Lubrication and cooling systems are critical components that directly affect engine performance. In a working car, the circuits through which oil and antifreeze circulate are sealed against each other and the liquids should not interact in any way, much less mix.
If suddenly the presence of oil is detected in the expansion tank, then it is necessary to urgently carry out diagnostics and identify the cause of the incident. As a rule, lubricant can enter the cooling system circuit due to two malfunctions:
- Violation of the tightness between the head and the cylinder block due to loosening of the fastening bolts, violation of the integrity of the gasket between them, changes in the plane of the head or microcracks in the cylinder block. As a rule, these malfunctions occur due to engine overheating.
- On diesel engines - due to a leak in the oil cooler.
In any case, if signs of the presence of oil in the coolant are detected, competent vehicle diagnostics and repairs are necessary. After the cause of mixing fluids has been found and eliminated, the remaining oil must be removed from the cooling system.
The fact is that an aggressive environment with high acidity, which occurs when mixing antifreeze and oil, will quickly corrode plastic and rubber parts (pipes, gaskets, seals), as well as contribute to the formation of pockets of corrosion and its development on metal parts. Oil can also form into clumps and clog the channels in the cooling jacket of the cylinder block.
Simply draining the contaminated coolant and adding new one will be ineffective; oil residues may remain on the internal surfaces and mix with the antifreeze again. To avoid such problems, the engine cooling system must be flushed. This can be done with special chemicals in a car service, or independently, or by resorting to traditional methods.
About the causes and consequences of pollution
The engine and cooling system elements of a new car are absolutely clean. Heat exchange in radiators and the engine water jacket is as efficient as possible. Over time, deposits form on the internal surfaces of the channels, impairing the transfer of heat from the coolant. The reasons for the phenomenon are as follows:
- natural oxidation and decomposition of antifreeze;
- pouring untreated water rich in metal oxides (salts) into the system;
- use of low quality antifreeze;
- a crack in the gasket between the main engine block and the cylinder head (cylinder head), through which engine oil penetrates into the cooling channels.
Note. The circulating hot liquid also interacts with gaskets and various sealants, gradually washing away particles of materials. The latter travel through the system and clog the bottlenecks - the radiator honeycombs.
The decomposition process of antifreeze is considered natural and is observed on all cars. The result is sediment in the form of a slippery coating on the inner walls of the pipes and ducts. The phenomenon has virtually no effect on heat transfer until the insulating layer becomes too thick (10–15 years of car operation).
Other reasons arise from improper vehicle maintenance or engine breakdowns. Separately, it is worth mentioning about pouring ordinary water - scale forms when it comes into contact with the cold surface of the heat exchanger tubes. This is a durable heat-insulating coating that often blocks the flow of fluid through the engine cooling radiator.
Clogged cooling system pipes cause the power unit to overheat. Then it’s clear - the wear of the cylinder-piston group accelerates sharply, and the car owner has to repair the engine ahead of schedule.
What do you need to know before the procedure?
Flushing the cooling system is a serious procedure that requires car maintenance skills. Improper cleaning can lead to problems, so before starting the procedure you need to familiarize yourself not only with the structure of the mechanism, but also with the cleaning rules.
For example, if the air conditioner condenser is made of aluminum, then the use of citric acid may cause thinning of its walls . At the same time, cast iron and steel parts completely retain their integrity.
To avoid problems that arise during radical cleaning, it is recommended to carry out prevention, use the original antifreeze composition and change it on time.
Why do you need to flush the cooling system?
Oil getting into the cooling system can cause a number of problems. Firstly, oil clots can clog the holes in the pipelines and interfere with the normal circulation of the coolant, secondly, the oil film on the cooling surfaces disrupts the established heat exchange, thirdly, the oil has increased adhesion and suspended particles, always present in the liquid, will stick to the oil layer, reducing the clearance in the pipeline and reducing heat transfer.
Why flush the engine?
What should I do, you ask?! You don’t have to do anything, you just have to wash it, that’s all. Many people are skeptical about engine flushing, for good reason. A lot of junk has appeared on the market, supposedly washing products that contain an ultra-high solvent and are in no way suitable for the engine. Don't pay attention to cheap washes.
DO NOT grab the first one you see off the store shelf. A good flush is a product that will restore compression in the engine cylinders, effectively remove sludge and dirt, and not only allow it to fall off, but also dissolve it, so that it does not clog the channels and is easily removed from the mixture system. Also, a good flush should cover all microscopic defects in the engine, and restore both the oil seals and all rubber seals.
