It's no secret that the suspension is one of the most important parts of any car. This design involves performing a wide range of tasks related to traffic control, as well as ensuring comfortable movement of both the vehicle and the driver. There are a large number of different types of automobile suspensions, among which there are mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, etc. designs. At the moment, the so-called electromagnetic suspension is becoming increasingly widespread. This modern device, created using the latest technologies, is increasingly found in automotive use. In the article we will talk about all the pros and cons of the EM suspension, as well as the prospects for the development of such technologies.
Basic elements of magnetic suspension.
Each electromagnetic suspension consists of a specific set of components that ensure the fulfillment of its main task:
- Elastic structures with the ability to receive and transmit vertically applied forces.
- Guide structures that form the pattern of movement of the wheels of a vehicle, as well as ensuring the connection of the wheel row with each other. The guides are also responsible for receiving and transmitting forces applied horizontally.
- Shock-absorbing elements, the main task of which is to reduce the force of vibration of the body when moving on the road surface.
Conventional representatives of modern suspensions consist of many elements, each of which can perform a wide range of tasks. But at the same time, these are amazingly complex mechanisms, each component of which has unique properties. This approach to suspension production technologies provides a good increase in vehicle controllability, comfort and stability.
EM suspensions also have all of the above components, only in a more advanced, technologically improved version. Magnetic suspension is a special mechanism, the basis of which is an electric motor. The engine has two running modes, ensured by the presence of an elastic and damping element. A special microcontroller is responsible for switching between them. Due to this design, the EM suspension is capable of playing the role of a conventional automobile shock absorber.
Production prospects
Unfortunately, in addition to its undoubted advantages, magnetic suspension has serious pitfalls. The most problematic thing about putting it into wide production is its cost and the price of installation on a car. Even leading automobile companies cannot equip their models without dramatically changing their price tag.
In addition, the implementation of this system will require special software, separate equipment and maintenance specialists. There are services that can solve repairs of this nature, but not more than two dozen in the world.
Another important point is the weight of the structure. The Bose suspension weighs one and a half times more than the similar McPherson. Nowadays, manufacturers are trying to make the weight of the car lower, so this aspect requires a compromise solution.
At the moment, developments and searches for solutions to key issues continue. Engineers test experimental samples using different materials to make elements. Thus, a ’99 Lexus ls sedan was converted to test a new version of the Bose electromagnetic suspension. Work is actively underway to improve the program code and its support.
The undoubted benefits from the introduction of this system are obvious, so in the foreseeable future, bright prospects await motorists. In addition to safety and comfort, the risk of accidental damage to the car will be significantly reduced, which means car repairs will be less significant for your pocket. This will be quite affordable in terms of costs and will fully justify them in the future.
Many people have probably already become interested in how the electromagnetic suspension works. The operation of the electromagnetic suspension is based on the principle of electromagnetism, that is, the dependence of electric and magnetic fields.
- Electromagnetic suspension - how does it work?
- 1. What is unique about the electromagnetic suspension.
- 2. How does electromagnetic suspension work?
- 3. Types of electromagnetic suspensions.
- 1. What is unique about the electromagnetic suspension.
- 2. How does electromagnetic suspension work?
- 3. Types of electromagnetic suspensions.
Since the times of Maxwell and Faraday, the founders of the theory of using the electromagnetic field for practical purposes, designers and engineers have been constantly trying to expand the boundaries of the use of such phenomena as superconductivity and magnetic induction. After all, this opens up enormous opportunities for humanity.
But only in the 80s of the 20th century the phenomenon of electromagnetism began to be used for practical purposes. In 1982, the first train was built, which moved on a magnetic levitation and reached a speed of 501 km/h. This marked the beginning of new developments, including in the automotive industry.
What is unique about the electromagnetic suspension.
An electromagnetic suspension, like any other, performs the following functions:
1. The connection between the wheels or axles of a vehicle and its body or frame.
2. Transfer to the supporting system (body, frame) of moments and forces that arise when the wheels interact with the road.
