The vehicle's on-board network is powered by a lead-acid battery with thick or liquid filler. The performance of the battery is affected by both normal wear and negative factors, in particular, the level and density of those components decreases. liquids. When the electrolyte level decreases, it is necessary to add liquid, depending on the measurement results. This will restore capacity and extend the life of the battery.
Adding electrolyte to the battery is necessary when its level decreases.
Why do you need to add electrolyte to the battery?
There are standards that determine the normal density of the electrolyte. The indicator is affected by the season, ambient temperature, and battery age. For example, for the central zone of the Russian Federation, a density of 1.25-1.3 g/cm3 is considered normal. If the battery is frozen or overheated, the density will most likely change, as a result the battery will discharge faster, and as a result, the car may simply not start in the morning and will not be charged from the car’s generator.
If you correctly add electrolyte to the battery, the problem will be solved, unless the reason lies in the natural wear of the battery plates or problems in the vehicle’s on-board network.
What to do with a lower electrolyte density?
So, the problem is this: the battery has stopped holding a charge. Is it worth changing it? Is it possible to add electrolyte to the battery at low density, or can the battery’s performance not be restored? The answer to this question depends on the age of the battery and the hydrometer readings when tested.
If the battery is old enough (for example, it is about 4-5 years old), then its inability to hold a charge is primarily due not even to the density of the electrolyte, but to a violation of the integrity of the plates in the battery banks. In this case, even restoring the previous density indicators will not solve the problem. However, if the battery is relatively new, the problem can be solved by adding electrolyte. The only question is whether it is necessary to fill in the electrolyte?
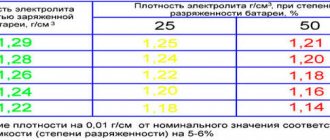
The average electrolyte density in a “working” battery is approximately 1.25-1.30 g/cm³. Moreover, this value should be approximately the same for each battery bank with a deviation of no more than 0.01-0.03. If the density of the electrolyte is less than 1.25, but more than 1.20, most likely adding electrolyte will help solve the problem.
We also watch a video on how to properly increase the density of the electrolyte in a battery: We also recommend reading the article on how to extend the life of a car battery. This article describes the main reasons for a short battery life, how to extend it, and signs that your battery will soon stop working.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Checking the fluid level
Notches for checking the electrolyte level.
You can determine whether electrolyte needs to be topped up in the battery by looking at the control marks on the body
batteries. The marks are located inside or outside the housing. Some battery models have a viewing window made of transparent material. The notches determine the minimum and maximum technical level. liquids. During normal operation the value is in the middle. Manufacturers prohibit the use of batteries with abnormal electrolyte levels.
If there are no notches, they do not allow you to accurately determine whether electrolyte can be added to the battery or not, a glass tube will be required for measurements. To test, you need to clean the battery from dirt and dust, unscrew the plugs, and insert the tube until it stops. Next, the other side is clamped with a finger, so that the liquid remains inside the tube.
As an alternative, you can use a folded sheet of paper for measurements, determining the level by the moistened part.
The level is determined visually. This method does not allow obtaining accurate results, but it is sufficient to ensure the operation of the battery. If the liquid is below normal, it is necessary to add distilled water or electrolyte; if it is higher, pump out the excess using a pear.
The maintenance-free battery has a sealed case where access to the banks is not provided. Accordingly, to check the electrolyte volume you will need to drill holes, which is highly not recommended.
Closer to practice
If everything is clear with the definition of the problem, then the question arises: what is added to the battery - water or electrolyte? The result of measurements with a hydrometer will help with the answer: if the solution is too dense, then adding water will solve the problem. If the solution has too low a density, then you cannot do without an electrolyte.
Let's deal with water. Why is it so important to add distilled or, in extreme cases, melt water? The fact is that bottled water or tap water contains impurities that, when interacting with electricity, will at least produce sediment, and in worst cases will lead to complete deterioration of the battery. Therefore, the most purified water is necessary.
To add water, you will need an ordinary funnel, then charge the battery and re-check the density of the resulting mixture.
What can you add to the battery?
To determine what to add to the battery, you need a special measuring device - a hydrometer. This is a glass tube with a bulb, inside of which there is a float. A scale indicating the density is applied to the outer wall.
Verification algorithm:
Checking the electrolyte level with a hydrometer.
- Charge the battery to 100%.
- After fully charging, wait 3-5 hours for the chemical reaction inside the cans to normalize.
- Unscrew the plugs (if the battery is maintenance-free, drill holes in the housing).
- Immerse the hydrometer in the jar and scoop up the electrolyte with a bulb.
- Take measurements in each section one by one.
Battery Maintenance
After a series of these manipulations, ensuring convenient maintenance, specialists carry out a complete diagnosis of the technical condition of the battery. Basically they consist of six points:
Before deciding what to add to the battery: electrolyte or water, you must fully charge it with a special device.- Next, measure the density in all jars using a hydrometer and record all the results in a notepad. When recording readings, it would be more convenient to put a number on each jar and indicate the value from the scale opposite it.
