Geometric cross-country ability is just a theory
At the very beginning, we must understand the difference between geometric cross-country ability and the ability of a car to overcome obstacles. Geometry is objective data that describes a car as a model. The data, which has nothing to do with practice, is intended only to inform the user about his vehicle. Information on maximum ground clearance is provided by the same data as on the length of the car, but in practice it does not mean very much. It is not necessary that a longer car will by definition be more spacious than a short car.
This must be understood before giving preference to one or another car. Moreover, the data provided by manufacturers is almost never consistent with reality. This is especially true for ground clearance, which in the eyes of a car enthusiast is usually something sacred in the understanding of off-road capabilities.
Longitudinal flotation angle (roll angle)
In the classic description, this is the maximum angle at which a car can move onto a horizontal surface without hitting the corner of the obstacle with the bottom or elements located lowest below it.
It is also worth noting that ground clearance, also known as ground clearance, is the distance between the road surface and the lowest point of the central part of the car.
Examples [edit | edit code]
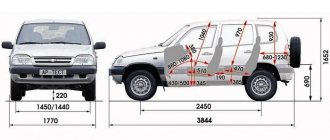
The main parameters related to the cross-country ability of some passenger cars:
5.1 Climbing
Determination of climb angles based on engine, transmission and tire capabilities
When determining the maximum surmountable inclines, it is assumed that the car moves uniformly and at low speed. In this case, the forces and are equal to zero and from formula (10) it follows that
Dividing all terms of this equation by and solving it for , we get
Limit angles of ascent for the adhesion of the driving wheels to the supporting surface
When overcoming a rise, it is considered that the car is moving at a low and constant speed, the adhesion coefficients of the driving wheels with the road and the rolling resistance coefficients f
a are constant along the entire length of the lift.
For single three-axle four-wheel drive vehicle
5.2 Determining trailer weight
The weight of a trailer that can tow a car at a speed v i
= 50 km/h on a given road, is approximately determined by the formula [3].
where is a dynamic factor with a certain margin that compensates for the unaccounted increase in resistance to the movement of the road train.
By specifying the speed according to the dynamic characteristic graph, we determine the corresponding value of the dynamic factor.
Using the graph of the dynamic characteristics of the car, we determine D:
We introduce a reserve of dynamic factor equal to 0.01, which is considered as a traction reserve in case of possible fluctuations in the resistance to vehicle movement caused by the appearance of road sections with a high drag coefficient, compared with its specified values for the type of the main part of the road. Taking into account the reserve, the value of the dynamic factor D' = D – 0.01.
Then the maximum possible total weight of the trailer Gп when the road train is moving at a uniform speed V, determined by formula (36) is equal to:
After finding the weight of the trailer, determine its mass:
5.3 Determination of the maximum lifting angle of a vehicle with a trailer
The maximum elevation angle overcome by the adhesion of the driving wheels by a road train consisting of an all-wheel drive tractor and trailer is equal to:
The lifting angle of a given car with a trailer, the mass of which is equal to 50% of the car’s mass, is equal to:
The run-out path is determined when the vehicle coasts on a horizontal section of road with asphalt concrete pavement from a speed of 50 km/h to a complete stop. The length of the run-out path allows you to evaluate the perfection of the design and technical condition of the vehicle chassis. When the car is coasting, the engine is disconnected from the transmission, power is not supplied to the drive wheels and it moves with deceleration.
Power balance equation in coasting mode:
where is the coefficient for taking into account rotating masses in the run-down mode;
– friction force in the transmission in coasting mode (neutral position in the gearbox), N;
– vehicle speed, m/s.
From the solution of equation (38) regarding deceleration it follows:
where is the total coefficient of road resistance.
The coast down starts at a speed of 50 km/h. For the speed range from 0 to 14 m/s we construct a dependence (Fig. 8). Data for constructing the dependence j h = f(V)
are given in Table A. 5.
