cloth that can be used to wipe the fan blades. As for the radiator, its cells are washed with a directed stream of water under low pressure. Please note that washing with Karcher-type high-pressure washers can damage the soft honeycombs of a car radiator.
Article on the topic: Engine tuning: fuel and air system
We also recommend reading the article about how to properly wash the engine and whether it is worth doing it with Karcher. From this article you will learn about the features of self-washing the engine compartment and power unit using high-pressure washers, as well as other available methods.
Now let's move on to the so-called internal cleaning, that is, directly to flushing the cooling system. It is necessary to flush this system to remove scale and rust, as well as deposits that inevitably arise after the decomposition of additives in the antifreeze/antifreeze composition. In engines that have certain malfunctions, engine oil or gases from the combustion chamber may additionally enter the cooling system, which also negatively affects the overall condition of the system.
This washing is carried out using various special means, solutions or water (both ordinary and distilled). Each of the cleaners used has certain advantages and disadvantages, which we will talk about a little later.
It is necessary to begin flushing by draining the old antifreeze from the system by unscrewing the drain plug on the radiator, which is structurally located at the lowest point. You will also need to unscrew the drain plug on the cylinder block (if equipped) to remove residual coolant from the engine cooling jacket. To drain, unscrew the cap of the expansion tank, place containers under the radiator and BC, and unscrew the drain plugs.
It should be remembered that unscrewing the upper or lower radiator cap, the plug on the BC, as well as the expansion tank cap on a hot engine is prohibited! Increased pressure builds up in the system, causing fluid to splash out and cause serious burns and other injuries!
The further washing process itself is extremely simple:
- After draining, all plugs are screwed in. Then water or a special flushing liquid is poured into the system through the expansion tank.
- then the engine idles for about 10-15 minutes (until the engine reaches full operating temperature and the cooling fan turns on).
Deviations in the process of heating the engine to operating temperature may indicate the presence of an air lock. Such a plug must be eliminated by bleeding the gas at idle or disconnecting the pipes for subsequent bleeding of the system with the engine running.
Please note that the fan may turn on unexpectedly. Do not allow any foreign objects in the engine compartment that could get into the fan. This will cause it to break. Also, protect your limbs from being hit by the cooling fan blades!
After reaching operating temperature, the engine is allowed to cool, then the liquid is drained again in the manner described above. Do not forget that during washing the stove in the cabin should be turned on to maximum heating. This allows you to flush the heater core, through which coolant also circulates. The end of flushing can be considered the moment when, after the next drain, clean flushing liquid or water flows out of the cooling system.
When to add antifreeze
Checking the coolant level
The next interesting question is how often to add antifreeze, and in what cases this procedure should be performed. Let's look at this information in more detail. There are several reasons why topping up is necessary. In particular:
- Visible decrease in the level of antifreeze in the system. This phenomenon can occur at any time due to a leak in the body of the expansion tank, radiator, pipes, connections, and so on. There are two marks on the expansion tank of the Hyundai Solaris car - L and F (LOW and FULL, respectively, low and high level). If the level drops below the L mark, then it is necessary to add antifreeze. On other machines, instead of the mentioned marks, there may be other marks, but their essence will be similar.
Low coolant level indicator
Remember that if there is insufficient amount of coolant, an additional load is placed on it, which, firstly, it is not always able to cope with, and secondly, the properties of antifreeze in this case are lost much faster. In addition, in such a situation, the coolant may not fully cope with the tasks assigned to it, and accordingly, the engine will overheat (this may increase oil consumption and other unpleasant consequences). This concludes the theoretical part of the material, and we move on to practice, that is, directly to topping up.
WASHING THE SYSTEM WHEN REPLACING THE COOLANT: HOW TO DO THIS AND WHAT TO USE?
Flushing the cooling system is a necessary step when replacing antifreeze. It is especially relevant when the drained liquid is contaminated with slag, oils, rust, silicate gel and other compounds. This operation can be omitted only if the drained antifreeze is clean and the replacement poured in is of exactly the same type and brand.
Why is flushing necessary? It solves two problems at once. The first is cleaning the system from contaminants that have arisen during operation and interfere with heat removal and fluid circulation. The second task appears when you decide to change the brand or type of antifreeze, and is to remove the remnants of the previous composition. This is necessary so that the two liquids (“old” and “new”) do not enter into a chemical reaction, which can significantly reduce the anti-corrosion properties of the filled antifreeze.
