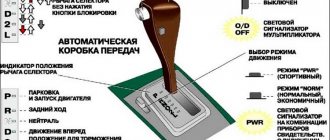
What do the position symbols mean?
The range selection lever (RVD) has several positions, which are designated by letters and numbers. The number of these positions is different for different car models, but on all cars the RVD necessarily has positions designated by the letters “P”, “R” and “N”.
Position "P"
Selected when parking the car for a long time. In this position, all controls in the automatic transmission are turned off, and its output shaft is locked, so movement is impossible. In this mode, engine starting is allowed.
Position "R"
Reverse. Moving the lever to the “R” position while driving can lead to gearbox failure. In this position of the RVD, starting the engine is impossible.
Position "N"
All controls in the transmission are turned off or only one is turned on.
The output shaft locking mechanism is disabled, i.e. the car can move freely. In this mode, engine starting is allowed. For vehicles equipped with four-speed transmissions, the range RVD has four forward travel positions: “D”, “3”, “2” and “1” (“L”). If the lever is installed in one of these positions, starting the engine is impossible.
Range "D"
Basic mode.
It provides automatic shifting from first to fourth gear. Under normal driving conditions this is what is used. “D 3” - movement is allowed at the first three speeds. Recommended for use when driving in stop-and-go traffic. “D 2” - movement only in first and second gears. Used on mountain roads. Shifting to third and fourth gear is prohibited.
“D 1” - driving only in first gear is allowed. Allows maximum implementation of engine braking mode. For example, when driving on steep slopes.
On some cars, permission to use the fourth, overdrive gear is carried out using a special “OD” button. If it is recessed and the lever is set to position “D”, then upshifting is allowed. Otherwise, engaging the fourth overdrive gear is prohibited. The system state in this case is reflected using the “O/D OFF” indicator.
- Types of automatic transmissions - how they differ
Overdrive means overdrive. Identified as "OD", "D" or D in a circle. Overdrive is used for economical driving on the highway.
Range P (Park) - parking mode.
This mode is selected when the car is parked for a long time. In this position, the controls in the box are disabled, the output shaft is blocked, and as a result, the machine cannot move (the drive wheels are blocked, the blocking is not associated with the parking brake and is located inside the box itself). Starting the engine in this mode is allowed.
Do I need to use the parking brake when parking? On flat areas, provided that it is in good working order, blocking the output shaft of the box for reliable fixation is quite sufficient. When stopping on a slope, it is advisable to use the parking brake. In this case, you first need to pull the handbrake, and only then put the gear shift lever in P mode. Thus, you remove additional load from the locking mechanism of the output shaft of the automatic gearbox.
Why do you need economy, sport and winter modes?
Most cars with automatic transmissions have multiple shift control options. These include - economical, sports, winter.
Economical program
The program is configured to ensure movement with minimal fuel consumption. The movement is smooth and calm.
Sport program
The program is configured to maximize the use of engine power.
The car develops significantly greater acceleration compared to the economical program. To implement an economical or sports program, a special button or switch is located on the dashboard or next to the lever, which may be designated “POWER”, “S”, “SPORT”, “AUTO”.
Winter program
Electronic control units have a special program for starting off on slippery roads. There is a special button for activation, which are marked “WINTER”, “W”, “*”. If it works, different algorithms for automatic transmission operation are possible. But in all cases, starting is carried out from second or third gear.
Additional automatic transmission operating modes
In automatic transmissions of later models, which have a larger number of operating ranges, there are additional operating modes. In the automatic transmission control system they are present in the form of switch buttons. An experienced driver knows how to use automatic transmission modes , so let's look at everything ourselves.
Economy mode (“Eco” or “E”) - ensures minimal fuel consumption while driving, since the engine is limited in the speed range at each stage. Thus, the joint operation of the engine and automatic transmission takes place in such a way that in each higher gear the engine actually starts working at idle speed, subsequently increasing it, but not bringing it to maximum. In this mode, the vehicle's movement is calm and smooth.
Sport mode (“S”) - in this mode of operation of the automatic transmission, engine power is used to the maximum. Each subsequent gear is engaged at frequencies close to the maximum torque. Accelerating further, the rotation of the crankshaft reaches its maximum, and thereby the engine develops its full power and begins to work with full efficiency. And the car in this mode moves much faster than in the economy mode. A special switch designed to implement a sport or economy mode is located, as a rule, next to the gear shift lever and can have various designations, such as POWER, S, SPORT, AUTO, A/T MODE, etc. Also widely used sports automatic transmissions, which have slightly different transmission control algorithms. In this case, switching between different operating modes can be done both by the selector and by using the corresponding function buttons, when the position of the automatic transmission lever remains unchanged.
Kickdown is a mode that allows the engine management system and automatic transmission to achieve high acceleration values, for example, to overtake. The automatic transmission enters this mode after sharply pressing the accelerator pedal, switching to one or two downshifts. The torque transmitted from the engine to the wheels will increase, while the speed range in the engine is such that its output is almost maximum. And when the engine reaches maximum speed, the machine switches to the next overdrive gear. If the accelerator pedal is released, the automatic transmission will return to normal operation. Sometimes when Overdrive is turned off, Kickdown mode is disabled. It is necessary to take into account the fact that on a slippery surface, with a forced downshift, slipping of the drive wheels and further skidding is inevitable.
Winter mode (Snowflake) - to activate this mode, there is a special button or switch with the following designations: Winter, W, Hold (or Snow). To avoid slipping of the drive wheels on a slippery road when starting off, the torque transmitted to the wheels from the engine is required to be minimal. This is done by starting the car from second or third gear - this risks overheating the automatic transmission, so driving constantly in this mode is contraindicated.
Emergency mode - this mode of operation of the automatic gearbox is activated in the event of malfunctions in the control system or transmission that can lead to breakdowns of the automatic transmission. The control unit includes a transmission protection program and this allows the car to get to the service station under its own power. As a rule, during emergency mode, shifts are prohibited and only one gear is operated. The number of such a gear usually corresponds to the gear in which the shift solenoids are in the off state. Also, when the emergency mode of the automatic transmission is triggered, locking of the torque converter is prohibited and the maximum pressure in the main line is set.
Adaptive automatic transmission mode (automatic transmission) | Automatic transmission adaptation.
Adaptive gearboxes owe their appearance to progress in the development of electronic automatic transmissions. Control algorithms are becoming more intelligent, hence new qualities appear in the same transmissions from a mechanical point of view. Now the on-board computer monitors the characteristics and driving style of the driver and, according to them, adjusts the operation of the automatic transmission and engine properly. When driving smoothly, the computer, by making appropriate adjustments, does not bring the engine to maximum power output, which significantly reduces fuel consumption. If the driver prefers a sharp, “impetuous” driving style accompanied by frequent squeezes of the accelerator pedal, the computer emphasizes frequent accelerations and intense driving speeds and puts the engine at maximum speed. In order to make the most dynamic acceleration, the control system makes switches to two, sometimes three steps lower. It is curious that taking into account the wear of the friction elements of an automatic gearbox is already included in the operating algorithm. Which has a beneficial effect not only on the comfort of driving such a car, but also increases its efficiency and service life.
Operating mode of automatic transmission AUTOSTICK (StepTronic, TipTronic)
This is an automatic transmission control system that provides both automatic and semi-automatic control modes (the first implemented by Porsche), here the shift command is given by the driver, and the control system ensures the quality of such shifts. Depending on the manufacturer, this mode may have different names: AUTOSTICK, STEPTRONIC, TIPTRONIC. It is only available on cars with an electronic automatic transmission control system, and even then not on all of them.
What is TipTronic (Video)
The gear shift knob on cars with this system has a special position in which the AUTOSTICK mode is activated. This mode has two non-locking positions, designated UP ,,+,, and DN ,,-,, , necessary for shifting to low or high gear. In this mode, the driver selects a gear manually; the selector lever is pushed in the direction ,,-,, or ,,+,, shifting gears up or down. When the engine speed drops to idle, the gear reduction is automatically carried out only in the canonical design. Some transmission manufacturers automatically upshift at maximum engine speed.
The mechanical part of such a box is indistinguishable from a regular automatic box; only the automatic control and selector lever are changed. Such automatic transmissions are characterized by a cutout for moving the selector lever in the form of the letter H, and the symbols ,,+,, and ,,-,, . However, this mode (AUTOSTICK) is more semi-automatic than manual, since the transmission computer controls the driver’s activities and will not allow him to select a gear that exceeds the permissible engine speed or will not allow him to move from top gear. The rest gives the impression of using a manual gearbox. If such a desire arises, you can easily return to the mode of a conventional automatic transmission by placing the speed mode shift knob in position D, so it is more likely to be driving an automatic transmission than “poking” the handle.
Powerful modifications of cars are equipped with sports automatic transmissions, which are equipped with a manual gear shift function. Moreover, such manual gear shifting can be done not only by moving the selector up and down, but also using small steering wheel paddles, pressing which allows you to lower or increase the gears. This is quite popular on sports cars and executive sedans that are equipped with powerful engines.
Switching the lever on the fly
It is possible, but not in all positions.