Pros and cons of engine flushes.
Poor flushing: – Corroded seal due to engine leakage – Loss of compression – Increased oil consumption – loss of power – clogged passages in the engine
Pros of a good flush: – Engine compression is restored (You can do a test before and after use) – Reduced fuel and oil consumption – Sludge removal – The car becomes more efficient and lighter – Engine noise is reduced – There is TUV RUF ROHS approval
Flushes that do not work or are very dangerous for engine parts
If the substance used for cleaning is simply useless, then nothing bad will happen, even the deposits suspended in the liquid will be washed away. But the unpredictability of some foreign substances in the system can cause harm, often irreparable.
Plain water
Water is used for primary and final rinsing due to its cheapness and availability. It is advisable to use water with a minimum of mineral salts that form scale, as well as without acidic properties. Ideally, distilled, but it is not free. The replacement will be thawed or boiled.
Although many water supply systems have water of quite sufficient quality. It is not suitable for batteries, but will not harm the cooling system.
Signs that it's time to clean your cooling system.
If one of the following signs is detected, then it is imperative to clean the engine cooling system:
- The engine temperature rises sharply, and this happens often.
- When the engine is at operating temperature, cold air blows from the heater.
- The pump is not working well.
- The fan turns on early and runs at high speeds.
If such signs and causes appear, you need to study the flushing scheme, how to flush, what to flush with, and how to correctly fill in new coolant.
Danger to vehicle condition
A small volume of emulsion resulting from natural processes of moisture condensation does not cause harm to the engine. After a run of 30-40 km, foreign impurities evaporate, the vapors are pumped out through the crankcase ventilation hose into the cavity of the intake manifold. When the gaskets break, an increased volume of antifreeze enters the oil, worsening the lubricating characteristics of the substance. Scores form on the surface of the cylinders, the replacement crankshaft liners are damaged, and parts of the gas distribution mechanism suffer because of this.
Supplying a large volume of antifreeze into the cylinder of a running engine leads to water hammer. As a result, the connecting rod is deformed, piston fragments damage the cylinder bore and the upper part of the combustion chamber.
Piston fragments that have fallen into the crankcase can damage the crankshaft or break off the connecting rod, which pierces the side wall of the crankcase. The damaged power unit requires major repairs with replacement of the main components.
How to clean a radiator from oil and dirt
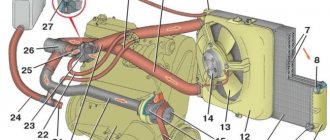
Those car owners who are not particularly interested in the structure and insides of their iron friend will also not be very interested in knowing that the number of heat exchangers in a car can reach seven units. The most important ones are radiators in the cooling system, the intercooler of the turbocharger compressor, and the air conditioner condenser. It is obvious that the above components will work normally only if the surface is clean, ensuring optimal heat dissipation.
How to properly flush the cooling system
Any car engine cooling system (ECS) consists of water pipes (hoses), radiators (main and heating), a thermostat, and a water pump, which ensures forced circulation of coolant. As a result of constant interaction with heated metal, as well as from aging, various deposits accumulate in the liquid (antifreeze or antifreeze), and it begins to become cloudy. Oil from the engine can also get into the antifreeze; it penetrates into the ODS due to a leak in the cylinder head gasket.
There are different methods for flushing cooling channels and radiators, in general they are not fundamentally different from each other, the difference lies only in the use of compositions and the sequence of actions. You can flush the engine cooling system with water without resorting to any chemicals, but this is the case when it is not too dirty and there are no traces of oil in it. Properly flushing the SOD means completely getting rid of dirt or oil (emulsion), while the antifreeze must be transparent and the engine must be at operating temperature (not overheat). And it is very important to choose a composition suitable for washing that will not harm the car, but will only benefit it!
What is the best way to flush the cooling system?
For flushing, industrial and folk remedies are used, the effectiveness of which is determined based on experience. The most popular “folk” compositions for effectively cleaning cooling channels are:
- lemon acid;
- Fairy dishwashing composition;
- milk serum;
- bleach "Whiteness";
- vinegar solution;
- anti-scale agent “Cinderella”;
- diesel fuel;
- caustic soda;
- Cillit Bang detergent.