If you neglect flushing, rust and other contaminants will be washed away by the new coolant - and all these sediments will remain in it, further creating the threat of clogging of the radiator channels and pipes.
In the photo below you can see the “damaged” pipe located in the bus cooling system. The system was not washed, but antifreeze was immediately poured into it, as a result of which the silicate components included in the previous fluid, coupled with rust, accumulated in the pipe and blocked it. The result was that the heating system was not working (and this was at the beginning of winter), as a result of which the antifreeze had to be replaced again, this time with flushing.
Washing methods
Soft rinsing. This method is the simplest and does not require any tricks. You simply fill the cooling system with water (necessarily clean!) and start the engine at 10-15 to idle. If you add about 10% concentrate or 20% new coolant to this water, the flushing efficiency will increase significantly. This technique allows you to remove the remnants of the previous antifreeze (silicates in particular), as well as partially coat the metal with new antifreeze.
The argument in favor of this method is that it poses a much lower risk of leaks, while strong agents can cause holes to form in places where the metal is already corroded.
20% of new antifreeze added to the flushing water also increases the service life of the new fluid. As is known, in the first minutes of operation, a significant amount of additives leaves the solution, settling in the foci of metal corrosion, as a result of which the pH of the antifreeze decreases by 1-1.5 units. Thanks to gentle washing, a kind of “primer” appears on the walls, which helps to retain more additives in the antifreeze and keep its pH at the same level.
If the contamination of the system is quite severe (this is indicated by the state of the drained liquid), it is worth re-flushing. Attention: do not pour cold water into a hot motor, let it cool down - otherwise the engine may simply crack.
In addition, different automakers have their own methods for flushing the cooling system. Companies that produce trucks approach this issue especially scrupulously. Let's give a few examples from practice.
Thus, Caterpillar insists on flushing before replacing coolant, especially if we are talking about replacing the conventional composition with the company’s proprietary antifreeze - Cat ELC. The washing itself occurs as follows. The first stage is rinsing with water, the second is with a specialized cleaning composition Caterpillar Standard Cooling System Cleaner, the third is water again. If severe contamination occurs, the pipes are removed and cleaned separately. Next, you need to continue washing with water while simultaneously starting the engine and warming it up to 50-60°C. Flushing can only be stopped when the water flowing out of the system is spotlessly clean.
A slightly different approach is practiced by specialists at MAN service centers. The first flushing is carried out using a 60% solution of new coolant concentrate and the engine is started for about 20 minutes (no more). After this, the antifreeze is drained again, carrying out a similar flushing, but now the concentrate content is only 10%. The third stage is pouring new antifreeze diluted with water in a ratio of 50:50.
And finally, the last example is Cummins. According to the requirements of its specialists, washing is carried out in this way. First, even before draining the old antifreeze, start the engine for half an hour. This is necessary to open the thermostat and freely circulate fluid through the radiator, cabin heater and additional heat exchangers. After this, you should drain the old antifreeze as soon as possible, before all the contaminants contained in it have time to settle on the walls again.
Next, the system should be washed with a specialized cleaning agent. The engine runs at idle, again for half an hour, and the fluid temperature is at least 85°C. The next step is to fill the system with water and flush for 15 minutes, still at idle. If oil residues are found in the drained liquid, the flushing must be repeated - with a cleaning agent, then again with water. The pipes are removed and cleaned separately.
The cleaning agent should be selected according to the table, focusing on the content of acids or alkalis in it, as well as on the effectiveness of use for certain types of contaminants.
| Type of pollution | Alkaline cleaner (such as Fleetguard Restore) | Acidic cleaner (such as Fleetguard Restore Plus) |
| Silicate gel | Excellent | Bad |
| Oil, grease or fuel | Excellent | good |
| Scale | Bad | Excellent |
| Rust | Bad | good |
| Solder slag | Bad | good |
Functions performed by coolant
Many people know that antifreeze plays an important role for engine operation, that you need to check its level and, if necessary, add it to the expansion tank. But not everyone can immediately answer what functions this liquid performs. Let's look at this issue first. The term “antifreeze” refers to several types of liquid. All of them are needed to cool the internal combustion engine. Without it, overheating will occur, which can lead to serious consequences, including major repairs.