Rice. 8. Graph of changes in vehicle deceleration when driving in coast mode
We divide the speed interval into 7 sections and find the run-out length, m using the formulas:
where ?Si – run-out paths in each section, m
where Vсрi is the average speed value on the section, m/s
?ti – run-down time on the section, s
where jav is the average deceleration value on the section. m/s 2
The results of calculations using formulas (39) – (41) are given in Table A. 6.
Cross angle
photo: Erik Lando/flickr.com
The second important indicator affecting the geometry of the car. The term is little known among wide circles of motorists, but is no less important in its meaning. It indicates the distance from the ground to the lowest point of the car between the wheels (lowest points of suspension elements, drives, fasteners and other units).
Often, manufacturers use either the best setting or a general concept for ground clearance at any point in the vehicle.
Relatively speaking, this parameter indicates the lowest point in the area of the axes. One note: we are not talking about elements on the wheels themselves, such as, for example, mounting shock absorbers.
The transverse ground clearance in a car with suspension on solid drive axles is limited by the presence of a differential housing. In the case of independent suspension (split axle), the clearance is limited by the elements of the chassis itself (levers, silent blocks, and so on).
Most often, cars with independent suspension have higher ground clearance than cars with dependent suspension (solid axle). This applies to the vehicle, both loaded and unloaded (in the first case, the suspension is compressed, in the second, it is decompressed).
When a vehicle with independent suspension goes over a bump, the ground clearance changes. Under a rigid axle, ground clearance is always constant. It is also worth noting that ground clearance does not always correspond to the center of the axle. On some vehicles, the axle differential housing may be positioned slightly to the side (to the left or right).
The Hummer H1 is a prime example of the benefits of independent suspension. In a specialized all-round vehicle for the most difficult conditions, it is still better than the dependent version
In practice, although ground clearance is an important parameter, it is not the only parameter that determines the vehicle’s capabilities in field conditions. There is also no definite rule about what is better on a car - independent or dependent suspension. Because a lot in real life will depend on how the car is used.
For example, dependent suspension and high ground clearance will work better in ruts. On the other hand, when driving dynamically on large bumps, the dependent suspension ensures that the ground clearance will not always be constant and the chance of hitting an obstacle with a suspension element will be lower for such a car. Plus, the driver will be able to maneuver between obstacles with greater precision and chance without hitting them. This is especially true if there are stones and other serious obstacles on the road.
Technical characteristics overview
How to drain gasoline from the tank of a modern car
The cabin and controls of the KAMAZ 4310 are designed to provide maximum comfort to the driver while operating the vehicle. The cabin is located above the engine and is equipped with a ventilation and climate system. The control system is based on the lever-steering principle of influencing the adjustment of operating functions. There is a function for tilting the driver's cabin, if necessary, to gain access to the V-engine. There are two cabin design options for this vehicle model. Regional cargo transportation does not require a sleeping place in the car, since the time period of one flight is short. For long-distance vehicles, a driver's cabin with a sleeping bag is installed so that you can rest at the transshipment point.
The KAMAZ 4310 all-terrain vehicle is equipped with huge fuel tanks, each of which can be filled with up to 125 liters of fuel. Some modifications of this series of trucks are equipped with a 250-liter fuel tank. If we take into account the standard fuel consumption for such vehicles, then the possible supply of fuel fluid does not allow for long trips without refueling. But the use of inexpensive engine oils reduces the cost of operating equipment.
The brake system of KAMAZ 4310 has a rather complex design and includes such mechanisms as drum brakes, a device for parking and emergency adjustment of the vehicle chassis, and an additional device for slowing down the operating process of propulsion equipment with a pneumatic drive device. One of the advantageous features in the mechanical design of the car is the winch mechanism. The KAMAZ winch is equipped with a worm gear unit and is a powerful drum connection. Here, a special tape is used to brake moving components. The cable pull level is fifteen tons, with the ability to use a winch rope of 83 meters. The winch mechanism operates thanks to the power take-off unit.
