The brake disc is no less important in the braking system of a car than the pads. And if the latter are replaced when worn out, then almost no attention is paid to the former. But the efficiency of the system also depends on them. Let's find out how to determine the wear of brake discs so that they can be replaced on time.
Most of the discs that lie on the shelves of car dealerships are made of cast iron. The popularity of such products lies in their low cost and good friction characteristics. But the problem is that in the process of reducing the speed, the cast iron alloy product heats up. This leads to deformation, warping, and uneven abrasion. To reduce wear and tear from heat, manufacturers began to produce products with ventilation. Grooves are also cut on the surface of the disk. This allows you to increase the life of the disk.
What affects wear?
Each manufacturer prescribes brake disc wear standards. These parameters are obtained based on engine power, vehicle weight and other factors. But it is very difficult to calculate the mileage after which you will need to change the discs. Wear is influenced by various factors that cannot be taken into account.
First of all, it's your driving style. If the car owner prefers to drive more extreme, where sharp accelerations are replaced by equally sharp braking, then the service life of the disc is significantly reduced.
The conditions in which the vehicle is used also affect wear and tear. If you constantly move through puddles in winter, the moisture that gets onto the heated disk can cause deformation and uneven wear.
Mechanical factors also affect the service life. The material from which the brake disc is made is important here, as well as the quality of the pads. Often, discs are made from cast iron and its alloys - the material wears out more often than ceramics. The use of low-quality pads (for example, with asbestos) also leads to uneven wear.
Suspension and wheels
Approximately the same result is obtained by wear of some components of the suspension.
Silent blocks, ball joints, and support bearings that have exhausted their service life will cause the wheel to develop lateral play, which will be the source of the problem.
It should be noted here that an additional sign of wear on the suspension components is knocking noises when driving over uneven surfaces.
It’s not difficult to check the condition of the suspension; just swing the levers with a mount, and if the silent blocks and ball joint are worn out, this will be immediately noticeable during the check. But before that, check whether the disk is screwed on well; loosening at least one of the bolts can lead to vibration of the entire car.
Although rare, vibration is caused by the hub and its bearing. As a result of severe wear of the bearing seat, play appears in this unit, which will be manifested by impacts on the steering wheel.
The wheels may also hit the steering wheel when braking, so you need to check:
- Damage or imbalance of the disk;
- Loose bolts (usually happens when a car is “re-shoeed.” The bolts are simply forgotten to be tightened);
- Tire defects;
- Violation of camber/toe angles.
As you can see, there are two main causes of the problem: play in the chassis and damage to the brake system elements.
That is, the brake discs, due to overheating, the suspension and steering mechanism have not been serviced for a long time, new wheels are installed on the car, which have not been balanced and as a result the driver receives quite unpleasant and dangerous consequences.
Symptoms of wear
Many people do not know how to determine the wear of brake discs, but it is very simple. There are several signs that it is time to change the disk.
The first indicator is vibrations, grinding noises, and extraneous sounds during the process of reducing speed. The second symptom is the car skidding due to the brake system being blocked. After the driver presses the pedal, the brakes may jam.
If one or more of the signs listed above appears, then it is worth moving on to visual diagnostics. Carefully inspect the working surface of the disk. There should be no beads, cracks or other damage on it.
Groove
During operation, the brake disc can become deformed; cracks, irregularities and other defects may appear on it. Their presence is manifested by vibration when the brake pedal is pressed. If the thickness of the disk is sufficient, then in this case it can be ground (grinded). Otherwise you will have to buy and install a new one.
High-quality grooving can be done using a special machine, which is installed in place of the caliper. The disc itself is not removed from the wheel.
Some craftsmen sharpen with a grinder, but in this case it is difficult to vouch for the quality. It is also impossible to guarantee accuracy when using a lathe, when the groove is made relative to its bobbin, and not to the wheel hub.
After grinding, the brake pads should be replaced, otherwise vibrations and beatings during braking will appear again.
How to find out the abrasion thickness?
In order to find out the permissible maximum thickness of the brake disc, you should look at the end of the product. There are two meanings to this part. This is the original thickness, as well as the minimum allowable. The numbers may vary depending on the car and wheel manufacturer. How to determine the degree of wear of brake discs? It is enough to simply measure with a caliper and compare the numbers with acceptable standards. This is how you determine whether the product can still be used or not. The disc should also be changed if it has different thicknesses at different points.
This indicates uneven wear.
Where to look for problems?
It is noteworthy that it can hit the steering wheel when braking on any car - VAZ-2108, Priora, Kalina, Ford Focus 2, Mitsubishi Lancer 9 and others.
No matter what vehicle this phenomenon occurs on, the malfunction must be eliminated urgently, and its sources must be looked for in:
Often car owners have to completely go through the above mentioned elements of the car in order to fix the problem.
