The design of the injection 8-valve VAZ-2114 engine
Many motorists, especially beginners who have just purchased a VAZ-2114, have wondered how the 8-valve injection engine that is installed on this car works. This article will discuss the design of the motor, its main characteristics, as well as dismantling and repair features. This information will be very useful for beginners and those who do not know how the main power unit works.
Video about the VAZ-2114 engine
Video review of the VAZ-2114 engine operation, features and characteristics.
What gasoline to use
This question is one of the most pressing for domestic car enthusiasts, because, on the one hand, gasoline prices are constantly rising, and you want to save money. But, on the other hand, the quality of fuel at most gas stations leaves much to be desired, and you don’t want to fill your car with anything.
That is why you should adhere to the basic principle - the 14th gasoline in the passport indicates exactly 95th gasoline, which means that this is what you need to fill it with.
Gasoline for VAZ 2114
As for bad fuel, if possible, you should choose from the nearest gas stations those that have the highest quality gasoline (based on the behavior of the car after refueling), and then refuel only at these stations.
True, you can also notice that many owners of the 2114 fill it exclusively with 92-grade gasoline and, according to them, do not see much of a difference in the operation of the car and in the rate of wear of the components of the gasoline system. Whether to follow these tips or use exclusively suitable fuel is up to everyone to decide for themselves.
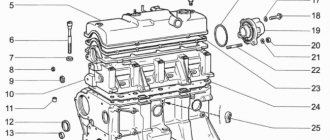
Engine diagram and structure
Before we begin to consider the issue of the engine design and description of the characteristics, it is necessary to consider the design of the components and parts that are located directly in the main power unit and outside.
Diagram and design of the Samara-2 engine
Also, it’s worth looking at a cross-section of the VAZ-2114 engine:
Cross section of the Samara engine
Characteristics of an 8-valve engine
Many motorists remember how at the end of the 90s of the 20th century and the beginning of the 2000s, the VAZ 2108-09, which was also called “Samara,” was popular on the roads of the CIS. These cars became legendary in that era. Due to the high popularity, the AvtoVAZ plant decided to resume production of these models with some modifications.
VAZ-2114 engine under the hood
Firstly, the VAZ-2114 received a modified engine . In essence, this is an injection version of the Samara. Although it received some features from modern engines. If we consider in more detail, the Samara-2 engine (this is the type installed on the VAZ-2114) is a mixture of two engine options into one: from the VAZ 2108 and VAZ 2110.
Many motorists liked the Samara-2 power unit and fell in love with it. The main indicator was ease of repair and inexpensive spare parts. Thus, the 8-valve engine has become the standard for “price-quality” indicator.
When the basic information has been reviewed, you can proceed directly to considering the characteristics of the motor.
Table of main characteristics of the Samara-2 engine 8 valves:
| Name | Characteristic |
| engine's type | In-line, longitudinal type, 4-cylinder, 8-valves |
| Fuel type | Gasoline (installation of gas equipment is possible) |
| Cylinder arrangement | 1-4-3-2 |
| Injection system | Distribution, injection type |
| Control | Bosch, "January" or GM |
| Camshaft location | Upper |
| Drive unit | Front |
| Piston and ring diameter | 82 – nominal (tolerances by group: A – 82.00-82.01, B – 82.01-82.02, C – 82.02-82.03, D – 82.03-82.04, E – 82.04-82.05) |
| Crankshaft | Cast iron |
| Cylinder block | Cast iron |
| Timing system | Belt and roller |
Disassembly and repair: basic facts
Let's consider this paragraph of the article as reference information, because if we talk about engine repair, then each individual component and unit is repaired separately. When operating the power unit, it may be necessary to dismantle it. In this case, you can consider replacing the power unit from a foreign car.
Therefore, let’s consider the main operations aimed at removing the engine from the car:
- At the preliminary disassembly stage, it is necessary to drain the oil from the engine, as well as the coolant from the system.
- Another point that should not be missed is turning off the power to the car. This is necessary in order not to short-circuit the system.
- Disconnect the fuel system.
- We dismantle the components that supply air to the engine.
- Disconnect the throttle, as well as all remaining air pipes and cooling system pipes.
- We dismantle the injection system and receiver.
- We remove the ignition system completely.
- Let's disassemble the gas distribution mechanism.
- We remove the thermostat and pump.
- Remove the ignition module.
- Now, you can dismantle the collector.
- Remove the pan, oil filter and pump.
- Disconnect the gearbox and remove the clutch. The gearbox can also be removed for convenience.
- Remove the cylinder head.
- We dismantle the power unit.
- We carry out final disassembly.
A major overhaul of the power unit will require more in-depth knowledge of the design and operating principle of the engine, but if desired, every motorist is able to understand this and carry out these operations with his own hands.
It is worth noting that when diagnosing malfunctions, it is worth carefully and carefully inspecting each part for defects.
Frequent internal combustion engine malfunctions
Let us immediately note that the design of the VAZ 2114 and the engines in particular on this model may have a number of differences. Early versions are simpler, while in the latest modifications the unit received more complex electronic equipment, ECM sensors, etc.
One way or another, most of the problems that the 2114 engine can present:
• the “check” light is on, the speed fluctuates; • the motor does not develop power; • the power unit stalls, stalls or does not start; • extraneous noises and knocks appeared in the engine;
As with any other fuel-injected internal combustion engine, it is necessary to perform engine diagnostics, since there are many possible reasons why failures occur.
For example, the failure of one of the ECM sensors may result in the ECU receiving incorrect data and the controller going into emergency mode. You also need to pay attention to timing, valve adjustment, etc.
If we consider the VAZ 2114 engine itself, its repair is not very different from the repair of the VAZ 2108 engine. In turn, this allows experienced car owners to repair the specified internal combustion engine with their own hands.
VAZ-2114 engine diagram, 8-valve injector
To independently repair a VAZ-2114 with an 8-valve injector, you need to know the structure and operating principle of the engine. With this knowledge, you can determine the cause of the malfunction without resorting to outside help. VAZ series engines are equipped with a distributed fuel injection system, which improves driving performance and typically reduces the percentage of toxins in exhaust gases. There are two types of fuel injection systems: with and without feedback, they may differ in details. Everything depends on the export or import of products. Feedback injection is usually used in car models supplied abroad and is equipped with a neutralizer. The open-loop system (sold domestically) contains a CO potentiometer that regulates the exhaust gases.
A little about the oil pressure sensor
Oil is a key element in engine operation. It significantly reduces friction, which prolongs the life of many powertrain mechanisms. However, to obtain such properties, high fluid pressure is required. The oil pressure sensor will notify you if it drops, which will protect the engine from damage and save a lot of money.
You will not find any signs of malfunction here; if the pressure lamp lights up, immediately turn off the engine. Personally, because of this device, I ruined quite a few engines of the old Zhiguli 2105. Either the oil pump failed, or the oil was of poor quality, and sometimes it simply leaked out of the oil seal. If I had a working sensor, this could have been avoided. However, it happens that everything is fine with the engine, but the electronics are acting up, then it is better to make sure of this for sure. Of course, you are interested in how to check a vital device for a car? Yes, it’s very simple, if you don’t have a new copy, then run to your neighbor for a pressure gauge. Insert the end of the meter into the place where the hole for the sensor is located and look at its readings. We carry out the procedure with the engine running. The minimum mark for a working motor is 0.65 kgf/cm2, if so, then breathe a sigh of relief, your measuring device has simply failed.
Sensors
The temperature sensor is a small thermostat in the cylinder head pipe; it is used to control the temperature of the antifreeze.
The knock sensor is screwed into the cylinder block and detects knocking phenomena occurring in the engine. If the slightest vibration occurs in the motor, the impulse is transmitted to it. After this, based on a signal emanating from the control unit, the ignition is adjusted, during which unwanted fuel flashes that lead to detonation are eliminated.
The oxygen level sensor is installed in a closed-loop system. Its mounting location is located in front of the muffler. The normal temperature reaches 360 degrees, and a special heating element is provided to actively warm up the motor.
The air flow sensor is mounted near the air filter. It consists of three elements, one of them determines the ambient temperature, while the rest are needed to maintain a certain temperature level exceeding that of the first. The air flow cools all heating elements, and the ECU uses this information to determine air flow and set the duration of opening or closing of the injectors.
The location of the CO potentiometer is the engine compartment (the wall of the air supply box). This element sends a signal to the computer used to adjust the desired proportion of air and fuel.
The vehicle speed sensor is located near the engine oil level dipstick. Through it, a signal is sent to the ECU similar to the speed of the drive wheels.
Synchronization sensor - located on the oil pump cover near the generator drive pulley. Based on the information coming from it, the control unit calculates the crankshaft speed and then sends a characteristic signal to the injectors.
How does this part work?
The barrel-shaped catalyst body is made of stainless, heat-resistant steel, thanks to which it can withstand high temperatures (500–800 degrees). From the front side it includes four exhaust manifold pipes, through which fuel combustion products enter the exhaust system.
A pipe is welded on the rear side, to which the exhaust pipe (muffler pipe) is connected. The catalyst itself is located inside the housing; it is made of ceramic and is pierced with through holes running along it, through which the exhaust passes.
Why do you need a catalyst?
From the front and back, the removed catalytic element looks like a fine-mesh honeycomb, the holes in which can be seen if you look through it into the light, but this only works with new catalysts.
In addition, holes are made in the front and rear parts of the body for oxygen sensors, which are also called lambda probes. They evaluate the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases before and after the catalyst, then transmit the data to the electronic control unit (ECU, controller), which, based on this information, adjusts the amount of fuel supplied to the cylinders.
Supply system
The air filter is located in the front part of the engine and is equipped with rubber retaining elements. If it becomes necessary to replace them, the corrugation is located on the same parallel with the center line of the car. The main function of the throttle pipe is determined by dosing the air flow entering the intake pipe. The air entering the engine is adjusted thanks to the throttle valve, which is connected to the accelerator pedal. The throttle pipe consists of two components: the throttle position sensor and the idle speed control.
Removing the carburetor and intake manifold
You need to have the following tool on hand:
- Flathead and Phillips screwdrivers.
- 8" socket or tubular wrench.
- Open-end or socket wrench set to “13”.
- Ratchet (if necessary).
To remove the VAZ 2109 manifold (carburetor), you must first dismantle the injection system. The disassembly process looks like this:
Disconnect the hose that supplies antifreeze from the cooling system to the carburetor starter
To do this, loosen the clamps and carefully drain the liquid. Work must be carried out on a cold engine. Remove the exhaust pipe
To do this, unbend the fixing plate and unscrew the nuts with a “13” wrench. Using the same wrench, unscrew the nuts that secure the pipe to the bracket. Remove the throttle valve drive cable mounting bracket. Remove the spring and loosen the nut, disengaging the cable. Disconnect the idle air solenoid valve. Disconnect the vacuum tube and carburetor heating hoses. Remove the crankcase ventilation pipe. Unscrew all four nuts that secure the carburetor body to the intake manifold. Carefully lift the carburetor body, being careful not to damage the studs.
The next step is to dismantle the intake manifold. You will need the same tools as in the previous step. The procedure consists of the following steps:
- Unscrew the two fastening nuts and bend the platform under the carburetor back.
- Remove the hoses that connect to the intake manifold.
- Unscrew all the nuts (there are 7 of them) that secure the manifold.
- Remove the intake manifold of the VAZ 2109, slightly rocking it to the sides.
Fuel system
It consists of many components: a fuel pump, a fuel pressure regulator, a fuel filter, a fuel line, injectors and a ramp, thanks to which fuel enters the engine. The ramp is a strip on which the injectors and fuel pressure regulator are located, and is attached with two bolts to the intake pipe. The injectors are mounted on the fuel rail, its function is to supply fuel to the engine. An injector is an electromagnetic valve that opens and sprays fuel under pressure in a thin stream after it receives a corresponding impulse from the ECU. Upon contact with the heaters, the fuel evaporates and is fed through the needle pin into the combustion chamber.
Source
How does a catalyst differ from a flame arrester?
The task of the flame arrester is to reduce the exhaust volume and burn out excess fuel that is not burned in the cylinder, so it cannot reduce toxicity. If you install it instead of a catalytic converter, then not only will the exhaust toxicity increase, but the engine will also not work properly, because the ECU will reduce the fuel supply so that the amount of oxygen at the output of the device approaches the norm.
When the catalyst on a VAZ 2114 car is removed to install a flame arrester, you have to either use “decoys” that simulate the operation of lambda probes, or change the firmware of the control unit so that it does not take into account the readings of these sensors.
VAZ 2114 engine - possible configuration options
The 2111 engine is conventionally considered “native” for the VAZ 2114, since it has been installed for 4 years since the creation of the car model. This version of the internal combustion engine has distributed injection and 4 valves and a volume of 1.5 liters. A tuned version of 21114 with a volume of 1.6 liters was also used by increasing the height of the cylinder block.