Some people even wash out SOD with Coca-Cola, but not all formulations are safe, and you need to know the exact dosage and procedure for cleaning. Among industrial products, car owners most often advise using special brand chemicals:
- Prestone;
- Abro;
- LAVR;
- Hi Gear;
- Liqui Moly;
- Fenom;
- WYNNS.
In some situations, flushing the SOD is required after the sealant (more precisely, after its use to eliminate an antifreeze leak); this situation arises if the dosage is not followed, and as a result the stove radiator is clogged. Here both folk and special industrial preparations (a whole complex) are used, and if they do not help, then there is only one way out - remove the heater radiator and clean it.
How often should you wash?
Flushing the engine cooling system can be internal or external. External treatment consists of flushing the outside of the radiator to remove dirt, dust, and insects. Internal treatment allows you to flush the system from the inside.
Recommendations for the frequency of internal flushing of the cooling system:
- The cooling system should be thoroughly flushed when changing antifreeze or antifreeze. In this case, flushing helps remove the remaining old technical fluid, since it is better not to mix different antifreezes.
- Also, flushing should be carried out for preventive purposes. Carry out washing once a year, it is better to do this in the spring season. Such manipulation will help solve many problems caused by clogged pipes, deterioration of their throughput and heat transfer.
- If symptoms appear that indicate the need for flushing, it should be carried out immediately before more significant damage occurs.
Non-working cleaning methods
When faced with the problem of oil getting into the car’s cooling system, drivers at home resort to different cleaning methods. But not all options are effective.
For example, they clean with “Whiteness”. But few people know that the product contains chlorine, which causes corrosion of aluminum components (and the radiator of most cars is made of this metal). In addition, “Whiteness” is not capable of properly cleaning the system, but will only cause damage.
Another option is baking soda. It effectively removes rust and scale deposits, but cannot fight oily deposits.
Can flushing products damage the system?
Improper use of cooling system cleaning products can cause great harm to your vehicle. To avoid this, you cannot use two or more specialized tools at once. You only need to flush the system with one product. Most solutions are sold in the form of concentrates; they must be diluted, since highly concentrated solutions can destroy rubber and plastic parts, especially acidic preparations.
ICE cleaning options
Today, car power units are cleaned of old grease in various ways.
Five minute rinse
This product is poured into the engine immediately before changing the engine oil, mixed with the “working off”. After this, the internal combustion engine is started, idling for 5-10 minutes. This is followed by the traditional draining of the used composition, changing the filter and injecting new lubricant.
Flushing oil
Here, a specialized motor lubricant is used, which is poured in after removing the used composition. The engine runs for some time with this oil at idle speed, after which the substance is changed to fresh motor oil and the filter is cleaned.
Flushings with which they travel
This option allows you to travel a certain distance with the cleaning agent. A special substance is added to the old lubricant about a hundred kilometers before the next oil change, and until that moment I operate the car correctly and carefully. When it comes time for maintenance, the engine oil is changed according to the standard procedure.
Extra grease
This option is recommended for use when changing the lubricant to a composition with a different base, or for flushing very dirty engines. First, you should drain the used lubricant and pour in the composition that will be used in the subsequent operation of the car.
The amount of fresh oil can reach only a couple of liters. The engine idles for a short time. After this, all the lubricant is changed back to fresh, and a new filter is installed.
How to clean the tank?
How to clean the inside of the expansion tank from rust? Maybe someone has experience, tell me what kind of remedy.
PS: The tank was removed from the car.
Comments 30
WARNING: CAUSTIC SODA REACTS WITH ALUMINUM. If the radiators and other parts are aluminum, then they will be damaged.
rust in the expansion tank... tin...
It’s a shame only for those who haven’t gotten into their cooling system yet.
yes, I climbed somehow. tore off the pipe from the heater radiator, changed the expansion pipe with a cap, changed the antifreeze, clean and red and no rye
So you got the car from a good owner, unlike me, I got it from a collective farmer.
I got it from a very shitty owner, it’s just that his crooked hands didn’t reach the cooling system)
It’s a shame only for those who haven’t gotten into their cooling system yet.
In general, antifreezes have lubricating and anti-corrosion properties. Apparently you once had water in the cooling system, I would advise flushing it completely, because... excess deposits can clog it, and this already threatens with much more serious consequences than cleaning the expansion valve
try ADRILAN, there is such a household chemical product that contains caustic soda. work in rubber gloves, otherwise the skin will peel off. Sold in a pink plastic bottle.
I removed it and cleaned it with white spirit from oil and rust... you can also use Sanox