Thanks to its high technical characteristics, repairing a KAMAZ 4310 does not require huge financial costs. All mechanical components of the machine are made of especially durable materials, based on the best grades of steel. Possessing properties with a large margin of safety, the car will be in regular use for a long period of time, without the need to replace or repair parts. At the end of the warranty period for using special cargo transport, despite the technical condition of the mechanical connections of the equipment, it is recommended to undergo standard maintenance, which can be carried out at any repair center.
The KAMAZ 4310 clutch has a double-disc design and, being a friction mechanism, makes it easier to start the operating functions of the vehicle. The vehicle body is made of solid metal and is equipped with a hinged rear door. Initially, used for the needs of the country's armed forces, the interior of the car body was equipped with folding lavas and covered with canvas material around the entire perimeter.
Ground clearance (clearance)
Ground clearance is the distance between the ground and the lowest point of the vehicle, but between the vehicle's axles (not the wheels). Typically, ground clearance is higher than the cross-country angle. Regardless of the suspension design, ground clearance will vary depending on the load and driving conditions.
Does this parameter mean anything? Certainly. For example, a tree lying across the road will be overcome, not least with the help of this clearance.
Approach and departure angles
The approach angle is the angle between the horizontal surface and the line drawn between the contact patch of the front wheels and the lowest point of the front of the car.
Simply put, the angle of attack determines the vehicle's ability to approach an inclined surface without hitting it with the front bumper or engine guard, that is, the maximum angle of the ramp that a car can enter without hitting it with the front of the body. The parameter is closely related to the front overhang.
A similar parameter is used for the rear of the car.
Departure angle is the same thing, but for the rear: the angle between the horizontal surface and the line drawn between the contact patch of the rear wheels and the bottom point of the rear of the car. It is tested on an inclined ramp when the car is moving in reverse, onto which the car can drive without touching the obstacle with the rear of the body.
Of course, for SUVs the approach and departure angles are much greater than for conventional passenger cars and can be 45°-50°, plus or minus a couple of degrees.
photo: lurkzilla/flickr.com
In reality, the angle of attack of entry and exit largely depends on the shape of the bumper or engine crankcase protection. For example, the farther the bumpers are located from the center point of the body, the greater the likelihood of them catching the slope and damaging them. In a car with a tow bar, this element will be the lowest point. In some SUVs, on the other hand, the angle of attack is determined by the presence of a large muffler, which can also be hit when moving up in reverse. That's why some SUVs have exhaust pointed to the side (Land Rover Defender).
Drive unit
The presence of all-wheel drive on SUVs is considered a prerequisite. All-wheel drive can be permanent, like on the Niva, or hard-wired, like on the UAZ. Permanent all-wheel drive is usually equipped with a center differential lock, which, when engaged, distributes torque equally between the front and rear axles. There are also more modern all-wheel drive systems, with electronic torque distribution and other features.
There is nothing to do here without all-wheel drive
Threshold height (term of foreign jeepers)
Threshold height (threshold height) is the height of a vertical obstacle that a vehicle can overcome with only its wheels in contact with it. We did not find such a term in the domestic literature, but in foreign sources it stands out as a separate category.
In general terms, this is the distance from the ground to the lowest point of the car, located in front of the wheels, when looking at the car from the side. In a sense, the sill height is the longitudinal gap between the bumper/crankcase protection elements.
This parameter complements the approach and departure angles. It may be that vehicles with the same angle of attack will have different threshold heights. A unique example is the Hummer H1 without a front bumper, which has no threshold height restrictions and its attack angle is 90 degrees. This is shown in the video below:
In practice, only real jeepers use it. All other car owners will be bothered by the bumpers on their cars and the small forward movement of the front axle wheels. Of course, the Hummer cannot do this trick in reverse.
