Basic principles of car alarm operation
The term “car alarm” correctly conveys the essence of the system. By and large, a car alarm can hardly be called a full-fledged security system that prevents burglary or theft. Simple car alarms block only the central locking of the car and allow you to open and close the doors remotely. More complex systems, in addition, block engine starting, operation of the fuel pump, and close individual hood and trunk locks. Separate sensors alert the owner of attempts to remove the car's wheels or steal the car using a tow truck.
The ease or difficulty of stealing a car depends on how the car alarm works. Qualified burglars have learned to select electronic codes for opening doors and removing locks using a computer code grabber. Therefore, all further improvements in car alarms are aimed at complicating such attempts at theft or searching for a stolen car using signals from autonomous GPS trackers.
The two main functions of the alarm are aimed at scaring away unskilled burglars (with sound and light signals) and warning the car owner about an attempt to break into or steal the car. When you put the car in “security mode” using the remote control key, the car alarm control unit, all sensors and locks are turned on. After this, the car alarm responds to all attempts to mechanically break locks or windows, remove wheels, or move the car manually or using a truck crane (tow truck).
The basic principle of operation of a car alarm is based on the activation of electronic sensors that send a signal about foreign influence on the car to the security system control unit. The control unit, in turn, turns on sound (siren), light (flashing headlights and hazard lights) alarm signals and sends a radio signal to the car owner's key fob. Engine and fuel pump blockers prevent the engine from starting unless the main alarm control unit is turned off.
Features of connecting an alarm system with auto start
Automatic engine start is a useful option, especially for regions with harsh climates. But before you begin installation, you need to know that there may be a conflict between the general alarm system and the autostart system. However, such situations arise only if the integration of these systems was not performed entirely correctly. If a connection is provided, bypassing the standard immobilizer, then the systems will not conflict. An important point is that when the engine starts, the anti-theft system is turned off and the car is protected only by mechanical locks. To further protect the car, microsensors are installed, the operating principle of which is based on the reaction of movement around the car. Depending on the sensor, the range may vary. Installing such elements, on the one hand, ensures safety, but on the other hand, it adds nervousness (depending on the specific element), since the alarm will react both to a dog running past and to passers-by.
When installing an alarm with auto-start, a conflict is possible between the auto-start system and the alarm itself, so experience in working with such devices is important
It is worth noting that installing an anti-theft system with auto start is a complex process. If you do not have sufficient experience in installing such devices, then it is better not to take on this matter. Situations are possible when the battery is low, the gas pedal is in the wrong position, or the gearbox is in gear, then the engine simply will not start. Despite the fact that a diagram and instructions are included with such an alarm, there may be some nuances during the installation process that only a knowledgeable person can figure out.
Devices providing security functions
The main devices that provide protective functions and control the car alarm are the electronic control unit and the owner's key fob.
Alarm control unit
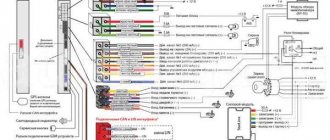
Device diagrams and electronic codes of the control unit are the most secret and protected part of the car alarm system by manufacturers. When installing an alarm system, it is recommended to camouflage the miniature control unit in an inconspicuous place in the cabin or engine compartment.
Despite the official approval in Russia of a single frequency for car alarms at 433.92 MHz, many accessory manufacturers produce systems operating at frequencies of 434.16, 371, 868 MHz. Car alarms for mobile communications are tuned to GSM frequencies (from 850 to 1900 MHz).
Information about operation on a single frequency or accurate data about the radio frequencies used makes the tasks of car thieves easier, so information from the Internet should not be trusted unconditionally.
An important secret part of the control unit was a device that encrypts electronic access codes. Having abandoned static (unchangeable) codes, almost all modern alarm systems have switched to the use of dynamic coding, in which the alarm control unit generates a new signal every time it is turned on.
Dialogue between the key fob and the alarm control unit
The next step to complicate the hacker's tasks was an interactive coding system. When there is radio contact between the remote control (owner's key fob) and the main control unit, each stage of friend-foe recognition and changes in alarm tasks is step-by-step encrypted with a separate dynamic code. The technical part of the control unit is a transmitting and receiving radio antenna, the design of which does not affect the security functions.
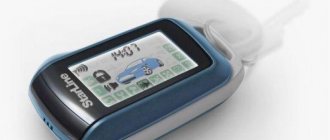
Remote control
The remote control of a modern car alarm contains a miniature radio signal transceiver from the main control unit and the second part of a dynamic coding generator in one housing. The main task of the remote control is to turn the alarm on and off inaccessible to others. The main improvements of this function are to reduce the sensing distance and make it more difficult to intercept the encoded signal.
Additional functions reflected on the key fob display can signal the activation of a specific sensor (shock, volume change, door opening) and the activation of the siren. Flashing characters on the remote control display are usually accompanied by a sound signal or vibration of the key fob.
