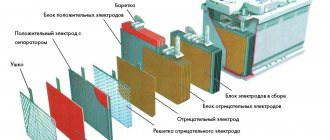
Many motorists consider purchasing a car battery a “blind” purchase: if you’re lucky, the battery will last at least as long as it should, but if not, then after a year you have to plan a trip to the car store again. In fact, the service life of a battery depends on its operating conditions, proper care and, of course, on the type of battery.
Recently, there has been a lot of talk about calcium batteries as a serious alternative to conventional batteries. Let's try to understand this issue.
What you should know about calcium batteries
Some car enthusiasts believe that the plates of Ca/Ca batteries are made from calcium rather than traditional lead.
However, in reality this is not the case. If the plates of car batteries were made of calcium, then we simply would not see the electrochemical charge-discharge reaction from the battery. Therefore, the plates are made of lead, and calcium is present only as an additive, and then only 0.07 percent. In batteries made using Ca/Ca technology, calcium is added to both the positive and negative plates. In Pb/Ca batteries, which are otherwise called hybrid batteries, calcium is found only in the negative plates. The principle of operation, as well as the electrochemical reactions of calcium batteries are absolutely identical to traditional lead batteries. The difference between them is the presence of calcium, which under normal conditions prevents the battery from boiling and also helps protect the lead from corrosion. (Normal conditions mean operating the battery in a car, where it is charged at a voltage of approximately 14.4 - 15 V, and, accordingly, does not boil). Also, due to the addition of calcium, lead plates become more durable, which has a positive effect on service life. Thanks to Ca/Ca technology, it has become possible to make thinner plates (relative to the plates in lead batteries). Due to this, the surface areas of the plates increased, which, in turn, affected the growth of the so-called inrush currents.
Result:
batteries manufactured using Ca/Ca and Pb/Ca technology are designed for use in cars with an on-board voltage of up to 15 V. At the same time, the battery charges normally, does not boil, and the self-discharge current is lower compared to traditional batteries. Battery boiling and damage to the plates occurs at higher voltages, which do not occur in a working car. The properties of calcium batteries lead to the conclusion that they are easier to maintain and retain their charge longer.
How to properly charge a Sa/Ca battery
- If the battery in your car is not fully charged (the reasons may vary: low outside temperatures, short and infrequent trips, problematic alternator, etc.), you need to charge it using a regular charger
- The charge voltage should be in the range of 14.4-15V
- The charge current should be no more than 10% of your battery capacity
- Algori standard for lead-acid batteries; charge with constant current to a threshold voltage, then charge with constant voltage with a decrease in the charge current.
- “Boiling” calcium batteries is strictly contraindicated. Since, at best, it leads to a decrease in the technical characteristics of the device, and at worst, to failure of the device.
- To achieve a more “dense” charge, better dissolution of sulfates and increased service life, it is necessary to charge the battery with the lowest current value.
Nowadays there are many fakes on the market. To distinguish a high-quality battery from a fake, and also to understand whether the device in front of us is original or not, you need to pay attention to the markings. The following characteristics must be indicated on the battery case:
- starting current
- voltage value
- rated capacity value
- release date of this device
- detailed information about the manufacturer
Everyone has the right to choose their own charge voltage and current. But have you noticed that we are not talking about a charge of 16 volts or more? These batteries are charged in the same way as lead-acid ones.
Benefits of calcium batteries
- Long service life. With proper use, the service life of a calcium battery is, on average, about five years.
- Low self-discharge level. Compared to low-antimony varieties of batteries, the performance of calcium batteries is lower by almost 70 percent.
- Increased strength of battery plates. This allows the plates to be resistant to vibrations.
- Reducing the intensity of corrosion processes. This increases the service life of the battery.
- Calcium batteries are equipped with overcharge protection. Characterized by the ability to withstand voltages up to 14.8 V.
- Most calcium batteries (about 90 percent) are maintenance-free.
- It is possible to produce plates of smaller thickness. Manufacturers have the opportunity to produce batteries with an increased number of plates, which affects the power - it becomes more.
- An excellent option for novice motorists. As we have already said, in most cases, a Ca/Ca car battery is maintenance-free. This allows the driver not to carry out additional actions, such as measuring the level and density of the electrolyte.
Batteries of this type are ideal for installation in cars with fully functional electrical equipment. It is desirable that the vehicle has systems that can independently turn off the music, side lights, and lights in the event that the motorist forgot to do this himself.
Demand creates supply
Why are calcium batteries used everywhere now? Maybe science has found a way to get rid of all the above disadvantages? Not really. The main factor here is the basic law of a market economy, which can be formulated as follows: “Demand creates supply.”
Automobile boom
Remember how many cars there were in the yards of your houses just 30 years ago? How many are there now? In any city, courtyards are literally filled with cars. There is a car boom. Previously, a car was a luxury and literally “the specks of dust were blown off”, but now? Do you think that owners of cars that “live” on the street do not sleep at night, thinking about how to service the battery on their car? Nothing like this.
Set it and forget it
People's priorities have changed a lot. The car has become a common means of transportation, and the choice of battery has shifted towards the increasingly popular “set it and forget it” principle. Whatever they say, most motorists don’t care what happens to their battery. They just don't want to deal with their service.