- If the density readings of a charged battery in some banks differ and are not within the recommended standard (1.25-1.29 g/cc), this means that the driver needs to make an adjustment. It is as follows: if the density reading is low, you need to calculate how much electrolyte to add to the battery and fill it, and if the density is high, add distilled water.
- The density of each can is at its limit, and for some reason the electrolyte level is falling lower and lower. The best solution for this problem is simply adding water.
- Sometimes it happens that the density in sections is lower than the nominal value (less than 1.21 g/cc). To find a solution, you need to take a small acid solution using a special enema and pour it into a measuring cup. Next, record the volume readings and pour the electrolyte into a glass mug. Using the technical table, pour the required amount of high-density sulfuric acid solution into a measuring glass and, using an enema, pour it into the jar from which the electrolyte was taken. In situations where there is a significant difference in the direction of decreasing density, it is best to add acid with a density of 1.40 g/cc. see. It is important to achieve the required level with distilled water.
- After the density has become the same in all banks, you need to connect the battery for a small recharge. This is done so that the recently poured solution is thoroughly mixed inside. After this, measure the density again, and if its level has changed, then repeat the operation.
Every car enthusiast needs to know that before switching to winter operation of the car, it is important to increase the density values in the battery, and lower it when switching to summer time.
And also every day before each departure you need to check not only the oil level in the engine, but also the cleanliness of the battery terminals and the reliability of the plugs on its body.
When to add electrolyte and when to add water?
Under normal conditions, the hydrometer scale shows 1.27-1.30 g/cm3. If the density is less, it means there is a lack of sulfuric acid in the battery, if there is more distilled water. In a standard operating scenario, sulfuric acid from the electrolyte is practically not consumed, so distilled water is often poured into the jars.
It is not recommended to fill in excess fluid above the level - this can lead to the release of acid into the engine compartment.
Pure electrolyte is used both to increase the density and to completely replace the process fluid in the battery banks - the filling volume depends on the battery model.
How to cook it yourself
Before you replace the battery electrolyte yourself, you must take appropriate safety measures and prepare personal protective equipment:
- Gloves
- Apron
- Protective glasses
- Soda solution in case of contact with skin or clothing
- Vinegar or citric acid - to neutralize alkali
Actions should be carried out in a well-ventilated area with an air temperature no higher than +25 C°. You should know in advance how much ready-made electrolyte will be required to fill the batteries. On average, in modern batteries the amount of solution ranges from 2.6 to 3.7 liters. Therefore, you should immediately focus on the maximum quantity. You can use 4 liters of the final solution as a basis.
To prepare the electrolyte, you must prepare the following items in advance:
- Utensils of sufficient capacity, made of material resistant to acid and alkali
- A small stick for stirring the electrolyte
- Tools for measuring density, temperature and solution level
- For an acid electrolyte - sulfur liquid, for an alkaline electrolyte - alkali in solid or liquid form, lithium or silica gel
Important! All materials used must be chemically neutral to avoid the occurrence of unnecessary reactions upon contact. Ordinary glass jars are quite suitable as containers.
The process of preparing alkaline electrolyte
The ingredients for the preparation of this composition can be either in liquid or solid form. If everything is clear with the first one, then before pouring, the alkaline electrolyte from the solid will need to be diluted in distilled water.
The required density is indicated on the battery manufacturer's website, and information can also be found in the attached operating instructions. The solid electrolyte is taken in proportion to the required amount of the final liquid solution and is:
- 1/5 – to obtain a solution with a density of 1.17-1.19 g/m³
- 1/3 – for a solution with a density of 1.19-1.21 g/m³
- 1/2 - for a solution with a density of 1.25-1.27 g/m³
The cooking process consists of the following steps:
- Pour distilled water into the bowl
- Add the required amount of alkali
- Stir the solution
- Close the lid tightly
- Leave for 6 hours
After the infusion process is completed, it is necessary to drain the light solution. If part of the composition precipitates, you need to stir it regularly. When filling, you need to make sure that it remains at the bottom and does not get into the battery, otherwise it threatens to cause the battery to fail.
This is interesting: Correctly charging a calcium battery for your car
Preparation of a solution for lead batteries
Before diluting the acid electrolyte, it is necessary to determine the required proportions. They depend on the climatic conditions in which the device is planned to be used.
To obtain an electrolyte with a density of 1.28 g/m³, which is acceptable for average climatic conditions, you will need to pour 0.36 liters of sulfuric acid into one liter of distilled water. For hot regions, the amount of sulfuric acid is reduced to 0.33 liters for the same amount of water.
How to dilute battery acid:
- Pour distilled water into the prepared container
- Carefully pour the acid into it in a thin stream.
- Measure the density of the resulting solution
- Leave the solution to infuse for 12 hours
Important! You can't pour water into acid! That's right - pour acid into water. Do not rush into adding acid; allow it to gradually dissolve in the water.
Features of maintenance-free batteries
Most batteries on sale are of the maintenance-free type. This decision has both positive and negative sides. In particular, if there is a need to add electrolyte to the jars, you will need to drill the battery case, which breaks the seal and automatically voids the factory warranty. The channels are made with a sharp awl all the way to the lead electrodes. The width of the hole must be sufficient so that a hydrometer tube can be inserted inside, which is necessary to determine the density of the electrolyte and what liquid to pour into a maintenance-free battery.
If the density is normal, but the level needs to be changed, a bulb or syringe will be required. Top up, depending on the hydrometer readings, with distilled water or pure electrolyte. To ensure normal operation of the battery, the technical level. liquid should be 10-15 mm above the edge of the electrode. Thus, it will be completely immersed in liquid, even when the car is parked on a slope, as a result, normal operation is ensured, and the possibility of oxidation of the plates associated with contact with air is eliminated.
Adding electrolyte to a maintenance-free battery.
Upon completion of the procedure for topping up each battery tank, it is recommended to pump the battery, thus speeding up the mixing of acid and distilled water. The IP should be shaken carefully, and under no circumstances should it be turned on its side - this leads to sludge getting between the electrodes, which reduces the service life. The next stage is a control measurement of the level and density of the electrolyte. If there is not enough fluid, it is refilled to the normal value.
The last step is to seal the holes with sealant and fully charge the battery.
What does the battery consist of?
The battery in a car is responsible for starting the engine, the proper operation of all the car’s electrics, and also “smoothes out” voltage surges. Inside the housing, it consists of 6 series-connected elements consisting of positive and negative conductive plates. These elements are filled with electrolyte, interaction with which ensures the result of the work.
The liquid itself consists of distilled water and acid mixed in a certain proportion. The norms of proportions change depending on the required density of the mixture, and the norms of mixture density, in turn, depend on the temperature and climatic characteristics of the area where the car is used.
Complete electrolyte replacement
To completely replace the electrolyte in a battery, you will need to go through several steps:
The battery plugs can be unscrewed with a coin.
- Place the car on a level surface, and before turning off the power, make sure that the driver has service codes from the radio and other equipment necessary to unlock them.
- Open the hood, remove the mounting cover, remove the terminals, wipe the body from dirt, dust, and electrolyte residues.
- Unscrew the cans (for a maintenance-free battery, drill holes).
- To pump out the liquid, take a medical syringe or a rubber bulb with an extension tip attached. During the procedure, you should not turn the battery over - this will prevent sludge from getting into the plates, as a result, the possibility of a short circuit.
- When draining, it can be tilted at an angle of up to 45°, which will simplify the complete pumping out of the electrolyte.
- To completely get rid of the remaining old liquid, you need to rinse the jars several times with distilled water. Slight rocking of the battery is allowed. It will not be possible to completely wash the jars - the solution will still remain in the cavities between the electrodes.
- Pour in new clean electrolyte: level is above the top edge of the electrodes.
- Let the battery sit for 5-6 hours.
- Fully charge the battery with a current of up to 0.1 A. Duration of the procedure is 18-20 hours. To fully restore capacity, you will need to perform 2-3 low-current charge cycles.
- Carry out final charging with a current of 10% of the rated capacity of the battery.
- Check the level and density of the electrolyte, if necessary, bring the values to normal.
- Install the battery on the car and connect it to the on-board network.
Adding electrolyte to the battery normalizes battery operation, allows you to restore capacity, reduces the likelihood of plate sulfation, and eliminates premature failure. You can perform the procedure yourself at home; this does not require special equipment or knowledge.
How does the electrolyte structure change?
Before we figure out what can be put into a battery, let’s consider the processes that occur inside the battery during discharge and charging. This will help avoid mistakes when adding liquid to it.
So, car batteries contain 65 percent distilled water. The rest is sulfuric acid. With this ratio, the density of the electrolyte is about 1.28 grams per cubic centimeter (error up to three percent). This is the optimal level at which the desired voltage is produced. Note that during charging the temperature of this liquid increases. This process is called electrolysis. Gas is released while the battery is charging. In this case, part of the water evaporates. The acid concentration also changes. The electrolyte density increases. At first glance this may seem like a good thing. In fact, high density results in lower battery capacity.
If we consider modern maintenance-free batteries, they have a sealed closed case. Thus, the evaporated water after charging turns into condensate. And after a while it flows back into the “jar” (these are holes in the battery). The characteristics of the solution do not change and the density remains at the same level. Such a battery can last quite a long time - up to five years or more. But if the seal of the housing is broken, the distillate level drops. This negatively affects the battery life and its capacity.
It is worth talking about one more factor, which is called sulfation of the solution. This is a process in which salts from the acid begin to settle on the lead plates themselves. This usually happens when high current is applied or when the battery is idle for a long time (two months or longer). Sulfation also leads to a decrease in battery capacity and a decrease in acid concentration. Therefore, to extend the life of the battery, you need to regularly monitor the concentration of the solution inside and, if necessary, replenish its level.