In addition, antifreeze protects not only from overheating, but also from freezing. Unlike water, it is very resistant to low temperatures. Also, the coolant is characterized by a minimum coefficient of expansion. Thus, during the freezing process, water can increase its volume by up to 9%, and antifreeze - only up to 1.5%.
Thanks to the additives included in the composition, protection is provided not only from overheating, freezing, damage to parts, but also from corrosion processes. It is quite easy to check the presence of additives in a liquid. Just watch the antifreeze. It constantly circulates in the system and gradually loses its performance properties. Water evaporates from it. The liquid itself takes on a dark tint.
Cooling system VAZ 2106
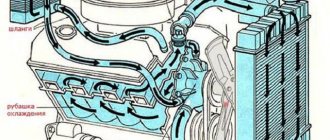
When driving any car, including the VAZ 2106, in operating mode the engine heats up to 85–90˚С. The temperature is recorded by a sensor that transmits signals to the instrument panel. To prevent possible overheating of the power unit, a cooling system filled with coolant (coolant) is designed. Antifreeze (antifreeze) is used as coolant, which circulates through the internal channels of the cylinder block and cools it.
Purpose of the cooling system
Individual engine elements become quite hot during operation, and it becomes necessary to remove excess heat from them. In operating mode, a temperature of about 700–800 ˚C is created in the cylinder. If the heat is not forcibly removed, jamming of the rubbing elements, in particular the crankshaft, may occur. To do this, antifreeze circulates through the engine cooling jacket, the temperature of which decreases in the main radiator. This allows you to operate the engine almost continuously.
The cooling system is designed to remove excess heat from the engine and maintain operating temperature
Cooling system parameters
The main characteristics of the cooling system are the type and amount of coolant required for smooth engine operation, as well as the operating fluid pressure. According to the operating instructions, the cooling system of the VAZ 2106 is designed for 9.85 liters of antifreeze. Therefore, when replacing, you should purchase at least 10 liters of coolant.
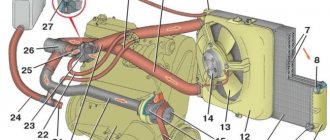
Engine operation requires expansion of antifreeze in the cooling system. To normalize the pressure in the radiator cap, there are two valves operating for inlet and outlet. As the pressure increases, the exhaust valve opens and excess coolant enters the expansion tank. As the engine temperature decreases, the volume of antifreeze decreases, a vacuum is created, the intake valve opens and the coolant flows back into the radiator.
The radiator cap contains inlet and outlet valves that ensure normal operation of the cooling system.
This allows you to maintain normal coolant pressure in the system under any engine operating conditions.
Video: pressure in the cooling system
conclusions
- If you are planning to replace the antifreeze in your foreign car, then remember that the color will help in choosing the right mixture for the engine and, in general, can be the best distinguishing feature of a company that develops and manufactures engine coolants.
- You can replace our classic antifreeze for the cooling system after a certain period of time; it is worth remembering that this time averages about six months (antifreeze is changed after 30 thousand kilometers).
- To flush the inside of the cooling system, special products from a car store are usually used. It is necessary to add these products (although much depends on the type of product) to distilled or filtered water and pour into the tank.
- After a week of driving, look under the hood and see what level the antifreeze is and, if necessary, you can add the required amount there to the designation.
- To carry out a planned replacement of the working refrigerant in your car, it is ideal to replace the old refrigerant with the highest quality and most expensive one.
Sources
- https://autozhidkosti.ru/antifreeze/kak-chasto-menyat.html
- https://AutoVogdenie.ru/kak-pravilno-menyat-antifriz-v-mashine.html
- https://fix-my-car.ru/texnicheskoe-obsluzhivanie/zamena-antifreeza
- https://AvtoTachki.com/zamena-ohlazhdayushhej-zhidkosti-kogda-nuzhno-menyat/
- https://FB.ru/article/274040/kak-pomenyat-ohlajdayuschuyu-jidkost-poshagovaya-instruktsiya-osobennosti-i-rekomendatsii
- https://avtopravo.guru/ekspluataciya-avto/kak-pomenyat-antifriz.html
- https://rad-star.ru/pressroom/articles/kak-slit-antifriz/
- https://tolkavto.ru/remont-i-obsluzhivanie/sistema-ohlazhdeniya/zamena-ohlazhdayushhej-zhidkosti-kak-pravilno-pomenyat-antifriz.html
- https://maslo.biz/antifreeze/zamena.html