3. Ensuring the desired nature of wheel movements relative to the car body or frame.
4. Ensuring the smooth running of the vehicle.
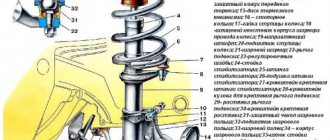
Car suspensions consist of the following main components:
1. Elastic components that are capable of receiving and transmitting forces in the vertical plane.
2. Guide components that form the characteristics of the movement of car wheels, their connections with each other, and also perceive and transmit lateral and longitudinal forces.
3. Shock absorbers, which are designed to dampen vibrations of the supporting system while moving on the road.
How does electromagnetic suspension work?
Many people have probably already become interested in how the electromagnetic suspension works. The operation of the electromagnetic suspension is based on the principle of electromagnetism, that is, the dependence of electric and magnetic fields.
How does maglev work?
Modern mechanisms, called magnetic suspensions, operate on an operating principle based on the phenomenon of electromagnetism. This effect describes the relationship between two types of fields: electric and magnetic.
Standard products installed on cars perform their main task thanks to such design elements as springs and elastic parts. Electromagnetic suspensions use electromagnets as their main elements. It is because of this mechanical composition that modern suspensions get their name.
The way the device works is to create a special control system by installing an on-board computer on the vehicle. This computer, also called an electronic unit, takes the characteristics of the wheel set in real-time mode and, depending on them, sends the appropriate commands. The control is carried out in a fairly simple way: the circuit is much simpler in nature than the same springs or hydraulic structures or a flywheel.
Principle of operation
The function of mechanical systems is provided by a group of elastic parts, and in hydraulic analogues, the task of the working component is performed by liquid. In turn, the electromagnetic suspension assumes the presence of a power plant, which is controlled via a computer. The functional element in this case is electromagnets. In practice, this means that the driver can monitor in real time the performance of wheels and assemblies that cover the entire perimeter of the body. Based on the transmitted indicators, the system can independently make decisions about making the necessary adjustments by sending appropriate signals.
Manufacturers
Like any other product in the automotive industry, electromagnetic shock absorbers are produced by several different concerns. Apart from the marketing name, devices from different manufacturers are based on different technologies. There are three leading companies producing electric suspensions, each of which produces products that work on a different principle from the others. We'll take a closer look at all three companies and look at each product.
Bose electromagnetic suspension.
The history of this technology begins back in 1980. It was in the early 80s of the last century that the outstanding professor Amar Bose, who teaches at the university in the department of electromagnetic phenomena, created his first product. He carried out countless calculations, and, after systematic analysis of the data, obtained the optimal shape and characteristics of the car suspension. Since Professor Amar Bose was also the head of the Bose company, his research made it possible to create a new type of pendants that exploit the principles of electromagnetism. The experiments of the outstanding scientist attracted wide public attention and directly influenced the entire automotive industry market.
The Bose suspension, completed and improved by the company, is considered the standard of magnetic suspension. According to the tests carried out, they cope with the assigned tasks almost one hundred percent - they level out the level of any fluctuations that arise. The main component of the product from the Bose organization is a linear electric motor that operates in two modes:
- As an elastic component.
- As a damping component.
The permanent magnets included in the design ensure reciprocating movements along the entire length of the stator winding. This technology not only reliably protects the car from vibrations in the plane, but also improves its handling to an unimaginable level.
"SKF" on electromagnetic shock absorbers.
This product, which has high levels of simplicity and reliability, was first released in Sweden. As the main element of the SKF design, a special capsule is used, the components of which are special electromagnets and magnetic shock absorbers.
As the vehicle moves, the main computer receives data from sensors installed on the wheels, reading their characteristics in real time. The same computer is responsible for transmitting signals that change the fluidity of the damping structure. Also, the SKF product implies the presence of springs included in the design in order to level out vibrations in the event of a main computer shutdown.
"Delphi" with single-tube magnetic shock absorber.
The main component of the Delphi product is a monotube electromagnetic shock absorber. Its internal part consists of a special magnetic substance (suspension), the dimensions of which range from 3 to 12 microns. There are approximately 30% of such parts in the product; the rest is occupied by an electromagnet in the form of a piston head and a special coating that prevents the substance from spilling out. The electromagnet is also controlled from an electronic unit, automatically. At the moment the magnetic field is applied to the substance located inside the shock absorber, the following happens: the particles of the substance take on a special, ordered structure. Thanks to this, the viscosity of the substance increases, with the help of which the operating mode is switched.
