Rechargeable batteries are used everywhere. In conventional portable devices, batteries do not require additional maintenance. In the case of car batteries, you should carefully monitor its condition and, if necessary, add distillate. To do this correctly and not cause irreparable damage to the battery, you should know how to add distilled water to the battery.
Maintenance free battery
But if you take a maintenance-free battery (for example, BOSCH, VARTA, MUTLU and many others), then you won’t be able to add it here so easily. The design does not provide for adding water inside, that is, you will have to “chemically” it.
To be fair, it is worth noting that often maintenance-free batteries are made using calcium technology and their water loss is very small. However, after 4–5 years the level still drops and it is advisable to bring it to normal
BY THE WAY - many of these batteries are handed over to specialized stores when they no longer start the car and they buy new ones. BUT NOT MANY people know that you just need to add water there and then performance will be restored.
HOW TO ADD, STEP-BY-STEP INSTRUCTIONS:
- First, determine the electrolyte level. Lightly shake the battery left and right, if there is a minimum level, then you should add water. If there is a feeling that there is enough of it there, then perhaps water will not help you (maybe you have shedding or sulfation)
- We determine where your plates are located (at what height). If the battery is transparent (has a white casing, like BOSCH's), you can illuminate it with a flashlight. But if the body is black, then it won’t work out that easily, you have to figure it out “by eye”
- We retreat from the plates approximately 1.5 - 2 cm upward. We take a 2-3 mm drill and drill small holes.
- Take distilled water and a syringe with a needle. Fill the syringe and pour it into the battery through the holes
- It is worth adding before liquid begins to ooze through the holes.
- Then we put the battery on its side and solder the holes with a regular soldering iron.
- Then we just charge
You have to “collective farm”, there is no other way. Some people drill holes from the top, but this way it is impossible to control the level (and you also cannot overfill).
Why maintain the electrolyte level in the battery?
Maintaining the normal level of electrolyte in the battery, and accordingly the amount of distilled water, is necessary in all serviced acid batteries. They do this for two reasons.
Composition of water and sulfuric acid in lead-acid batteries
The electrolyte of lead-acid batteries is 65% water and 35% sulfuric acid. During battery operation, when recharging, the electrolyte may boil. This process intensifies when the temperature outside or under the hood is too high. The acid is non-volatile and practically does not evaporate. But water, with strong electrolysis, evaporates especially actively. As a result, the electrolyte level drops, the proportion of water and acid is disrupted, which is why its density increases.
There is another factor. During operation (when discharging) the battery, during chemical reactions, the acid gives up its SO4 radical to lead with the formation of PbSO4 (lead sulfate), which partially settles on the battery plates. And if the boiling-off was not particularly strong (for example, in winter), then the electrolyte level is still normal, but the density decreases, because there is more water than acid. The problem is solved by charging the battery - during this process, acid particles “fall off” from the plates and return to the electrolyte.
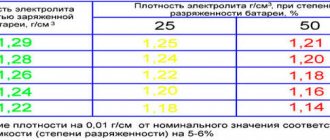
The normal density of the electrolyte is 1.27-1.28 g/cm³ (1.29 g/cm3 is allowed in the northern regions, and 1.25 g/cm3 in the southern regions). This is exactly the indicator that corresponds to the formula “65 to 35”. When water boils away, the density and proportion of acid increases. What happens if this is not fixed?
Firstly, an excess of acid in the electrolyte leads to accelerated wear of the battery plates. Secondly, if you do not add water at all, only acid remains in the electrolyte, which is not enough even to completely cover the battery plates. As a result, they will simply begin to crumble and collapse.
Therefore, it is very important to maintain the correct level of distilled water in the battery - this way you return the electrolyte to its normal state and ensure efficient battery operation. This parameter should be checked approximately every 10-15 thousand kilometers .
Sometimes batteries that the manufacturer declares as maintenance-free are not. It’s just that the caps of the cans are hidden under a sticker with the battery label. It is enough to remove it, open the cans, add water to the norm and extend the life of your battery.
If you have a truly maintenance-free battery that does not have plugs, we do not recommend that you drill holes in it or do other manipulations in order to add water to it and extend its life. Maintenance-free batteries are made using a slightly different technology, which does not involve strong evaporation of water and such a procedure is not provided for in the maintenance regulations.
Do I need to add water or electrolyte?
distilled water is always added to the battery , except in cases of replacing the electrolyte or increasing its density if its ratio has been violated.
For periodic battery maintenance, you should always add only distilled water. Because during normal operation of the battery, only water boils away from the electrolyte and its density increases. The problem is eliminated by reducing the density by adding water.