Daily use
Using the alarm is very simple. You have a keychain , and optionally a tag . The key fob has buttons (“Remove”, “Put on”, “Service”) and a small screen. The mark is a small plastic thin rectangle, inside of which there is a circuit. If the alarm is configured correctly, the car will not start, or even open, if the alarm does not sense a mark within a radius of 5-10 meters from the car.
If the alarm is triggered, the key fob will begin to make sounds and vibrate, and additional information will appear on the screen.
Many Pandora alarms support GSM channel operation . This means that a SIM card is installed inside the alarm unit, and when an alarm is triggered, an automatic call will be made to the car owner’s phone. The GSM module also allows you to use the Pandora Online mobile application , in which you can monitor all the parameters of the car, disarm it or start it remotely, all without leaving the couch.
Signaling sensors and alarm devices
Having locked the car and put it in security mode, the alarm control unit cannot independently track the various methods of hacking attempts. For this purpose, the system is equipped with a number of sensors. From the initial use of simple shock and door opening sensors, modern car alarms, as they developed, came to the use of several more types of sensors.
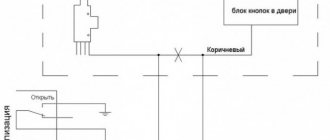
Door sensor
The main place for a car thief to enter a car is the car door. The door opening sensor was the first of the sensors used in car alarms. Most security systems are connected to the car's standard power supply using door lock limit switches or lighting microswitches. The same principle is used to trigger sensors that are installed on the hood, trunk lid or fifth door locks of hatchbacks and station wagons.
Shock sensors
The shock sensor is designed to prevent theft of wheels, exterior mirrors, attempts to break windows or mechanically break open a door. Various shock sensor designs use:
- closure of electrical contacts, triggered by shocks to the body, chassis, hood, or wheel rims of the vehicle;
- metal balls that roll when the car is hit or starts moving;
- piezo plates;
- counters of strength and number of alarm impulses.
Shock sensor
The complexity of shock sensors is due to the fact that this sensor is the main cause of false alarms in car alarms. The system, configured to be excessively sensitive, reacts to strong sound waves (thunder, noise from the engine of a passing truck), touching the body by yard animals, and falling snow.
Sensors for car windows have become varieties of the shock sensor - a pressure sensor on the glass and an air pressure meter. The security benefits of these sensors, which operate on the basis of a microphone (reacts to the sound of breaking glass) or on the barometer principle, are questionable. A thief or hooligan who decides to break glass is determined to act quickly and is ready to set off the alarm.
Volume sensor
The sensor, which records changes in the volume of the cabin, is built on constant scanning of the internal space with ultrasonic or microwave devices consisting of a transmitter and receiver. A number of experts consider such sensors to be useless. Manufacturers of car alarms do not comment on the difficult-to-explain point - how an attacker can get into the car, bypassing numerous other types of sensors. The grabber code, which disables the control unit, automatically turns off the signals from the volume sensors. Another disadvantage of most sensors of this type is false alarms if you leave bulky items in the cabin.
Tilt sensor
One of the most useful sensors, designed to prevent wheel theft or theft using a tow truck or truck crane. These actions by attackers require a relatively long time and are difficult to carry out when alarms are turned on. A reliable sensor design is considered to be a cylinder partially filled with mercury, which, when tilted, closes two electrical contacts connected to the car alarm control unit.
Tilt sensor circuit
Expensive alarm systems are equipped with several tilt sensors that operate in horizontal and vertical positions. Such a system responds to all ways of moving the machine. Correctly setting the sensors allows the alarm not to react to the natural movements of the car (swaying from strong winds, loss of pressure in one of the tires).
Motion Detector
High-end alarms use a motion detector consisting of a radar transmitter and receiver. An ultrasonic sensor is a type of such sensor. The device is capable of tracking suspicious movements of strangers near the car at a distance of two to five meters. Without turning on alarm signals up to a certain distance, the motion detector sends a signal to the remote control of the car owner, making it possible to call the police or scare away intruders.
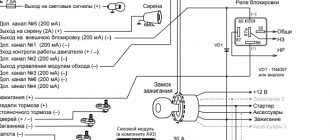
Alarm devices
At the command of the sensors, the control unit of most alarm systems turns on sound and light signals that should scare away intruders. Light signaling uses headlights, flashing brake lights and turn signals, to which a special relay gives an unnatural rhythm.
To sound a sound signal in a hard-to-reach place under the hood, a powerful siren is installed. Self-powered sirens (with their own batteries) that operate when the car battery is disconnected are more effective. Loudspeakers that use various sound modulations and voice announcements can be classified as devices that make signaling more complex (and more expensive). The originality of the sound signal does not in any way affect its basic functions.
Price
At the time of writing and publication of the article (spring 2014), the cost of car alarms is $30-$400. The price, as mentioned above, depends on the configuration, technical characteristics, functionality and manufacturer of the device.
As for advice on purchasing an alarm system, I would like to note that they do not save on such a purchase. If you are very financially limited, then try to buy a system in the mid-price range. And if money is not a problem for you, then the advice is obvious.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel