Overheating of the motor is a very dangerous phenomenon. It threatens serious repairs or replacement of the power unit if measures to eliminate the malfunction are not taken in time. The reasons why the engine on a VAZ 2114 (injector, 8 valves) heats up can be different. There are 7 main ones. Information about them, as well as what temperature of the power plant is considered normal, can be found in this article.
We also recommend watching a video that clearly describes this problem.
How to determine if the engine is overheated
At first glance it seems very simple - according to the indicators of the engine temperature device, or - sensor. This is true, if not for one thing - novice motorists are so captivated by the road situation around them that they look at the instrument panel only in one case - how much fuel is left. Experienced motorists, on the contrary, due to their confidence in their abilities, also do not look at the car’s dashboard. And as a result, a situation often arises that overheating is detected when the engine temperature has long exceeded permissible limits, and irreparable damage has been caused to the engine. It is irreparable overheating that is one of the most complex malfunctions, which leads to very serious consequences. But more on that later. But there is a way that will not let you miss the moment of overheating. This is problematic in a traffic jam, and is not always clearly present, but here’s what you should be aware of:
— As soon as the engine temperature exceeds the permissible norm, when you sharply press the gas pedal, or when accelerating the car, even slightly, detonation knocks are clearly heard , which are popularly called “tapping fingers.” This is not true, but everyone knows this definition. If you hear such a sound, there is a 99% chance that the engine has overheated, and action must be taken.
Detonation knock is a loud metallic knock, the frequency of which coincides with the engine speed. You've probably heard such sounds when refueling with low-quality fuel. I personally don’t know where the concept of “tapping fingers” came from.
But the real reason for such knocking noises is a disruption in the fuel combustion process. What you hear is nothing more than explosions of the fuel mixture. During normal engine operation, the combustion process is controlled, but as soon as one of the operating parameters is violated, the process goes out of control and combustion turns into an explosion.
Hence the concept - detonation (from the word detonate - explode) knocks. When the engine overheats, this is the first sign.
Before continuing the conversation, let's define what is normal temperature and what is overheating. There is no one-word answer, but there are general rules. The engine temperature is within 85-95 degrees Celsius, which is working.
Engine temperature up to 100 degrees is acceptable. This means that a short-term increase in temperature to 100, sometimes up to 105 degrees is allowed. Just for a short time - up to 5 minutes.
Engine temperature above 105 degrees Celsius means overheating and action must be taken.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Chronicle of events
In the initial stage of overheating, the pistons burn out, molten metal settles on the cylinder walls, friction increases even more, the engine may stall, or it may continue to work. At the same time, the oil heats up greatly and its lubricating properties are lost; as a result, the connecting rod bearings stick to the crankshaft, and some of them may turn.
Then the cylinder head becomes deformed and the valves burn out, the valve seats begin to fly out, and a ringing metallic sound of the engine appears, which may stall or may continue to run.
Such overheating can have two endings. In the first case, the piston turns out to be the strongest element, then the crankshaft breaks, but the engine may not stall. In the second case, the piston jams and breaks in two, the skirt falls into the oil pan, and the bottom remains in the cylinder. The connecting rod with the piston pin begins to hit the cylinder walls chaotically, and eventually breaks through the block - that’s the “fist of friendship”, the engine stalls.
Reasons that can cause overheating
1. Lack of coolant. The liquid in the engine boils not because there is not enough of it, but here’s why: remember about the outer surface for cooling?
If there is a lack of fluid, the contact surface between the fluid and the heated engine is insufficient, and heat transfer to the environment is poor. This is where the overheating comes from. The engine cooling system is not sealed, as many believe, and fluid evaporates during operation - do not forget to check its level regularly.
And of course, monitor the condition of the radiator and pipes - leaks are unacceptable. There are cases of internal leakage - as a result of damage to the gasket between the head and the cylinder block. Water will not flow out of the exhaust pipe, but a constant decrease in the fluid level without visible leaks is a reason to be wary and contact a specialist.