Topping up the electrolyte may be necessary only if its density is greatly reduced. This means that there is a problem with the battery. For example, liquid leaked through cracks. Then you need to solder the case and add ready-made electrolyte of the correct density. Also, a decrease in density may be a sign of strong sulfation of the plates, but in this case, adding electrolyte will simply not be a very effective way to extend its life.
It won’t last long anyway, because the sulfation process is almost irreversible. The last time it is necessary to top up the electrolyte is when the battery is actively recharging. This also requires eliminating the cause itself, and not just the effect.
How much water should I add to the jars?
Another important condition. Some batteries have a special level (usually on the side of the case) to which you should add water (you cannot overfill).
However, a large number of batteries do not have this level, so how much should you pour?
ONE very simple rule. The plates must be covered with electrolyte by 1 - 1.5 cm (measured with special measuring tubes). At this level, a density of 1.27 g/cm3 is obtained
You shouldn’t pour more, otherwise the density will drop to 1.20 - 1.24 g/cm3 and there is a high probability that the battery may freeze in winter.
Now let's watch a small but useful video.
This is where I end, I think my article was useful to you. Sincerely yours, AUTOBLOGGER
Similar news
- Is it possible to charge a maintenance-free battery? A regular charger...
- Black or cloudy electrolyte in the battery. What to do? Let's sort it out...
- The car battery is frozen. Can this happen and what...
Add a comment Cancel reply
About flushing
We noted earlier that when taking measurements, an opaque liquid can be detected. This indicates that the solution contains destroyed particles of lead plates. If you restore the battery, they must be completely removed. What to put in the battery? First you need to use distilled water. Fill all damaged jars with it, close the lid and mix thoroughly. Don't be afraid to turn the battery upside down.
This way we can better clean the insides of the jar from dirt. After mixing, pour back all the dirt. What should I put into the battery next? Let's use water again. We already know how to fill the battery with water. If after repeated mixing it does not change color, it means that we have removed all the dirt from the plates. Now you can safely pour electrolyte here and measure the density. By adjusting the water and electrolyte levels we will reach the ideal value of 1.28 grams per cubic centimeter.
In what cases should electrolyte be added?
- Linear recharge. The reason is a faulty car charging system, as a result of which the electrolytic fluid boils. You can check the charging system with a multimeter. The charge level at idle and when overloading should not exceed 14.8 V. If you notice streaks on the case and oxidation on metal surfaces near the battery, after eliminating the cause of the malfunction, be sure to check the level and density of the electrolytic fluid. Prolonged operation of the battery while overcharging is dangerous because the plates are exposed, as a result of which they heat up and lose active mass, and a sulfation reaction occurs. You can see a dark coating on the inside of the plugs. It is better not to try to revive the battery by adding electrolyte, but to replace the battery.
- Electrolyte leakage from one of the cans due to damage to the housing. Cracks and chips most often occur due to mechanical damage or freezing of water inside the case in severe frost. If the damage is minor, the housing can be repaired. In this case, you should correctly determine the ratio of electrolyte and distilled water in the battery. If the battery was damaged before use, it is necessary to fill in the electrolyte with the same density that remained in the damaged jar. If the battery was used in a damaged state, add both electrolyte and water, equalizing the density of the damaged and adjacent sections.
- Loss of electrolyte due to the battery being overturned or tipped over.
- Commissioning of dry-charged batteries. This production technology has retained its relevance only for motorcycles. All car batteries are supplied ready for use.
Water inside the battery
How we figured out water AJ - 65%! But it is not simple (from the tap) , but distilled without any impurities (this is necessary for many reasons, if only because the resistance inside decreases, there is no sediment on the plates, etc.).
But its level is not constant. As is known from high temperatures in the engine compartment, from charging the generator (sometimes overcharging ), water can evaporate from the cans, and the electrolyte level drops.
Sulfuric acid does not evaporate, and therefore its concentration begins to increase; this is bad for the battery in several ways:
- High density negatively affects the plates, destroying them
- The level drops, which means the plates are exposed, thereby reducing the battery capacity and it is not able to start your car.
- At high acid concentrations, sulfation of the plates
To avoid this, you must replenish it - add water inside the battery to the required minimum.