Historical aspect
Renault Logan Front Suspension DIY RepairRenault Logan Front Suspension DIY Repair
Until the early 1980s, maglev technology was just a theory. But in 1982, a real breakthrough occurred, marking the beginning of a new era. It was this year that construction began on the world's first maglev train.
The device was called a magnetic plane. The results of the first tests exceeded all expectations; the speed shown by the device exceeded 500 kilometers per hour. Unfortunately, these developments were completely unsuitable for use in cars.
However, scientists and engineers from all over the world could not so easily give up the advantages that maglev trains provided. Most important of all was the lack of friction.
Unable to modernize all the roads, scientists focused their attention on working on the chassis. By introducing electromagnetic control elements, they were able to achieve a significant increase in dynamic performance and controllability. This was the beginning of the introduction of magnetic levitation into modern production
This marked the beginning of the introduction of magnetic levitation into modern production.
The magnetic suspension is controlled using the on-board computer. As a result, the driving process acquires unprecedented softness. The car handles well on the road. This, in turn, significantly increases comfort inside the cabin.
Pros and cons of magnetic suspensions
Like any other product, the EM suspension has its own characteristics and qualities. When installing such a design on your car, you get a fairly impressive increase in terms of its handling. It is also worth noting the following advantages:
- Softer, smoother ride.
- High response speed of the on-board computer, which also increases the level of controllability.
- Saving energy consumption.
- Multifunctionality - it is possible to choose between automatic and mechanical operating modes.
The main negative factor worth mentioning is the availability and installation of software on the car. You will have to install additional software separately. At the moment, a small number of cars coming off the production line have a similar design, including magnetic suspension of the car. Also, as a minus, it is worth mentioning the high cost of such an “upgrade” of the chassis.
Market reaction
Bose considered major automakers of sports and luxury executive cars as consumers of its products. The suspension was tested by Honda, Ferrari and others, and each of these well-known manufacturers noted a significant advantage of the development over existing designs. However, when it came to cost calculations, company management took a pause to think, and in the end no one decided to implement the project.
The introduction of a new suspension required the development and implementation of a complex vehicle power supply system, which ultimately influenced a significant increase in the cost of the final product. For example, in addition to the processor, operation required a magnetic system using high-power neodymium magnets, the price of which is high. However, Bowes, confident that in the near future the cost of the components necessary to create the structure would drop to an acceptable level, did not see this as the main obstacle.
Two other problems seemed much more serious to him:
- Large weight of the suspension structure (the Bose design weighed 90 kg more than the usual one). This directly affected the deterioration of dynamic performance and increased fuel consumption, which, against the backdrop of increasingly stringent environmental requirements, turned into an absolutely unsolvable issue.
- The need for extensive, expensive testing and, as a result, investment. If successful, this could bring huge profits, but if the research failed, such a serious financial investment would make Bose bankrupt.
General information
What is the suspension in a car?
This is a kind of intermediate link between the body and its wheelbase. The chassis provides the connection between the axle and the frame, as well as with other components of the vehicle.
In the design of a car, the suspension plays a vital role, because it transmits torque from the wheelbase. As a result, the car elements transmit the required motion vector to the wheels.
As for the electromagnetic suspension, one of the characteristic features of its design, which distinguishes it from standard suspensions, is the fact that it may completely or partially lack torsion bars, springs and other attributes of a conventional chassis.
Advantages of a new type of suspension system
Installing an electromagnetic suspension on a car allows you to completely dampen vibrations that occur while driving on uneven roads. In addition, during sharp turns and braking, there is no lateral or longitudinal deflection of the vehicle body (the corresponding footage can be seen in the Bose promotional video).
The range of movement of linear electric motors is tens of centimeters. Passengers sitting in a car with electromagnetic suspension do not feel shocks at all while driving over rough terrain. The electric motor used as a shock-absorbing element has the ability to recuperate. This means that part of the wasted energy is returned to the amplifiers. Operating the electromagnetic suspension requires enough power to power three car air conditioners.
The presence of special software opens up wide opportunities for professional drivers. The car owner can program the operation of the car’s wheels in order to safely perform complex maneuvers. The created algorithms can be saved in the memory of the on-board computer.