In 2007, the engines were “pulled up” structurally to Euro-4 standards; the “four” was equipped with a 1.6 liter modification 11183 with 8 valves, an electronic gas pedal and an electric throttle, and a polymer receiver instead of aluminum.
Since 2009, the VAZ 2114 model has been modernized by its subsidiary Super-Avto CJSC. A 16-valve internal combustion engine 21124 with a volume of 1.6 liters and a power of 89 hp began to be used. With. A year later, the power unit was upgraded again; a modification of the 2126 engine of the same volume of 1.6 liters was used, but with a power of 98 hp. With.
Grill selection and installation
Tuning the Lada Vesta radiator grill allows you to better protect it from dirt thanks to smaller holes, and also give the car a unique style. Replacing the part involves removing the bumper. The fastening of the tuned element coincides with the factory one, so its installation will not take much time. The average price for a product with small cells is 1,300 rubles.
The Vesta radiator grille without a nameplate is gaining great popularity. It does not have a special place for the car logo, thereby making it undetectable to others. The mesh can be of any color, but most often it is black. A radiator grille without a badge costs more than a regular one - from 1,700 rubles.
Characteristics of motors 2114
Since the release of the Lada Samara VAZ-2114, the technical characteristics of the gasoline drive have been constantly improved. Owners of domestic cars, in principle, do not have questions about what kind of oil to pour into the engine, since standard requirements apply for Zhiguli, Lada and Samara - 5W30 or 10W30.
In addition, you should know what kind of oil to use in transmission gears - the instructions from the AvtoVAZ manufacturer recommend using the GL-4 group of lubricants with a viscosity of 80W85 (mineral), 75W90T (synthetic) or 85W90 (semi-synthetic).
After filling with synthetics, the box becomes noisy, the oil is more expensive, but the lubricant is mostly imported, which provides additional guarantees. Domestic manufacturers most often produce semi-synthetics of average quality for engines and transmission gearboxes.
The technical characteristics of the engine are as follows:
| Characteristics | Engine modification | ||||||||
| 2111 | 21114 | 11183 | 21124 | 21126 | |||||
| Years of installation | 2003 – 2007 | 2003 – 2007 | 2007 – 2009 | 2009 – 2013 | 2009 – 2013 | ||||
| Volume | 1500 cm 3 (97.9 hp) | ||||||||
| Torque moment | 115.7 Nm (3200 rpm) | 125 Nm (3000 rpm) | 120 Nm (3200 rpm) | 131 Nm (3700 rpm) | 145 Nm (4000 rpm) | ||||
| Weight | 127.3 kg | 112 kg | 112 kg | 121 kg | 115 kg | ||||
| Compression ratio | 9,8 | 9,6 | 9,6 | 10,3 | 11 | ||||
| Nutrition | injector | ||||||||
| Engine diagram | Inline (L) | ||||||||
| Ignition | module | coil | coil | coil for each spark plug | |||||
| Number of cylinders | 4 | ||||||||
| Location of the first cylinder | TVE | ||||||||
| Number of valves on each cylinder | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Cylinder head material | aluminum alloy | ||||||||
| Intake manifold | aluminum | plastic with receiver | |||||||
| An exhaust manifold | with catalyst | ||||||||
| Camshaft | 2110 | 2111 | 2112 | ||||||
| Cylinder diameter | 82 mm | ||||||||
| Piston stroke | 71 mm | 75.6 mm | |||||||
| Pistons | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | ||||
| Valve bend | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | ||||
| Crankshaft | 2112 | 11183 | |||||||
| Fuel | AI-95 | ||||||||
| Environmental standards | Euro 4 | Euro 2 – 4 | Euro 3 – 4 | ||||||
| Fuel consumption highway/combined cycle/city | 5,7/7,3/10 | 6/7,3/10,4 | 6/7,8/11 | 5/7/9,5 | 5,4/7,2/9,8 | ||||
| Oil consumption per 1000 km | 0,7 | 0,5 | |||||||
| Engine oil for 2114 | 5W-30 and 10W-30 | ||||||||
| Engine oil volume | 4 l | 3.8 l | 3.5 l | 3.6 l | |||||
| Operating temperature | 95° | ||||||||
| Motor life | declared 150,000 km, real 250,000 km | ||||||||
| Adjustment of valves | washers between camshaft cams and tappets | hydraulic pushers | |||||||
| Cooling system | forced, antifreeze/antifreeze | ||||||||
| Coolant quantity | 7.8 l | ||||||||
| water pump | plastic impeller | ||||||||
| Candles for 2114 | A17DVRM, BPR6ES | AU17DVRM, BCPR6ES | |||||||
| Gap between spark plug electrodes | 1.1 mm | ||||||||
| Timing belt | length 698 – 1125 mm depending on attachments | ||||||||
| Cylinder operating order | 1-3-4-2 | ||||||||
| Air filter | Nitto, Knecht, Fram, WIX, Hengst | ||||||||
| Oil filter | Mann W914/2 | ||||||||
| Flywheel | 2110 | ||||||||
| Flywheel mounting bolts | M10x1.25 mm, length 26 mm | ||||||||
| Valve stem seals | code 90913-02090 inlet light code 90913-02088 exhaust dark | ||||||||
| Compression | from 14 bar | ||||||||
| XX speed | 750 – 800 | 800 – 850 | |||||||
| Tightening force of threaded connections | spark plug – 31 – 39 Nm clutch bolt – 54 – 87 Nm bearing cap – 59 Nm (main) and 43 – 53 Nm (rod) cylinder head – four stages 20 Nm, 71 Nm + 90° + 90° | ||||||||
For high-quality maintenance of internal combustion engines, the engine manufacturer issues a manual containing a description of the drive parameters, the frequency of replacing consumables and step-by-step repair operations. The same operating manual recommends the volume of oil in the gearboxes in the engine.
Repair manual for VAZ 2108, 2109, 2114, 2115
For malfunctions and repairs of the electronic engine management system, which also includes the power and ignition systems, see the separate repair and maintenance manual for the engine management system with multipoint fuel injection.
Rice. 2.1. Longitudinal section of the 2111 engine
Rice. 2.2. Cross section of a 2111 engine
Longitudinal and cross sections of the engine are shown in Fig. 2.1 and 2.2.
Repair manual for VAZ 2108, 2109, 2114, 2115 VAZ 2109 engine, VAZ 2114 mounting block, VAZ 2115 air filter. Removing the 2108 steering rack, replacing the engine mount, replacing the VAZ 2112 thermostat. Replacing antifreeze or antifreeze. Temperature sensor VAZ 2114. Clutch and ignition adjustment. Spare parts for engine repairs, piston pistons. . SM German rings affordable price. Fret turn relay. fuse diagram, oil pressure drop. Clutch cable tension on VAZ 21099. VAZ gearbox repair.
Engine design features
Initially, the engine of the VAZ-2114 was 8 valve, had a volume of 1.5 liters, complied with Euro-2 standards, and was marked 2111. In 2005, these engines were boosted:
- to increase the volume to 1.6 liters, the block is increased in height by 2.3 mm;
- Several configurations have been created - for Euro-2 version 21114-00, for Euro-3 model 21114-20 and for Euro-4 modification 21114-70;
- The crankshaft, valve system, camshaft correspond to 11183;
- The cylinder head received an enlarged combustion chamber of 5 x 8.1 cm, which increased power.
An important feature of the 21114 internal combustion engine is phased rather than pairwise-parallel injection, which was used in the original 2111. The attachments have become more compact:
- catalytic collector instead of the neutralizer and exhaust pipe;
- injector ramp instead of the fuel return line.
The modernization also affected other components, for example, a January 7.2 or M7.9.7 controller was used, the ignition module was replaced with a coil with 4 terminals.
At the same time, VAZ-2114 began to be equipped with engines from Kalina 11183, which have some differences from the previous version:
- the shape of the combustion chamber has been improved;
- The generator is secured with a bracket, the tensioner is modernized.
In 2008, the 2114 engine received a new M73 ECU, and in 20011, the M74 “brains” to achieve Euro-4 standards. The control became completely electronic, but for another whole year the designers corrected firmware defects until they created its final version I414DE07.
The next engine, 2114, was installed on the car by a subsidiary of the manufacturer AvtoVAZ, called Super-Auto, in 2009. It was the 16 valve engine 21124 of the “tenth” VAZ family with improved characteristics:
- “high” blue block (197.1 mm);
- injectors pressed into 2–5 main bearing supports, cooling the pistons with oil;
- The groove depth of the holes in the valves is 5.53 mm, which ensures the safety of the valves in the event of a timing belt break; major repairs are not required.