Proper battery maintenance
Currently, the industry mainly produces low-maintenance batteries for cars; they require a minimum of care, however, preventive maintenance must be carried out regularly. To service the battery, you must:
- Remove the battery from the car:
- take it to a warm room;
- clean the housing from dirt and salt deposits (do not turn the housing over);
- clean the terminals from deposits with sandpaper; if they are oxidized, wipe dry with a clean rag;
- let it sit for 10-12 hours (you can do it for a day; it is especially important to let the battery “dead” in winter).
Then you should check the electrolyte level in the jars, add distilled water if necessary, and charge the battery. You can’t do without a charger, just like you can’t do without a hydrometer, and it would also be nice to have a multimeter and a load plug. After the battery has settled, we check the voltage without load with a multimeter; it should be in the range of 12.4-12.7 Volts. When connected to the terminals of the load plug, the voltage should not fall below 9.6 V, the load lasts about 5 seconds.
After adding water to the required level, we check the density with a hydrometer; in those jars where we had to add more, the density will be lower accordingly. Then we place the plugs in their places without tightening them, connect the charger to the terminals, if the battery is in fairly good condition, automatic mode is suitable for charging.
The battery is charged most efficiently at room temperature +20ºC; after charging, it is again necessary to let the battery sit, but 5-7 hours is enough. Then we repeat all the checks again, the most optimal values are:
- voltage without load – 12.7 Volts (up to 13.0 V);
- under load – from 9.6 to 10.4 V;
- density – 1.27-1.28 g/cm³.
For northern regions, the electrolyte density can be set higher (up to a value of 1.31); for southern regions, 1.26 g/cm³ is often sufficient. Depending on the type of battery, it is recommended to carry out battery maintenance once or twice a year; low-antimony batteries require maintenance more often, approximately once every 3 months.
Many novice motorists have a question about how to add distilled water to the battery if it is from the category of serviceable batteries. Accordingly, the second question arises, how much liquid needs to be added and whether this can be done independently at home.
How much distilled water should I add to the battery?
In a modern battery, the easiest way is to understand how much distilled water needs to be filled. Its body is made of transparent plastic with a scale printed on it. It is enough to ensure that the level recommended by the manufacturer is not exceeded.
If you have a different type of battery, use the following tips.
- In some batteries, metal or plastic is located just below the neck of the can. The electrolyte level should be 5 mm above the “tongue”.
- If there are no marks in the jar, add distilled water so that the electrolyte level is 10-15 mm higher than the lead plates.
- If you cannot visually determine how much electrolyte is in the jar, take a glass tube, lower it into the compartment, pinch the top with your finger and carefully remove it. The amount of liquid in it will be equal to the distance from the lead plates to the surface of the electrolyte.
Try to follow the pouring rules to achieve the correct ratio of hydrochloric acid to distilled water.
If there is more acid, it will destroy the lead parts of the battery; if there is less acid, the battery will defrost at subzero temperatures.
How to add water to the battery?
First, let's look at the serviceable option - when there are plugs on top of the battery. Everything is elementary here:
First , you need to buy distilled water in a store or make it yourself at home .
Second , just unscrew the plugs on top and look at the plates. If they are bare, the electrolyte level is lower, you need to add so that the water covers them. I’ll tell you how much to pour below.
Third , after adding it, put it on charge; you can use automatic chargers
As you can see, everything is elementary - there are no problems.
Electrolyte
As you and I know, the electrolyte (inside the battery) consists of two main components:
- This is sulfuric acid. Its approximately 35% of the total volume
- Distilled water. Its approximately 65%
When these two substances are mixed, the electrolyte needed for work is obtained, with a density of 1.27 g/cm3. It is not recommended to add more than 35% acid; if you raise the density to 1.3 - 1.4 g/cm3, then at this concentration the lead plates will suffer and may collapse prematurely.
However, it is also not recommended to pour less acid; a reduced density of 1.2 - 1.23 g/cm3 can contribute to the freezing of the electrolyte at extremely negative temperatures (-25, -35 degrees).
That is, this density has been verified by many experiments and is a reference; it is worth noting that in the north up to 1.29 g/cm3 is allowed
Is this water suitable for drinking?
In conclusion, it would not be amiss to answer a question that interests many, which is not directly related to our topic: is it possible to drink distilled water?
Since this is purified water, it does not pose any danger to drinking. Moreover, it was always drunk for gastrointestinal disorders. With proper storage, it does not lose its properties for a long time and can be used as drinking water.
There is no need to waste time preparing it at home. There is always the opportunity to purchase it in specialized stores for motorists. It is often produced in convenient plastic canisters. You can carry them with you in the trunk if there is enough space.
Thus, we learned not only about how much distilled water should be poured into the battery, but also how to do it correctly - so as not to harm the battery.