It is strictly forbidden to move the lever to the “P” and “R” positions when moving forward. The lever can only be moved to both positions when the machine is completely stopped. Violation of this rule may result in transmission failure. It is not recommended to move the lever to the “N” position while driving, since the connection between the wheels and the engine is lost and sudden braking can cause a skid. And you can easily transfer to all other positions. In some cases it is recommended to do this on purpose. So moving the lever from position “3” to position “2” will increase the efficiency of engine braking. Should the lever be moved to "N" when stopping? It makes sense only during long stops in traffic jams in hot weather, to reduce heat generation and prevent overheating of the oil in the box. In other cases, this is not necessary.
Using other driving modes on an automatic for beginners
Modes “1”, “2” and “3” are selected based on the vehicle’s driving conditions. Some are convenient for towing heavy loads, while others are suitable for descending steep mountains. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
The inclusion of the “third” mode tells us that the automatic transmission operates in three-speed mode. In this mode, the car can move at any speed, but not higher than third. Driving in mode “Three” allows you to accelerate to a maximum of 150 km/h.
It is preferable to drive in this gear when your car is heavily loaded, as well as when driving around the city.
The “second” driving mode is also limited at upper speeds. When driving in mode “2”, only the second and first speeds are used. There are cars that combine “second” speed with “winter” mode. In this case, the car starts and moves only in second gear.
In most cases, the “deuce” is used on slippery roads, off-road or when towing. The maximum speed at this value is limited to 90 km/h. It is also convenient to move in second gear using engine braking when you have to go down a steep slope or a long climb has begun.
The “first” selector mode has the highest gear ratio, which is suitable for driving at low speeds, namely only in first gear.
At this speed, you can safely drive on loose snow, sand or washed-out roads at a speed not exceeding 45 km/h. This mode is also convenient for getting out of snow, sand or mud if the car is stuck.
If this happens and the car is slipping, then you should not apply gas. Try to “rock” the car by moving forward at first speed and back alternately. You can try to find better grip by turning the steering wheel from side to side. Also monitor the speed and revolutions on the tachometer, they should not be high, and the numbers on the speedometer should not be raised more than 30 km/h.
How to tow a car with an automatic transmission
There is no single answer to the question of how to properly tow a car with an automatic transmission. Some cars have strict restrictions. Cars with a three-speed automatic transmission can be towed at a speed of 40 km/h for a distance of 25 km, and with a four-speed automatic transmission - at a speed of 72 km/h for a distance of up to 160 km.
- How to properly tow a car with a cable
In the case of a faulty transmission, a tow truck is preferable.
In an automatic transmission, lubrication is carried out forcibly, i.e. oil is supplied to each friction pair under pressure. If the transmission is faulty, then there is no confidence in the presence of lubricant. Carry out towing with the engine running and the lever in the “N” position.
What to look for when buying a contract automatic transmission
When purchasing a contract automatic transmission, you need to pay attention not only to compatibility in all respects, but also to its condition. If you personally pick up a unit from a warehouse, it is worth looking at the conditions in which it was stored before sale, and also inspecting the box itself:
- it is preferable to purchase automatic transmissions that are combined with the engine at the time of sale - this provides maximum protection from contamination;
- spare parts must be stored in a closed warehouse, protected from moisture, wind, and dust;
- if the automatic transmission has dents, traces of impacts, wires, rods and pipelines are not carefully disconnected, but are bitten off with wire cutters, the holes are not closed from dirt, it is better to refrain from purchasing such a unit;
- pay special attention to the dipstick - it should be intact, not broken, without a burning smell;
- If there are traces of rust on the drain plug, and there are metal filings or powder in the pan, the automatic transmission will not last long.
Contract automatic transmissions are removed from cars without mileage in Russia
And one more thing - be sure to ask the seller for a guarantee and carefully study the conditions for its provision.
What are the main advantages and disadvantages
A car with an automatic transmission is equipped with a passive safety system that does not allow the engine to be started in positions other than “P” and “N”. It also prevents spontaneous movement of the car when parked on an uneven surface, because You can remove the key from the ignition switch only in the RVD position “P”. The disadvantages include lower efficiency than that of manual transmissions, which increases fuel consumption.
But modern automatic transmissions in some driving modes make it possible to achieve higher efficiency compared to manual transmissions by maintaining optimal engine speeds and “intelligent” control of torque converter lock-up. Another drawback is the worse dynamic acceleration of the car. The difference is not so great and is insignificant for the majority of drivers. Also, a car with an automatic transmission cannot be started except with the help of the starter.
Advantages of contract automatic transmissions
Buying a new automatic transmission, especially an original one, will be expensive, so motorists are usually looking for an alternative, which can be:
- used automatic transmission purchased on the domestic secondary spare parts market;
- a restored automatic transmission, that is, a unit with previously existing defects, removed from a used car and undergone a major overhaul;
- contract automatic transmission from a foreign car dismantling site.