The following year, the fourteenth models began to be equipped with 21126 engines from export Priors. After tuning the 21124 engine, the internal combustion engine device differs in the following nuances:
- honed cylinders, gray block;
- crankshaft pulley and timing belt with semicircular tooth;
- the weight of the connecting rod and piston group is reduced;
- there is no friction in the lower head of the connecting rod;
- candle glasses are built into the head.
The internal combustion engine uses the principle of hydraulic compensation of valve clearances; the 0.45 mm thick cylinder head gasket is made of multilayer metal. The motor is equipped for Euro-3 with a collector 11194-1203008-10 or Euro-4 with a collector 11194-1203008-00. The service life of the pump has been increased due to a new design of the oil seal and bearing, and changes to the toothed pulley.
The ignition system has a separate coil for each spark plug. Phased injection, stainless steel fuel rail, January 7.2 or M7.9.7 controllers.
Improving dynamic characteristics (tuning)
For many owners, the standard dynamics of the VAZ 2114 are not enough. Engine tuning allows you to improve the dynamics and customize the character of the car.
As practice has shown, chip tuning of VAZ 2114 engines does not lead to tangible improvements.
Let's look at more serious improvements:
- For owners of eight-valve engines, the easiest way to improve dynamics is to install a cylinder head from a 16-valve engine. Modification of the 1.5l block is also possible.
- The easiest way to tune a VAZ 2114 engine is to install camshafts different from stock. For example, OKB Dynamics 108 will give an increase in the highs without a noticeable loss in the lows.
- By supplementing the shaft with a sliding timing gear and a suitable phase setting, you can get + 7 hp. With.
- Installing an enlarged throttle valve (54 mm), a receiver and a 4.2.1 spider will improve cylinder purging and give noticeable changes during acceleration (the level is close to Priora).
- A modified cylinder head, lightweight valves and a modified intake manifold paired with an increase in engine volume to 1.6 liters will allow you to achieve a power of 110 hp. With. Tuning up to 120 horsepower will take place without loss of resource.
The principle of improving the power characteristics of sixteen-valve engines is similar to the process of refining V8 1.5i l and V8 1.6i l. More evil camshafts, direct-flow exhaust, a receiver, an enlarged damper, a lightweight Priorov piston group, in the case of the Kalina engine (124) and proper tuning will give a significant increase in dynamics.
Regardless of the number of valves per cylinder, the power of the VAZ 2114 engine can be significantly increased by installing a compressor or turbocharging. Engines modified in this way easily reach 170–190 hp. With.
There are many different configurations and options for improving the vehicle's dynamic performance. You can decide for yourself how to increase the power of the VAZ 2114 engine. Remember that the selection of mechanical modifications and software must match each other.
Cons and pros
Depending on which 2114 engine is used, the owner’s risks differ:
- 2111, 21183, 21114 and 21124 – do not bend the valve if the timing belt breaks;
- 21126 – valve bending due to insufficient groove.
The main disadvantage of the latest 16 valve versions is the lighter crank mechanism:
- the engine is adjusted to Euro-4 standards;
- to reduce weight, the length of the piston skirt is reduced;
- Accordingly, the width of the oil scraper and compression rings decreases;
- The resource of the internal combustion engine is sharply reduced.
For example, in Japan, manufacturers abandoned Euro-4 standards, considering that the reliability and high service life of the motor are more important for the consumer.
The drive power increased from 77 horsepower to 81 hp, then 82 hp, 89 hp, and 98 hp. In models with hydraulic compensators, periodic adjustment of this unit is not required, however, the quality of the oil in the system must be high for normal operation of the pushers.
Catalytic converter - what is it for?
Car designers are increasingly paying attention to reducing harmful emissions.
To achieve this, the power supply systems of power plants are being modernized in order to achieve the lowest possible fuel consumption, without affecting power performance.
Also, more and more cars are equipped with catalytic converters installed in the exhaust system.
The essence of the catalyst's work comes down to the breakdown of harmful elements into harmless ones through chemical reactions.
The catalytic converter consists of a housing, inside of which active catalysts, the so-called bobbins, are placed.
Device
Nowadays these bobbins are often made of ceramic, but some are also made of metal.
The reel contains a large number of honeycombs through which the exhaust gases pass.