Here are the words of one motorist: “As practice has shown, all 3 new cars that I bought (over the last 15 years) had batteries that lasted 2 years, maximum 3” (I’ll add that this motorist is from the northern regions of Russia). Then I asked him: “Have you tried charging it?” To which he replied: “Why? It’s easier to buy a new one.” How do you like this answer? Strange, isn't it? However, there are more and more such people every day.
Competition between battery manufacturers
Now it’s clear why battery manufacturers go out of their way to offer consumers a battery that doesn’t require any attention, in a word – “set it and forget it.” And the competition among battery manufacturers is now being conducted in one single area - whose battery will last longer without any maintenance
.
Disadvantages of calcium batteries.
Unfortunately, there are no ideal things in our lives. Therefore, calcium batteries also have a number of disadvantages.
- Sensitivity to deep discharges. This is the main difference between calcium batteries and their hybrid and antimony counterparts. It is highly not recommended to discharge calcium batteries below a voltage of 12 V. With just one deep discharge, such a battery will lose a fifth of its capacity. With a single full discharge, the battery loses half of its capacity, while a device that has survived 9-10 discharges becomes completely unusable.
- Quite a high cost. This is due to the expensive and complex production process.
- Not suitable for urban travel mode. Long downtime, if the car is used infrequently and for short distances, has a negative and even detrimental effect on calcium batteries.
Please note that calcium batteries are only suitable for use in automobiles. We advise you to refrain from installing such devices in a boat or boat (where they may be subject to deep discharge).
Manufacturing technology of Ca/Ca batteries
It would seem that replacing one component with another should not significantly affect the manufacturing technology of battery plates, but this is not the case. Antimony ones are made by casting, which is quite simple and inexpensive. Replacing antimony with calcium revealed a significant problem: during casting, calcium burns out almost completely. It was necessary to make the lattice base of the plates using the stamping method. Calcium is added to lead, the alloy is made in the form of a tape, which is then perforated in the desired spatial and geometric shape. As it turned out, such plates turned out to be more effective than traditional ones.
But the main limiting factor for their widespread distribution is precisely the complexity of production, which affects the cost of calcium batteries.
Incorrect - “correct” charging of calcium batteries
Let's assume that we have a calcium battery. We supply the standard 14.4 V to it and wait until the current consumed by the battery drops to 0.1 A (remember that this is one of the signs that the battery is charged). Next, turn off the charger and measure the density of the electrolyte. The density, with a charged battery, should be 1.27, but when measuring we do not see this figure. What to do? In this case, many on the Internet advise charging calcium batteries with a voltage of 16.1 - 16.5 V. Let's figure out what will happen if we follow these tips.
When charging at this voltage, the density will still increase, as we wanted. However, by applying such tension, we provoked the very boil that src=»https://orionspb.ru/articles/ca_02.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»3840″ height=»2160″[/img] V In modern batteries, the electrolyte that is in the envelopes reacts predominantly. However, the one that we drew in with the hydrometer is located outside the electrochemical reaction zone, from which we conclude that the density of this electrolyte should not increase at all at the same time as the battery is being charged. When 16 V is applied to the terminals, the electrolyte on the envelopes begins to “boil”, due to which it begins to intensively mix with what is located above the plates. This is the only reason that after re-measuring we saw a density of 1.27. Although this density has already been achieved inside the envelopes. While we were boiling the battery, the plates degraded, losing some of the lead. Let's assume that we nevertheless charged the calcium battery using a method from the Internet and installed it on the car. What will happen next? After the first start, the charge that was accumulated by “boiling” is spent on the operation of the starter. And then the battery is recharged at a voltage of 14.5 V.
Stages of the procedure
Charging a calcium battery consists of the following steps:
- Identification and cleaning of sulfated plates. Before charging the battery, it must be checked for sulfation. The main sign of this problem is the presence of brownish formations on the battery terminals. In the case of a serviceable battery, sulfation can be identified by inspecting the plates. If they have increased in size and become off-white in color, then sulfation has occurred. Pulsing voltage will help remove sulfates from the outer surface of the plates and restore battery capacity.
- Checking the battery's ability to receive energy from the charger. There is one more procedure that needs to be done before charging the Ca/Ca battery. Whether the device is suitable for working with a particular type of battery should be written on its box or in the instructions. Of course, you only need to carry out this procedure once, during the purchase of the charger. This stage intentionally comes after cleaning the sulfated plates, since you can get rid of sulfates using almost any charger.
- The next stage is to charge with maximum current until the battery reaches 80% of its capacity.
- The last 20% of the Ca/Ca battery is charged using a moderate current. This allows you to avoid that very “boiling”.
- After restoring the battery, you need to check whether it is capable of holding the received charge. If the battery quickly loses its capacity, then it’s time to replace it with a new one.
Summing up
To choose the right battery that is suitable for your specific vehicle, you must consider the following parameters:
- Battery compatibility with your vehicle model
- operating conditions and intensity
If you have any doubts when choosing a suitable battery, we advise you to seek help and advice from specialists. You can also get advice on our forum https://forum.orionspb.ru/ Calcium batteries are more suitable for motorists who drive frequently and over long distances, and also prefer high quality driving. With timely recharging, the device will be used for a long time - for the period stated by the manufacturer and even longer.