The appearance of beating in the steering wheel during braking can occur for various reasons, for example, wear or damage to the components of the chassis, for example, a bent disk.
Fix defects or replace?
When the measurements are completed and the exact diagnosis is clear, the car owner is faced with the question of whether to restore the old product or purchase a new one. It should be remembered that the disc can be sharpened only if there is residual thickness (from 22 millimeters). This is true for ventilated discs. Many experts recommend replacing only. However, if the price of a new disk is too high, and there is a spare thickness, you can try to restore it.
Small beads and grooves can be removed by grooving using special equipment. Some even do the grooving with a file, but this is unreliable. The essence of the operation is that a thin layer is removed from each side of the disc. Then the product receives a perfectly flat surface.
Do not forget that the more layers are removed during grinding, the shorter the service life of the restored brake disc will become. Sometimes you need to remove two or even three layers. It is not recommended to install used or refurbished drives. It is unknown where and how they were used. However, knowing how to determine the wear of brake discs, you can measure and find out whether they are acceptable for use.
Before boring the disc, the cause that caused the deformation or beads on the surface should be resolved. Otherwise there is no point in restoration. Among the causes of uneven wear, brake pads are in first place. If they are of poor quality or installed incorrectly, they can easily damage the surface of the disk.
What should be the thickness of brake pads?
A clear sign indicating that the pads are running out of service life is the appearance of a characteristic whistle when the car is braking - every time you press the pedal you will hear an unpleasant noise, similar to glass rubbing against metal.
If such a symptom appears, it is recommended to diagnose the brake system as soon as possible - remember, operating a car with faulty brakes negatively affects the safety of the driver and passengers.
| Characteristic | Wheel Bridge | Minimum thickness, mm |
| Disc diameter, mm | Front | 256 |
| Rear | 238 | |
| Structure thickness, mm | Front | 12 |
| Rear | 12 | |
| Possible runout, mm | Front | 0,07 |
| Rear | 0,07 | |
| Thickness of the brake lining together with the pad body, mm | Front | 18 |
| Rear | 18 | |
| Minimum permissible thickness of the lining together with the block body, mm | Front | 6 |
| Rear | 6 | |
| Minimum permissible disk thickness, mm | Front | 10.6 |
| Rear | 10.6 |
It is also important to remember that these indicators may differ if the car has a power unit with a capacity of more than 125 horsepower or a total volume of working chambers of 2.0 liters or more. In this case, it is necessary to check the thickness level of the system components after first reading the data from the vehicle’s service book.
Note! On average, front and rear brake pads, regardless of the design of the system, wear out at different rates. This is explained by the difference in the applied dynamic force on the braking system - the front axle of the car experiences more pressure during a forced reduction in speed.
When to change pads?
We know how to determine the permissible wear of brake discs. But it’s worth paying attention to the pads, since these elements work in pairs and together affect braking efficiency.
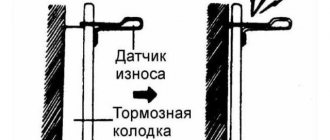
One of the signs of pad wear is a squeaking sound when the speed is reduced. The sound is produced by a special wear sensor. This is a special plate. When the friction layer of the pad is worn away, the plate touches the disc and causes the sensor to operate.
If the car does not have a wear sensor, then the pads should be replaced when the thickness of the friction layer is one and a half millimeters.
You can determine that the pads are worn out by the operation of the brake system. Brakes that are too weak or too harsh can indicate wear. In the first case, the braking is not intense, although the pedal is pressed quite deeply. In the second, the wheels are blocked due to the lack of friction lining.
How to determine the wear of brake discs and pads? This can be determined by vibrations during braking, as well as by visual inspection and a measuring tool. There are no other options.
How to replace a brake disc
You can replace the brake discs yourself. Of course, this will require certain knowledge, skills and tools. As already mentioned, the ideal option is to buy new discs and pads from a reputable manufacturer and check them for certificates and markings. Spare parts must be suitable for a specific car brand.
The installation algorithm is as follows:
- First, loosen the nuts on the wheel and then dismantle it. Of course, you can’t do without removing the wheel, since replacing disks requires free access to them.
- Then remove the caliper. To do this, use a screwdriver to unscrew the bolts that are located on the inside of the disk.
- The caliper is removed carefully. It may “stick”, so you may have to lightly tap it with a hammer. It is important not to touch the connection between the caliper and the brake pipe; it is best to tie the caliper to the car body. The fact is that there is pressure in this system, and a violation of the seal can lead to a leak of brake fluid - you will have to “bleed” it.
- Next, the old pads and plates are dismantled. In some cases, you will also have to remove the caliper seat mount. To do this, you need to unscrew the screws with a screwdriver.
We recommend
“How to improve brakes (vacuum brake from Priora)” Read more
- Then remove the brake disc itself. It happens that the disk and hub are connected by a castle nut, which must be unscrewed to remove the disk. But what often happens is that the hub and the disk “stick” to each other (high temperatures in the wheel area contribute to this). To fix this problem, you need to lightly tap the disc with a hammer through a wooden block.
- At the end of dismantling, check the hub mount; it must be intact.
Now you can install a new brake disc:
- if the installed disk needs to be cleaned of rust or any plaque, use only special products;
- then wipe the disc with a dry cloth;
- after these manipulations, carefully secure it to the hub;
- Next, install and secure the caliper seat;
- Untie the previously attached caliper, mount the pads to it (they must be released and installed on the brake disc);
- secure the caliper with bolts from the inside of the disc;
- then install the wheel, remove the car from the jack;
- Finally you need to tighten the wheel nuts.
This will complete the replacement of disks. Of course, before you start using the car, you need to check that everything is functioning properly. This is done in a place where there are no obstacles to the movement of the car, and it is important to start slowly.
To check the functionality of the brake system, you need to gently press the brake. The car should stop smoothly: jerking, pedal failure, vibration, heating of the discs, their beating - a bad signal indicating some kind of malfunction.
I would like to advise beginners to still seek help from car service specialists. After all, checking and replacing brake discs in general is not so easy; experience and dexterity are required. And the well-functioning operation of the brake system is the key to safety on the road.
We determine the mileage based on the condition of the disks
Today, cars are sold by so-called resellers, who often deceive buyers. Cars come with low mileage. Many of them only look normal outwardly, but technically they are in a deplorable state. Resellers often change the pads, but simply forget about the discs. And this is in vain - the average mileage of a car can be determined by the condition of the disk.
On average, brake discs are changed every 180-200 thousand kilometers. But this is not true for all cars. Also, different drivers drive differently. Some people manage to drive 150 thousand kilometers until they are completely worn out, and some even 250. But if the mileage of a car is 70 thousand, and the total thickness of the disk is 20 millimeters, this car has probably traveled at least two hundred. It is worth refusing to purchase such a copy.
Here's how to determine mileage based on brake disc wear. But disks can be replaced more than once. And the mileage can be twisted. Therefore, the condition of the discs is just one of a number of signs that you need to pay attention to when purchasing.
Steering wheel shakes when braking at high speed, troubleshooting
Many car enthusiasts, when operating their cars when braking, especially at high speeds over 80 km/h, begin to hit the steering wheel. But it happens that the driver feels vibration in his hands even when driving at low speeds.
This problem is quite dangerous, because during braking the driver loses control of the car due to beating in the steering wheel; in some cases, the vibration is so strong that it practically knocks the steering wheel out of his hands.
Disc brakes
Disc brakes are more modern and efficient, but require more frequent brake pad replacement.
Signs of Brake Pad Wear
A lot can be said about the importance of good functioning of the braking system. There are many parts in the system that can fail: vacuum booster, pipelines and hoses, brake master cylinder and much more.
All this requires attention and timely maintenance, but for now we will talk exclusively about the wear and tear of the main consumable components.
Vibration during hard braking. Worn brake pads show that the wear process is uneven. A worn brake pad makes noise, and when braking sharply, noticeable vibrations spread throughout the body.
Of course, similar behavior of the brake system can also occur when the brake disc wears out, so it is important to diagnose all elements. Brake disc wear is described in more detail below.
Inadequate vehicle response when braking. Newly installed brake pads require a little grinding in to ensure they are fully seated on the brake rotors and provide maximum braking performance. With new pads, the braking process is predictable, but with worn ones, braking may be weak or excessively sharp. In the first case, there is not enough braking force due to the pads being too thin; in the second, the pads are completely worn out, so the brake disc and caliper come into contact - this leads to metal-on-metal friction.
Metal shavings in brake dust on wheel rims. The formation of dust from the pads on the wheel cap is normal if there are no metallic impurities in the dust. But small inclusions of metal shavings are a clear sign that it is time to change the pads, as they scratch the disc. Please note that this brake wear monitoring method is not suitable for ventilated brakes or when using alloy wheels.
Determining the level of wear:
To accurately determine wear, it is best to use a visual inspection. This is long and requires removing all the wheels, but it gives a clear answer to the question: is it time to change the brake pads or not. Inspection can be done through a special hole in the caliper. Modern cars have special sensors that will notify the driver in time about the upcoming change of pads. Usually the warning light goes off a little early. Simple and effective mechanical wear indicators can also be used. It is optimal to think about changing brake pads when their thickness is halved or reaches the level recommended by the manufacturer.
Signs of brake disc wear
The brake pad is the main consumable in disc brake systems, but this does not mean that the brake disc will last forever. It also wears off over time, although this process can take many years.
You can determine brake disc wear by the behavior of the car during braking:
- Vibrations on the steering wheel and car body;
- Grinding noise from the front, in the area of the front wheels;
- Jerks;
- Extraneous noise.