But ceramics do not enter into a chemical reaction; for this purpose, the surface of the honeycomb is covered with a layer of noble metals - platinum, iridium. Thanks to these metals, a reaction occurs, which reduces the harmfulness of car emissions.
The operating efficiency of this device depends on the temperature - the optimal temperature is considered to be from 300 degrees, so there is also a heat-insulating layer inside the housing, and the element itself is placed as close as possible to the exhaust manifold.
You can learn more about the design features of the catalytic converter, as well as the principle of its operation.
One of the main disadvantages of the catalytic converter is its relatively short service life. On average, it is designed for 100-120 thousand km, after which it becomes inoperative.
Maintenance schedule
To avoid having to carry out expensive overhauls of the Lada Samara 2114 yourself, you should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for servicing the internal combustion engine:
| Maintenance object | Time or mileage (whichever comes first) |
| Timing belt | replacement after 100,000 km |
| Battery | 1 year/20000 |
| Valve clearance | 2 years/20000 |
| Crankcase ventilation | 2 years/20000 |
| Belts that drive attachments | 2 years/20000 |
| Fuel line and tank cap | 2 years/40000 |
| Motor oil | 1 year/10000 |
| Oil filter | 1 year/10000 |
| Air filter | 1 – 2 years/40000 |
| Fuel filter | 4 years/40000 |
| Heating/Cooling Fittings and Hoses | 2 years/40000 |
| Coolant | 2 years/40000 |
| Oxygen sensor | 100000 |
| Spark plug | 1 – 2 years/20000 |
| Exhaust manifold | 1 year |
If consumables are replaced within the recommended time frame, the operational life of the internal combustion engine will increase.
Typical breakdowns
The very first 1.5 liter engine 2114 has disadvantages:
- periodic valve adjustment;
- unreliable injection system;
- loosening the exhaust manifold nuts;
- Leaking gaskets of the fuel pump, distribution sensor of the ignition system.
The next 1.6 liter engine does not cause any particular problems for the owner, with the exception of high vibration and noise loads. The weak point traditionally remains the valves, which have to be constantly adjusted.
The internal combustion engine from Lada Kalina 11183 was installed on the fourteenth model solely to meet Euro-3 standards. It has typical disadvantages for a linear series and is no different.
The first sixteen-valve engine 21124 does not bend the valves, the gaps in which are adjusted by hydraulic pushers. However, the belt needs to be tightened after 15,000 km due to the large number of attachments. The second and last in the line of fourteenth ICE models, ICE 21126, has increased power. In addition to typical malfunctions, if the timing belt breaks, the piston will bend the valve due to insufficient recess depth.
Main components and how they work
The entire scheme of the VAZ 2114 fuel system is built on the injection principle, implying complete electronic control over the system’s operation process - starting with fuel supply and ending with the formation of a working mixture and combustion. Because of this, its constituent components are very different from devices characteristic of the carburetor principle.
So, it includes:
- fuel tank;
- pump (gasoline pump);
- pipelines for supplying gasoline;
- fuel filters;
- fuel rail;
- tank filler cap;
- nozzles;
- recycling block.
VAZ 2114 fuel system diagram
They perform the following functions.
Tank - provides storage of fuel reserves.
Pump - located inside the gas tank and serves to pump fuel to the ramp. Thanks to the sensor connected to it, it detects and transmits data on the level of remaining gasoline to the electronic unit.
Pipeline system - serves to move fuel to the engine and drain the remaining excess into the tank. It includes a system of metal tubes and flexible hoses, among which are the VAZ 2114 fuel hose, return hose, hose for connecting the adsorber and others.
Filters - serve to purify gasoline from possible impurities and sediments. The service life of the injectors, as well as the quality of the resulting fuel mixture, directly depends on their operation. That is why they should be replaced at least every 10,000 km.
Fuel rail - consists of two chambers separated by a diaphragm. One of them plays the role of a fuel container in which the optimal gasoline pressure is maintained, which changes when the diaphragm bends as a result of air being pumped into the second chamber of the ramp.
The tank lid is designed according to the valve principle and serves to relieve excess pressure.
Injectors are a system of valves with electromagnetic control. They spray gasoline directly into the combustion chamber, forming a working mixture in it.
Recycling unit - serves to absorb fumes generated in the throttle assembly (in accordance with the requirements of the Euro-3 standard). It is a container with activated carbon that adsorbs unnecessary fumes.