Domestic roads often cannot boast of a smooth and even surface. In order to smooth out the movement of a car on uneven roads with holes and potholes, suspensions were invented, which are now used everywhere in cars. Suspension elements are closely connected to the body, a pair of front and rear wheels and are able to reduce the level of vibration when driving on uneven road surfaces.
Regardless of the type of suspension, it always performs the same function. However, there are several types of pendants and it is necessary to understand the features of each type of pendant. Many experts believe that sports cars should use one type of suspension, while compact cars should use a different type of suspension.
Purpose and design
A vehicle's suspension performs several functions. Basic:
- ensuring elastic fastening of the wheel to the body
- vibration damping
- ensuring contact between the wheel and the road surface
It was invented at the same time as cars. She is as old as the first car released from production. At the same time, it has still not been possible to create an optimal suspension that would suit any car.
Despite the varieties, the products are similar to each other in their components. The design contains:
- Elastic elements - leaf springs, springs, etc. Their main task is to absorb the loads received when the wheel hits the chassis.
- Damping elements or shock absorbers. They dampen vibrations received from elastic elements through absorption and dissipation of vibration waves. That’s why they are usually installed next to elastic elements.
- Guiding systems. Designed to connect the wheel with the supporting part, which ensures the ability of the machine to move along the desired trajectory. This group includes levers, rods, beams.
All components perform a number of specific functions, and even without one element it does not constitute a single structure.
What is it for?
An important part of the chassis - the rear suspension - levels out road irregularities, creates a smooth ride, increasing the comfort for the driver and passengers when traveling.
The design also implements a number of other functions:
- physically forms the connection between the wheel (unsprung mass) and the frame or body (sprung mass);
- resists skidding and rollover of the car when cornering;
- additionally participates in inhibition.
By performing the above tasks, the rear suspension contributes to better vehicle cross-country ability.
Dependent suspension
The very first suspension produced and used on cars. It is she who is considered the longest-liver among existing structures. And the prototype for creation was a horse-drawn carriage.
A special feature is the reliable connection of the wheels, preventing the parts from moving relative to each other. The rear axle acts as the connecting axis. Elastic elements are springs, although not so long ago they were springs. The damping element is a shock absorber. Install it in two ways:
- Separate from the springs.
- On the same axis as them. This arrangement requires installation inside the spring.
The shock absorber is mounted from above to the body, from below - to the bridge. The shock absorber has two functions - one involves damping vibrations, the second - secures the wheels to the axle.
Levers and rods, located in the transverse and longitudinal directions respectively, are the components of the guide system. There are four of them in total. They make sure that the movement of the axle and wheels is predictable. The transverse link serves to reduce the roll angle when the car turns while it is moving. Pros:
- simple execution;
- reliability;
- ensuring high-quality grip.
The main disadvantage is the loss of traction between the wheels and the road if the car enters a turn. This can be very dangerous. Today they are not in demand, and they try not to use them. Mainly found on trucks.
Car chassis diagram
To give our article greater practical value, we will consider the design of the chassis using the example of one of the most popular cars among domestic motorists - the VAZ 2109.
Front axle
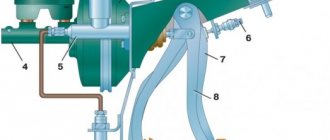
The front axle of the “nine” has a telescopic suspension equipped with coil springs and hydraulic shock absorbers. The transverse arm is of lower design, equipped with braces and anti-roll bars.
Due to the use of a front-wheel drive design on this car model, the technical complexity of the front axle, as one of the main elements of the chassis, is quite high, despite the relatively small number of components that make up the design. It consists of:
Struts with shock absorbers.
Mounting units to the body (transmission).
Rear axle
The design of the rear axle is much simpler, since it does not contain elements associated with the transmission (with the exception of rear-wheel drive vehicles). In addition, the rear axle bears a smaller load than the front part of the chassis. The relatively mild operating mode allowed the developers to significantly simplify both the circuit diagram of this unit and its design.
The rear axle of the VAZ 2109 consists of the following elements:
Hydraulic shock absorbers and a pair of springs.
Brackets that secure the axle to the vehicle side member.
Flanges for fastening wheels.
As the name suggests, the center beam serves as the main element of the rear axle. It is a combination of three separate parts (a connector and two longitudinal arms), connected by welding seams using reinforcing pads. Shock absorbers and wheel axle flanges are mounted to brackets welded to the arms.
Independent
The difference between this suspension and others, as you might guess, is the lack of connection between the wheels, which are on the same axis and located parallel to each other. This way, if for some reason the position of one wheel changes, it will not be reflected in the other.
They are divided into several types, and each of them deserves special attention.
Damping elements
Parts of the suspension that dampen vibrations while the car is moving are called damping elements. These include the following devices:
- Double-pipe shock absorbers, consisting of inner and outer pipes, and performing the function of a reservoir and a piston, which are connected by holes and multi-directional valves, which, due to the inertia of the working medium, slow down reciprocating movements and dampen vibrations.
Depending on the internal operating environment, shock absorbers are divided into:
- Hydraulic;
- Gas-filled;
- Gas-hydraulic.