2. Radiator condition. The gaps between the radiator honeycombs are quite small and can gradually become contaminated by representatives of the insect world.
This is not a joke; there was a case when minor contamination of the radiator (coupled with the poor condition of the engine) led to constant overheating of the car. Keep the radiator clean and blow it with compressed air at least occasionally.
3. Incorrectly set ignition angle. If the ignition angle is violated, the fuel combustion process is disrupted.
As a consequence, an increase in combustion temperature and a decrease in power. The power has dropped, but there is no need. What are we doing?
That's right - press the gas pedal harder. It turns out that more fuel is spent on the design operating mode of the engine (at which normal cooling occurs). Hence the overheating.
By the way, an ignition problem can arise (spontaneously, and not after your intervention in the finely tuned engine mechanism) if the timing belt or chain is stretched. This is not the only possibility, but it is common - keep in mind.
4. Fuel quality. An inappropriate octane number leads to a decrease in power and an increase in the temperature of fuel combustion. There is only one way out - refuel in one place, so the likelihood of getting bad gasoline is lower.
5. Deposits on the walls of the engine and radiator. The reason is simple - the use of low-quality coolant, or even water.
A little more detail. From a physics point of view, using water is better, since water has better thermal conductivity than alcohol-containing antifreeze. But - there are salts in the water (you can see them on the walls of the kettle) - the same thing happens inside the engine.
As a result, water circulation is disrupted, cooling efficiency is reduced and the engine overheats. If you are pouring water into the expansion tank, pour distilled water, it is free of salts. It is best to use special antifreeze.
Believe me, it is impossible to completely remove scale from the engine. And one more “beauty of water: if, after water, for example in winter, you fill in antifreeze - be prepared for drips (it can leak anywhere: radiator, pipes) - this is a fact. If you constantly drive “on antifreeze,” nothing will happen, but after water, antifreeze will flow 99%.
6. Engine wear. This can include many aspects, but in most cases it is wear of the piston group. During long-term use of the car, the piston rings, which serve to seal the combustion chamber, wear out, which leads to a decrease in compression, impaired fuel combustion, loss of power (remember the formula) and overheating of the car.
Somehow it turned out to be too difficult. To put it simply: fuel burns better at a certain pressure that is created in the combustion chamber. Pressure is about 12 atmospheres.
If you take a pipe, plug it with potatoes and blow inside, pressure will be created inside, which is called compression. The force with which you blow will represent the force of expansion of the fuel during combustion, which pushes on the piston and causes the crankshaft to rotate. The rings serve to fit the piston more tightly to the cylinder (in our case, potatoes and tube).
This is what happens in the engine when the piston group wears out (ring wear and cylinder wall wear). As a result, part of the expansion energy of the fuel during combustion passes by the piston (between the piston and the cylinder), and compression (optimal pressure in the combustion chamber) decreases, which worsens the quality of combustion. And again - loss of power and overheating. There is only one way out - contact a specialist.
7. Radiator fan. In some (older) car models, there was no such reason, since the fan was driven directly from the crankshaft through a belt.
Now, the fans are electric and turn on when the temperature sensor is triggered. The sensor may not work, and the fan may not turn on. This is a fairly common reason.
8. Air pockets formed when filling liquid. By the way, in this case the temperature sensor may not show an increase in temperature.
How to get rid of a traffic jam is the topic of a separate article. I’ll add on my own – when pouring liquid into the cooling system, the car must be horizontal.
9. Thermostat. The thermostat divides the cooling system into two circles - small and large.
The small one is used to warm up the car (the amount of liquid is reduced, the radiator is turned off), when a certain temperature is reached, the large circle is connected (the radiator is connected). If the thermostat is jammed, then only the small circle is used: the amount of fluid is insufficient, the radiator is turned off - the car is overheating. You can determine this by feeling the lower pipes leading to the radiator: if they are cold and the car is overheated, change the thermostat.
10. Pump. A pump is a pump that forcibly displaces water to improve circulation.
By and large, two troubles can happen to the pump: it will simply leak - you will see, and the second, which is more difficult to determine, is wear of the pump impeller. When the impeller wears out, the pump slowly pumps liquid, as a result, the liquid in the engine heats up faster than in the radiator (water circulation worsens). You can tell by uneven heating - the radiator is cold, but the engine is boiling. Attention - the same symptoms occur if the thermostat is malfunctioning or if there is an air lock.
There may also be other reasons - one of which is from the category “you can’t invent it on purpose.” For example, the parking brake is not fully weakened, which leads to the car slowing down, increasing the load on the engine, and overheating. The handbrake cable may get stuck - there was such a case. The car slows down slightly, but this is enough in the heat.
And some people also blame the air conditioner on. By and large, this is rather a far-fetched reason. Of course, the air conditioner creates additional load on the engine, but this was taken into account during the development.
If the engine is really bad - complete wear and tear - then this can happen. What to do - turn off the miracle of modern automobile manufacturing.
Perhaps we'll stop there. The only thing we'll talk about at the end is overheating in a traffic jam. No one is immune from this.
[custom_ads_shortcode2]
What should the temperature be?
The temperature arrow points to the red zone - overheating soon
According to the International Automotive Convention of December 1, 1992, which brought together 92 representatives of the automotive industry, it was decided to establish a uniform standard for engine temperature under operating conditions.
This indicator is 90 degrees Celsius with a maximum permissible deviation of no more than 3 degrees Celsius.
With the development of the automotive industry and a strong technological leap in the 2000s, in 2004 it was decided to revise this indicator. So, after considering all the facts and analyzing the design features of many cars, it was decided to install a floating indicator with acceptable standards beyond the border, which today is 85-105 degrees Celsius.
Operating range on the VAZ-2114
If we consider cars produced at the AvtoVAZ plant, including the VAZ-2114, the engine operating temperature range is considered to be 87-103 degrees Celsius. If we look at this problem from a functionality point of view, this is the optimal indicator.
If the temperature drops below the limit, the Samara-2 engine loses dynamics and power, and if it is higher, it can simply boil and suffer great damage. Therefore, in case of malfunctions related to the cooling system, it is necessary to eliminate them as soon as possible.
Cooling system design
Before considering cooling system malfunctions, as well as methods for eliminating them, novice motorists should study the cooling system.
So, let's look at what elements it consists of:
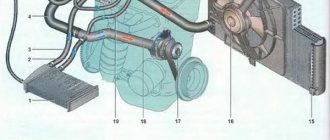
Cooling system design
1 — cap element of the expansion tank; 2 - expansion tank; 3 - pipe for draining liquid from the pipe; 4 — transition pipe between the radiator and the expansion tank; 5 — radiator outlet pipe; 6 — tank to the left of the radiator; 7 - aluminum tube; 8 - plugs; 9 — tank to the right of the radiator; 10 - drain plug; 11 — center of the radiator; 12 — electric fan casing; 13 — plastic wings of the electric fan; 14 - electric motor; 15 — gear pump pulley; 16 — pump impeller; 17 — camshaft drive belt; 18 — engine block; 19 — pump hose; 20 — radiator hose with power function; 21 — heater radiator hose with diverter function; 22 — coolant supply pipe to the throttle valve; 23 — outlet pipe; 24 — filling tube; 25 — heater radiator hose with power function; 26 — thermostat; 27 — coolant temperature sensor; 28 — coolant level indicator sensor.
Main malfunctions and ways to solve them
The operating temperature of the engine is directly affected by the health of the cooling system.
Almost any node can affect the change in this indicator in both directions, so it is necessary to monitor your health and prevent falls. It is temperature fluctuations that can lead to failures in other engine systems. So, let's look at the components of the cooling system, their malfunctions and solutions.
Cooling radiator
Dirty engine cooling radiator
The radiator is considered one of the most reliable parts. There are not many reasons that can lead to product failure, but this can be prevented. Debris on parts can cause the engine to overheat, but regular cleaning of the internal and external surfaces will return it to normal condition.
Cracks can cause the radiator to leak, but this problem can be fixed. There are two ways to solve the problem: weld the surface or replace the entire product. Thus, repair and restoration work normalizes the operation of the part, as well as the operating temperature in the system.
Pipes
Contamination and breakage of the SOD tube can lead to changes in engine operating temperature
Cooling system pipes can directly affect the temperature rise in the system. This is due to the fact that when cracks or delaminations form in them, it may happen that the coolant begins to leak out. In turn, the lack of “cooling” will lead to an increase in temperature, which can affect both the operation of the main power unit and increased wear.
Water pump
The water pump or pump is supposed to move coolant through the system, but if this device fails, low pressure can result in slow cooling, which in turn will cause the engine's operating temperature to rise. Often the water pump will simply leak and further movement of the car will become impossible.
It is quite simple to treat a malfunction by replacing a part.
Thermostat
Thermostat operation at different temperatures
The thermostat is the most capricious part of all available in the cooling system. Stuck product will result in improper engine temperature distribution, which in turn can increase wear on parts. So in winter it is normal that it is closed in a small circle, but in summer this can lead to malfunctions in the form of overheating, since the radiator fan does not always cope with this task. The fan will run without turning off.
Therefore, it is recommended that if the thermostat fails, replace it with a new one as soon as possible.
Radiator cooling fan
A fan is an electrical component of the cooling system that additionally and forcibly cools the fluid to operating temperature. Therefore, its main task is to prevent the engine from overheating. However, if the unit is faulty, especially when paired with the thermostat, the engine will boil up to 100% and can even cause the other main units to fail. Therefore, if a disk fails, the cause must be immediately found and corrected. Some owners are replacing the factory thermostat with a Grant model!
What to do if your car overheats in a traffic jam
When driving a car for a long time in a lower gear, the engine operates with increased power, which in itself leads to overheating. Add to this the lack of oncoming air flow necessary to cool the radiator. What to do?
The main thing is not to panic. Short-term overheating is not terrible, but if you see that the car is not cooling down, it’s time to act.
Important - do not turn off the engine unless absolutely necessary. Exactly - without extreme. A stalled, overheated engine is an almost 100% guarantee of repair. It will take quite a long time to describe what is happening in the engine in this case (rotating the liners together with the crankshaft, when the engine is subsequently started - the least of the possible troubles), just take it on faith.
Important - do not think about pouring water on the engine or pouring cold water into the radiator. The result is the same - repair. Moreover, you can try so hard that you cannot do without replacing the block and cylinder head. Another “beauty” of cold water is microcracks inside the block. Finding and eliminating will be very, very difficult, if not impossible. The car has overheated - try to pull over to the side of the road. If it doesn’t work out, don’t panic and don’t pay attention to those around you – it’s important for you to save the engine. Stop at idle, turn the heater on full, and wait. If after 5-10 minutes the situation does not improve, turn off the engine.
It’s a good idea to open the hood; the main thing in a panic is not to forget to set the car’s parking brake. The only reason to turn off the engine right away is clouds of steam coming from under the hood. Most likely, the cooling pipe has burst, and further operation of the engine will only worsen the situation.
This is what it looks like, engine overheating, if you look closely. Now you know why the engine gets hot and how to deal with it. Author: Igor
With the arrival of warmer weather, many drivers are faced with poor performance of the VAZ cooling system when the VAZ 2114 engine gets very hot. There are quite a few reasons why the engine overheats. You need to understand the reasons and find out ways to combat overheating.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Leaking cylinder head gasket
This problem is one of the rarest causes of engine overheating in VAZ 2114 cars. When it occurs, overheating is a secondary symptom that may be accompanied by a number of others:
- oil leaks from under the cylinder head;
- uneven engine operation and low compression;
- increased oil consumption, noisy engine operation and gas flow, black exhaust.
In this situation, at best, the solution would be to replace the cylinder head gasket. At worst, a major overhaul of the engine with cleaning of all internal cooling channels.
When the engine gets hot, it is dangerous not in itself, but because of its consequences. Long-term driving at elevated operating temperatures first leads to loss of properties of elastic parts: valve stem seals and piston rings. Because of this, oil consumption increases, and engine operation becomes uneven and dirty. All this leads to expensive major repairs.
The consequences of severe overheating are even more severe: the cylinder head and cylinder block are deformed and sometimes crack. An engine that has survived this can no longer be repaired.
The principle of operation of the VAZ 2114 cooling system
The cooling system in a VAZ car is a whole complex in which liquids that freeze at temperatures from -20 ° C are used as a working substance. The system is completely sealed and the working fluid circulation cycle is closed. The coolant circulates through the system forcibly. The cooling system in a VAZ car operates on the principle of internal heat exchange.
Heat is absorbed by the liquid, which is used as a working fluid. This is one of the most popular cooling schemes in the automotive industry. When the driver starts a cold engine, the thermostat is closed, and the pump forces the coolant to circulate in a small circle of the system. At the same time, the liquid is quite effective at removing excess heat from the fuel combustion chambers, and then transfers the resulting heat to those engine components that have not yet reached operating temperature.
This allows the engine to quickly warm up to operating temperature, and the risk of overheating is reduced to zero. When the engine has warmed up to the required operating temperatures and reached a certain temperature range, then the cooling system no longer needs only a small circle for effective cooling. Therefore, at this moment the thermostat valve begins to open, and the pump now forces the working fluid to circulate through the radiator.
When the car is moving, there is enough air flow to cool the fluid in the radiator. If the car is stationary and the motor is running, the controller starts the fan based on sensor data. If the car is moving at a slow speed, the electric fan is not running, or any temperature sensor is faulty, the coolant will heat up above its operating temperature. In this case, the driver will see a corresponding signal on the instrument panel. This is engine overheating.
In such a situation, you need to stop the engine and then open the hood. To start the fan on the radiator, you need to turn the ignition key to the position in which the fan will work, cool the engine and other components of the car.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Measures to take if the engine overheats
In the engine, within the limits of the cooling system, the hottest components are the surfaces adjacent to the combustion chambers. Designers and engineers were able to prove that the fluids that will circulate in these hot components can work effectively to remove excess heat. In this case, the heat transfer itself reaches such a volume that a boiling core can form in the channels or circuits where the liquid circulates.
It, in turn, instantly reduces heat exchange processes between the liquid and the hot metal. After this, the engine continues to warm up. Further heating and the reduced density of the coolant as a result of boiling cause other adjacent hot areas to boil. The pressure in the cooling system quickly increases and is then released through the radiator cap.
This engine overheating and excessive thermal stress can lead to serious problems. If a VAZ engine overheats, there is a certain risk of distortion of the cylinder head and liners, premature ignition is possible, low fuel efficiency threatens, and erosion processes appear around the liners, as well as the heads and pump.
If the temperature sensors are working properly, then you can understand that the VAZ is heating up by looking at the instrument panel. If, while driving, you notice that the temperature needle has begun to confidently move into the red zone, then you need to stop the vehicle and turn on the emergency stop signal. Then you need to open the car hood and check the coolant level.
If you see from the sensor that the engine is overheated and clouds of steam are actively escaping from under the hood, then you need to stop the engine and wait until the steam stops flowing. And only then you need to open the hood and check the fluid levels. Do not open the expansion tank cap while the engine is running, as there is a risk of being scalded by boiling water.
For your own safety, do not lean directly over the neck of radiators or tanks, which increases the risk of steam burns. When opening the expansion tank cap, protect your hands if possible by wrapping the cap with a rag or cloth.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode2]
Liquid pump failure
The role of the pump in the cooling system is to create pressure through which the refrigerant circulates. Its failure can not only cause the VAZ-2114 engine to overheat, but also cause a malfunction of the gas distribution mechanism drive. The fact is that the liquid pump is driven through a gear by a timing belt. Therefore, if the pump fails, it immediately affects the performance of the entire drive. In this case, the fluid pump and possibly the timing belt will need to be replaced.
Causes of overheating, troubleshooting
Why does the VAZ engine get hot? The main reasons are:
- radiator clogged externally or internally;
- a broken or inoperative fan;
- faulty thermostat;
- burnt cylinder head gasket;
- insufficient amount of coolant;
- water pump.
If the engine overheats only when running, it means that an exhaust gas leak has been detected. However, when the engine continues to heat up after stopping, then there is definitely one of the problems listed above. The engine will heat up if you give high speeds, but drive slowly.
Sometimes it is impossible to see and diagnose the presence of air or gases in the system. Then you need to put a bag on the neck of the expansion tank, start the engine, collect the vapors in the bag, and then smell them. If there is a smell of antifreeze, then you need to look at the pump, radiator or thermostat. If the vapors have a gasoline “aroma,” then the cylinder head gasket may be broken.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Methods for checking DTOZH
How to check the TOZH index yourself? To do this, you can use one of several methods; Diagnostics is carried out using a multimeter.
- First, the negative tester probe must be connected to the cylinder head, and then turn on the ignition by turning the key in the lock.
- So, using a multimeter you need to determine exactly what voltage appears at the output.
- If the controller is working properly, the value of this parameter should be at least 12 volts, of course, if the battery is fully charged. If the diagnostics showed that the obtained values were lower, then it is necessary to repair or replace the regulator (the author of the diagnostic video is the technical and mechanical channel).
Removing contaminants
In summer, various pollutants can significantly clog the radiator grille. Naturally, air cooling processes will not be as efficient. As the coolant cools in the radiator, this process also worsens.
Preventive action is cleaning the radiator. Paint that peels off honeycombs also causes this effect.
You can rinse the radiator thoroughly at a car wash. The jet from the Karcher sink should not be brought near the radiator honeycombs. Water or other water-based solutions will form scale.
When such compounds are oxidized, various impurities appear. Sand and dirt can easily cause the radiator to clog from the inside. What to do?
Flush the entire cooling system completely. As a result, we will see cloudy and dirty coolant.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Problems with fan, thermostat, radiator cap
Often problems with the fan can occur if the temperature sensor has failed. The fan motor itself is almost always in working condition. Possible blade damage. Fan failure may be due to a clogged radiator. The bottom of the radiator becomes covered with sediment and dirt.
The temperature sensor is in most cases located at the bottom. The sensor does not warm up well, and as a result the fan does not work (or works, but too late). If there is dirt present, then washing is needed.
The temperature sensor wire should be short-circuited. The service fan will start. Sometimes thermostats stick closed as a result of oxidative processes.
As a result, the coolant simply does not flow into the large circuit. Sometimes this can lead to serious problems. But such cases are quite rare.
Signs of thermostat malfunctions appear when, when the engine is warm, the heater blows hot and the inlet valve is cold. This means the closed thermostat is stuck. Thermostats need to be replaced occasionally.
If the radiator cap has expired, this may lead to the coolant boiling. This entails low pressure in the system. If the engine operates at normal temperatures when moving, but immediately boils when stopped, then this indicates a faulty cover. If engines get hot at idle, you need to pay attention to this too.
Return to contents.
[custom_ads_shortcode2]
What does an increase or decrease in this indicator lead to?
If the temperature drops below this norm, the engine loses power and dynamics. This will make it harder for the car to gain speed and consume more fuel. Especially often, a decrease in normal performance occurs in winter if the power plant is not warmed up enough or if the stove does not work properly. It is important to maintain the engine regularly to avoid this situation.
In summer, it is more dangerous to leave the operating temperature range, especially if the engine overheats, which happens very often at this time of year.
An increase in temperature causes fluids in the engine to boil, causing irreparable damage.
The main problem with the engine reaching operating temperatures is related to changes in the properties of the oil:
- as it decreases, it becomes more viscous;
- with increasing fluid.
This may result in under or over lubrication of parts. It is much more dangerous if the oil becomes more liquid and loses its properties, since in this case friction occurs between the iron parts, leading to their wear.
Antifreeze level VAZ 2114
Pipes VAZ 2114
Consequences of overheating
If the engine was in an overheated state for not very long, about 10 minutes, then it’s okay. If it’s a little longer, the pistons begin to melt. Modern cars don't allow this.
You need to worry if you see smoke. If the overheating lasted about 20 minutes, then serious problems with the cylinder heads, cylinder head gaskets, cylinder head cracks, destruction of the inter-ring partitions, and leaking seals are possible.
When the machine overheats too much, it starts to work poorly. In this case, a wave of destruction covers the entire engine, often without the possibility of recovery.
To prevent overheating of the power unit, it is important to carry out regular preventative measures. It is necessary to monitor the degree of contamination and replace parts that have become unusable. Care must be taken to ensure that the motor operates at normal loads. It is worth checking the condition of the air intakes.
Usually in the fall or winter, car owners find that the engine in the car does not warm up to 90 ° C, that is, operating temperature. Why does the VAZ 2114 engine not heat up, what are the causes of the problems and what are the methods for eliminating them? There are several possible reasons for poor engine warm-up:
- faulty thermostat;
- ruptures and cracks in pipes;
- faulty sensors;
- air in the system;
- low quality fuel.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Chronicle of events
First, the pistons burn out, which affects the operation of the cylinders. The crankshaft gets damaged and certain elements stick to it.
In the future, the cylinder head is susceptible to impact, this can significantly affect the functioning of the engine of your vehicle.
If the pistons are strong, the crankshaft will break, the unit can continue to operate. A seized piston breaks, it causes a lot of damage to the engine, the piston pin and connecting rod damage the cylinder - your vehicle becomes unusable.
Faulty thermostat
When a cold engine starts, the thermostat valve is closed, and antifreeze is pumped through a small circle of the system. Antifreeze removes excess heat from the combustion chambers to components that have not reached operating temperature and require heating.
Thus, the motor quickly heats up to the operating range. At an engine temperature of 95 °C, the cooling system switches from a small circle to a large circle. At the moment of switching, the thermostat valve opens, the pump begins to pump antifreeze through the radiator.
Mostly the problems are related to the thermostat valve. If the valve is jammed or is open, the temperature of the VAZ 2114 engine does not rise, an unheated engine does not hold speed well and stalls from time to time. To try to move the valve, you can tap the thermostat housing with a screwdriver several times.
To check the thermostat, start a cold engine and warm it up to 60 °C. If the middle of the radiator is warm, underheating occurs because the thermostat is moving to a large circle (has stopped functioning normally). If the radiator remains cold to 85 ° C, then there is a problem with the sensor or panel.
If the thermostat is broken and does not switch from small to large circle and back, it must be replaced.
The most trivial way to check a thermostat after purchase is to heat it on the stove in any container with water. Since there is a chance that the new thermostat may be defective (up to 50%), before installation, it is better to check at what temperature it will open, under “saucepan” conditions.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Faulty sensors
The engine temperature shown on the dashboard is data from a sensor installed on the engine. The sensor from which the readings are transmitted to the computer determines the temperature of the antifreeze in the thermostat. To control the engine, data from the coolant temperature sensor (coolant temperature sensor), a sensor next to the thermostat, is used.
If the VAZ 2114 does not heat up and there is a possibility that the sensors are faulty, it is better to contact a car service center to have their operation checked by a qualified technician.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]