And also upon visual inspection:
- Curvature of the brake disc;
- The presence of noticeable recesses;
- Presence of cracks.
The reasons for brake disc wear can be very different. The most common thing is a long service life, when the disk wears out evenly and gradually begins to crumble and collapse at the edges due to the very small residual thickness. The disc may wear unevenly if the brake pads are not replaced in time. Then the metal elements of the pad and caliper begin to touch during braking and leave deep grooves on the disc.
The disc may become warped due to improper use of the vehicle. The most common reason is overheating of the brake disc as a result of long and intense braking. A striking example is the long descents that novice drivers drive on the brakes and allow the discs to overheat.
Determining the level of wear:
- Remove the wheel;
- We measure the thickness of the disk.
The brake disc wear is allowed to be no more than 2-3 mm compared to a new one. For the brake systems of different cars, the optimal thickness of a new disc is different. Specific values of permissible wear are indicated on the disc itself in numbers and can be duplicated by special grooves that clearly show the wear limit.
Additional questions and answers
What is the service life of brake pads and brake discs?
There are many factors that influence the average lifespan of your brake components. These include pad type, rotor type, your personal driving style and maintenance. According to most brake pad companies and qualified mechanics, brake pads can last between 30,000 and 120,000 kilometers. At the same time, the front ones wear out about 3 times faster than the rear ones. On average, it is recommended to change pads on domestic cars approximately every 10,000 km, and on foreign cars - every 20,000 km. Actual service life can vary greatly, the main thing is to prosodicly check them and their thickness.
Left - new pads, right - old
The service life of brake discs is quite long - 3-4 times longer than that of pads. But again, it all depends on many other factors, such as how you maintain your braking system and how you drive your car. On average, this is more than 100,000 km. Here you also need to rely on the thickness of the rotors when taking measurements.
How much do new brake discs cost?
The average cost of new brake discs varies from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles each. Some rotors with the best characteristics can cost from 7000+ rubles each. Additionally, prices vary greatly depending on the type, brand, and quality.
New brake discs
When it comes to replacing brake rotors, some people often wonder whether they should buy new or remanufactured parts. Each of these types has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, aftermarket parts tend to be cheaper and available in a wide range of options, while new brake rotors are easier to select and offer greater quality assurance.
Can I drive with worn rims?
Brake rotors play an important role in allowing your car to stop while it is in motion. If the rotors are not working properly, you may not be able to stop the machine properly in an emergency. This can lead to many dangers if you need to stop to avoid pedestrians, bicycles, car accidents or other traffic situations. So when you find that your brakes aren't performing as well as they should, you need to take your car to a mechanic as soon as possible to have the thickness of your rotors checked.
Basic faults
The mass of a vehicle carrying passengers and cargo, friction force, high speeds are the operating torques affecting the brake discs. Maximum wear, within the tolerances established by the manufacturer, are the main reasons for their failure.
They represent the “erasure” of the disk surface that occurs during operation. There are two types of wear and tear:
- Uniform – characterizes the correct, “careful” driving style of the driver, during which the disc is ground equally along the entire rim.
- Uneven - has scratches, indentations that exceed tolerances and roughness, the reason is improper installation of the pads or aggressive driving with sudden, extreme braking.
The last type of wear is the most undesirable for the further operation of the car. In this case, the braking coefficient of the disk has the lowest value. During rotation, it can “catch” the brake pads, which causes their destruction and overheating, spontaneous braking of the car, and further destruction of the hub.
Uncertified, low-quality brake pads installed on a vehicle, their improper assembly and further vibration can increase the rate of wear.
Other reasons for replacing pads
In addition to situations with critical wear, it is necessary to change brake pads in the following cases:
- the thickness of the friction material is more than 5 mm, but the lining itself has begun to peel off from the steel base;
- cracks and chips appeared on the surface, the material began to crumble;
- stains of oil or brake fluid that reduce friction properties were found on the parts;
- when the brake drum or disc is replaced.
Another reason for replacement is due to the abundance of low-quality fakes on the automotive spare parts market. New pads purchased from an unreliable retail outlet begin to squeak or squeak terribly after 1-2 thousand km, although the working part is still far from completely worn out. The culprit is the material of the part, whose hardness is comparable to metal, causing the surface to “slick” and create a creaking sound. If the elements made from unknown materials are not replaced, then the production on the brake discs will increase sharply.
Many modern cars are equipped with special sensors that detect a decrease in the thickness of the friction layer and send a signal to the driver when it reaches a critical level. This is also a reason to remove parts with worn linings and install new ones.
True, the sensors often become clogged with dirt and lose their functionality, so it wouldn’t hurt for the car owner to check the condition of the brakes himself.
This is interesting: Why is there black smoke coming from the exhaust pipe?