The best option in terms of price, quality and service life is a contract automatic transmission. It is superior in quality to cheap analogues from third-party manufacturers and used parts removed from cars that were used in Russia, and is more affordable than original new and even restored boxes. Compared to analogues, contract spare parts benefit because they are original. What sets them apart from used spare parts from the domestic market is their condition:
- donor cars were operated only abroad, using high-quality oil;
- Cars with low mileage usually end up in scrapyards: cars are replaced abroad much more often than in Russia.
Contract automatic transmissions are often called a “pig in a poke,” although this can most likely be attributed to reconditioned units:
- there is no guarantee that new and original parts were used during restoration;
- restoration requires highly qualified craftsmen;
- during restoration, only some of the parts are replaced, but many others remain, the service life of which is already running out, so that another repair may soon be needed;
- Many restored automatic transmissions are repaired in the second round.
Contract automatic transmissions are usually removed from cars long before they need major repairs. But this unit requires maintenance before installation on the car. All filters and rubber products in the automatic transmission should be changed and the oil should be changed.
How to find a fault
The operation of “electronic” automatic transmissions is controlled by an on-board computer, which is designed as a separate device or combined with a control unit.
It receives signals from various sensors located in and outside the automatic transmission. It processes information and, based on analysis, generates commands to actuators. This is how the automatic transmission is controlled. The computer also performs another function - monitoring and diagnosing faults. For all input signals there are acceptable limits for their change. If any signal goes beyond acceptable limits, the computer writes into memory a certain sequence of numbers - a code (Diagnostic Trouble Code - DTC) corresponding to this malfunction.
To read codes in the computer's memory, special diagnostic equipment is required - a scanner. The scanner allows you to read and erase codes, and you can also determine the readings of various sensors. The procedure for reading and identifying faults using codes is often called computer diagnostics.
In case of serious problems, the control system goes into automatic transmission protection mode. Emergency mode has different names: Limp In, Limp Home, Safe Mode. The operation algorithms of the control system in emergency mode are largely determined by the transmission model. In some cases, the system stops monitoring the quality of switchings, and they occur with “bumps”. In other cases, the transmission shifts into second or third gear and all gear changes are prohibited.
In some cars, emergency mode is accompanied by a flashing constant indication of one of the signals: “Hold”, “S”, “Check AT”, “OD OFF”. The signal can also be “Check Engine” or a symbol in the form of an engine outline. If none of these signals on the panel are illuminated, this does not mean that there are no fault codes in the computer's memory. But if there is a signal, then there are codes in the computer memory.
Emergency mode does not involve operating the machine; it only serves to get to the service center and fix the problem. If this is not done, it may turn out that due to a minor malfunction that was not corrected in time, the entire box fails.
How did I come to this question?
I can’t say that I haven’t tried to find out information about these automatic transmission modes from my friends. However, none of them was able to answer this seemingly simple question. And I would have remained in the dark if one day my friend and I had not decided to take a trip outside the city.
Each of us drove our own car. And since the comrade knew the road better, he moved first. Ahead of us was a section with constant ups and downs, on which I constantly slowed down. At first glance, my friend was driving the same way, but I noticed that his brake lights did not turn on, despite the fact that the car was clearly slowing down.
Fearing a breakdown, I called him and asked him to stop. At a nearby parking lot I asked him a question about the brake lights. And imagine my surprise when he replied that he did not slow down at all on the slopes.
What are adaptive transmissions
This term refers more to the control system, and not to the automatic transmission itself.
The development of “electronic” transmissions has led to the emergence of adaptive gearboxes. The developed control algorithms become more intelligent, which leads to the emergence of new characteristics. The on-board computer monitors the driver's driving style and adjusts accordingly. The operating algorithm takes into account the wear of friction control elements. This increases the resource and efficiency of the box.
What is Autostick or Tiptronic
This is an automatic transmission control system.
In addition to automatic, a semi-automatic control mode is provided, in which the driver gives the command to change gear, and the quality of these shifts is ensured by the control system. This mode has different names (Autostick, Tiptronic). In cars equipped with such a system, the lever has a special position in which the Autostick mode is activated. Regarding this position, there are two opposite, non-fixed positions of the automatic transmission lever. These positions are designated “+” (“Up”) and “-“ (“Dn”), respectively for shifting to a higher or lower gear.
Mode "D" or "Drive"
The fourth main mode on an automatic transmission is the “Drive” mode, the main driving mode intended for driving the car forward. Most often indicated by the “D” icon and is located immediately after the “Neutral” mode. It turns on before you start driving and turns off by moving the selector to the “Parking” mode after it ends.
It is worth saying that on many cars the “Drive” mode has special protection against spontaneous activation, so it can only be turned on after pressing the brake pedal and/or pressing a special button on the automatic transmission selector.