Internal or external ramp slope
The slope of an internal or external ramp may exceed 15% only in specially justified cases. On ramps with a slope of more than 15% To prevent pedestrians from slipping, you have to think about installing steps or corrugating the surface of the road surface. If the ramp of a large garage also serves as an evacuation route, then on one side of the ramp a raised sidewalk with a width of at least 80 cm is installed. In places where the slope changes, it is necessary to ensure the passage of long vehicles and provide the necessary clear height for them. Although garage rules do not require the installation of longitudinal mating curves and. roundings in the vertical plane, they are recommended to be performed in all cases.
In a ramp with a variable slope, the radius of the inner edge of its surface should not be less than 5 m. Between ramps with a slope of more than 5% and the urban road network, a horizontal platform should be provided, which increases safety and ease of movement and provides the driver with the necessary overview of the road situation. The minimum length of such a platform is assumed to be 5 m. If the ramp is intended only for passenger cars, then the length of the platform is reduced to 3 m with a longitudinal slope of up to 10%.
External ramps should be protected from ice and snow. As structural measures, it is recommended to install canopies or heat the roadway. Storage areas in open garages and open ramps on the outside must have guards at least 60 cm high to prevent vehicles from falling. For the calculation of fencing, the standard DIN 1055, part 3, section is valid. 7.4.2 (1978) “Loads on structures, traffic loads.”
Since the existing general guidelines or rules regulating the size of parking spaces and driveways in garages are still not consistent with each other, it is necessary to streamline them when developing Garage Rules. In accordance with the new Garage Rules, parking spaces for passenger cars in garages must have a minimum length of 5 m and a width of 2.3 m. However, they must not be limited by side walls or partitions. Otherwise, the size of the storage areas should be increased. When installing cars at an angle of 45°, the passages must have a width of at least 3.5 m, when installing at an angle of 60° - at least 4.5 m and when installing perpendicularly - at least 6.5 m. When installing cars perpendicularly and with a minimum width For parking spaces of 2.5 m, it is enough to provide passages 5.5 m wide, which will improve the conditions for entering the parking lot. The minimum width of aisles can be determined by interpolation; if vehicles are placed at other angles and the dimensions of storage areas differ from those mentioned above, the minimum dimensions should not be reduced by columns and other building structures or equipment.
Construction of garages
Tipping angle
This is the maximum angle of inclination of the car around the longitudinal axis at which it will not fall to one side. In real life, this parameter depends on the combination of the vehicle's width and height, its track width, and the center of gravity.
The wider the vehicle's track, the lower the height and the lower the center of gravity (the parameters are not identical, but mutually influencing), the higher the rollover angle. That is, the more difficult it is to put the car on its side when driving along a longitudinally inclined surface.
In reality, understanding the rollover angle of a car (approximate, of course) can help off-road, in places with large slopes. Fortunately, there are no such slopes even on abandoned primers. Just somewhere in the forest.
Can a country have two types of railway tracks?
Maybe! It has already been said above that trams in some cities use a narrower gauge. The same applies to the mining industry. For example, such roads (750 mm gauge) are used on roads along which peat and timber are transported. True, now their number is rapidly declining and they are being “converted” to standard gauge or abandoned.
But such roads are much easier to build and maintain. They also allow you to make a smaller turning radius. This has its advantages, but in a world where everything strives for unification, there is less and less room for them.
Autonomous train received the title of “largest robot”
Another area of use for roads with a width of 750 mm is children's railways, which can be found in different cities of our country. Here, schoolchildren practice train control skills and the intricacies of movement in order to try out a profession and understand whether they want to connect their lives with the railway.
On the children's railway, children run the show. Under adult supervision, of course.
Fording depth
Everything is clear here: this is the maximum depth of a water obstacle that a car can overcome without “choking.” The parameter is adjustable and depends on the air intake outlet above the expected waterline. For this purpose, devices called snorkels are used. They allow prepared SUVs to dive into the water up to the hood and even below.
In real conditions, playing with water can still end very badly. Not only does it prevent water from getting into the intake and cylinders, it is important that water does not flood the electronics or, even worse, the car does not tip over due to the water flow.