MacPherson struts
Many people know this type as a “swinging candle.” The main difference is the presence of a shock-absorbing strut, which performs several functions at once. In this case, all functions are performed simultaneously. The design involves:
- shock absorber;
- spring.
The element is attached to the wheel hub from below, and to the body from above. In the second case, additional supports are also used. Thanks to this type of fastening, it is possible to ensure reliable fixation of the wheel with the body when rocking. There is also a guiding system. Its role is played by levers having a transverse direction.
The stand is the most popular and in demand type. Its purpose is to ensure comfortable movement on the road. The suspension is valued for its reliability and durability.
Principle of operation
Car suspension works as follows:
- When the car hits an obstacle, the wheel rises above the horizontal track, changing the position of the rods, levers, and swivel units.
- The shock absorber immediately comes into action. At the same time, the spring, which was previously in a free state, is compressed under the influence of the kinetic energy of the tire push in the direction from the plane of the ground - upward.
- The elastic compression of a shock absorber with a spring displaces the rod: rubber-metal bushings partially absorb shocks and vibrations transmitted to the car body.
- Then a natural reverse process occurs. A newly compressed spring always tends to straighten out and return the shock absorber, and with it the wheel, to its original position.
The cycle is repeated with all wheels.
Lever
The lever type is also a representative of an independent type of suspension. A fairly well-known option, which has two types of design:
- Double lever. The shock absorber strut is used only to dampen vibrations. Fastening is carried out by a control system, which includes two transverse arms with an A-shaped design. The part prevents unnecessary movement of the wheel when driving. However, in comparison, the MacPherson strut is softer and easier to control.
- Multi-link. Improved double-lever design. Two levers are complemented by eight more similar parts. Due to this, it was possible to improve the smoothness and comfortable driving.
Basically, preference is given to MacPherson struts and a double-lever design. They are found in most vehicles and are especially popular among modern and expensive models. Also preferable for installation in cars with soft suspensions.
Semi-dependent
This type of pendants is something in between the options described above. In appearance, the design resembles a dependent suspension. It also has a beam and trailing arms, thanks to which it is possible to connect two wheels located on the same axis.
The semi-independent suspension is secured using levers. Elastic and damping elements are the familiar springs and shock absorbers, respectively.
But the semi-independent beam is torsion bar, which allows it to also work in torsion. Thus, the wheels can move in a vertical direction independently of each other.
Pros:
- simplicity;
- reliability.
Often found on rear-wheel drive cars.
Types
The various variations of rear suspensions can, however, be divided into three main types:
- Dependent design. A pair of rear wheels is rigidly connected by an axle, a beam, or a split or continuous axle. Often there are combinations of suspensions that provide for the installation of an axle with a spring (dependent, spring), a spring (dependent, spring) and pneumatic elements (pneumatic, dependent). When the wheels are connected by a rigid beam, the load is directly transferred from one side to the other: then the ride is no different in softness.
- Semi-independent suspension. The same beam is used here, but with the characteristics of a torsion bar. Or the latter is built into the beam. This design feature adds smoothness, as the torsion bar softens the stress transmitted from one slope to another.
- Independent type. The wheels connected by an axle cope with the loads independently. Independent suspensions are pneumatic and torsion bar.
The third version of the mechanisms is the most progressive, but complex and expensive.
Hydraulic
Hydraulic suspension has a number of features. The main one is the modified shock absorbers. Unlike standard shock absorbers, conical shaped parts filled with oil are used. Additionally, each part is equipped with a spherical hydraulic accumulator.
Among the advantages:
- durability;
- smooth ride under all conditions;
- possibility of adjusting the ride height remotely.
They are strong and quite reliable. However, the downside is the presence of oil in the design. The fact is that if an oil leak occurs, not only the product will fail, but also the brake system and power steering.
Car beam replacement
It is necessary to raise the rear of the car, securely blocking the front wheels. Then remove the rear wheels. Disconnect the shock absorbers and springs from the beam. Release the beam from the hand brake cable. The brake system lines are also partially disassembled, disconnecting them from the hose tip. At this point, brake fluid may begin to leak from the system. To prevent this undesirable phenomenon, you need to plug the brake hoses using any available means. For example, brake bleeder caps work well.
Next, unscrew the bolted connections securing the beam to the body and dismantle the beam. Installation of the new part is carried out in the reverse order. The only caveat is that after lowering the car onto the wheels, you must once again tighten the bolted joints securing the beam to the car body.
Screw
Helical suspension is a general name for several types of suspensions, the design of which provides the ability to regulate the degree of spring pretension. The advantages of this design are:
- ease of maintenance;
- strength;
- durability;
- good job for Russia.
She is tough and almost indestructible. If it breaks, you can fix it yourself. At the same time, manufacturers recommend inspecting the structure as often as possible. To avoid frequent breakdowns, you can lubricate the surface of screw-shaped shock absorbers with a special lubricant.
How is the chassis of a car arranged?
There is a very big recommendation for drivers: always listen for knocks, squeaks or malfunctions of the car. This will allow you to contact a service station at the right time and fix the problem that has just appeared. This is especially true for the chassis, since it is the shell that keeps the vehicle moving.
- 1 Main chassis elements
- 2 Operating principle
- 3 Video “How a car’s chassis works”