A special algorithm could even make the car jump over an obstacle
History of appearance
Attempts to make the movement of a vehicle softer and more comfortable were made in carriages. Initially, the wheel axles were rigidly attached to the body, and every unevenness in the road was transmitted to the passengers sitting inside. Only soft cushions on the seats could increase the level of comfort.
Dependent suspension with transverse spring arrangement
The first way to create an elastic “layer” between the wheels and the carriage body was the use of elliptical springs. Later, this solution was borrowed for the car. However, the spring had already become semi-elliptical and could be installed transversely. A car with such a suspension handled poorly even at low speed. Therefore, springs soon began to be installed longitudinally on each wheel.
The development of the automotive industry has also led to the evolution of the suspension. Currently, there are dozens of their varieties.
Few people know, but the first scientific works explaining the principle of the magnetic field came to us even earlier than the internal combustion engine was used. The first mention of an outlandish device that uses physical laws previously beyond the control of humans belongs to the theoretical works of the English physicist and inventor Michael Faraday. This legendary scientist, back in 1862, was the first to explain and lay the future foundation for the thinking of many minds around the globe.
The second progenitor of the creation of electromagnetic theory is another British scientist, James Clerk Maxwell. Although his main layer only indirectly explained the principle of the influence of the electromagnetic field in nature, his work will largely predetermine the development of this movement, as well as all of physics in particular.
Read more: System for changing the geometry of the intake manifold - principle of operation
However, the first practical successes in the design of the automotive industry based on electromagnetic influence were achieved only in 1982. Then the first prototype of a train using a magnetic levitation was built. The M-Bahn was a truly unique reflection of the ideas of great minds, but its application in a wide area was impossible due to its imperfections.
German magnetic levitation train - M-Bahn magnetoplane
Having drawn public attention to the realism of such an invention, many engineers, realizing that a full-fledged “floating” transport is still only a dream, concentrated on creating less significant but practical automotive designs. As a result, in the 1980s, Bose was the first to produce electromagnetic car suspension, using the necessary calculations and calculations.
Unlike standard mechanical suspension, electromagnetic suspension cannot be used separately on different axles, but works in a coordinated system on two simultaneously.
Technical features
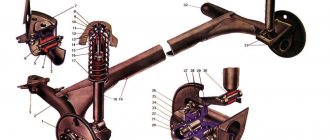
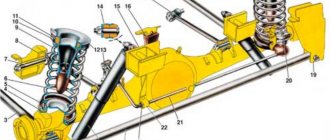
The design of the suspension system provides for the presence of a rod on which powerful magnets are attached. These elements can perform reciprocating oscillations along the stator winding. Magnetic suspension torsion bars serve as support for the vehicle body. The front corner module is made in the form of a connecting spacer. The vehicle's weight is supported by a specially positioned torsion bar that attaches to one of the lower control arms.
Linear electric motors are installed on each wheel. Electromagnetic shock absorbers are supplied with power and control cables. The front wheels can operate autonomously. The lower suspension link and steering gear are mounted directly on the vehicle body.
Application
When driving, the car body receives vibration waves caused by potholes, protrusions or other irregularities found on the roads. The car's suspension dampens or softens the resulting vibrations, preventing deformation of the iron horse. The purpose of the suspension is to provide a connection between the wheels and the body.
Thanks to the suspension parts, the wheels move separately from the body, which is why the direction of movement of the car changes. Also, through the suspension, it is possible to properly organize the chassis of the car. As for the structure, the design includes:
- Elastic elements. They are made from both metal and other materials. Elastic characteristics contribute to the change and redistribution of the resulting vibrations to the body.
- Extinguishing devices. With their help, it is possible to achieve leveling of oscillatory waves.
- Guides. They are a set of various parts that have the structure of a lever. Due to them, the connection between the suspension and the body is ensured, and the movement of the wheels relative to the body axis and plane is determined.
- Transverse plane stabilizer. Looks like a barbell. Made of metal. The stabilizer is used to connect the suspension to the body. Thus, the vehicle roll when driving is minimal.
- Supports. They are called steering knuckles. The load from the wheels is transferred to them, and they then distribute it to the system.
The design also includes fastening elements. With their help, parts and devices are connected. Often bolts and hinges are used as fastening elements.