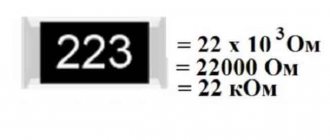Few people pay attention to such an important antifreeze parameter as density. However, the performance of the coolant at low temperatures depends on how well it complies with the standards.
Most often, antifreeze can be bought ready-made, but some car enthusiasts prefer to dilute the concentrate themselves. In order for the resulting mixture to maintain its performance characteristics, certain rules must be followed.
Let's look at how the density of an automobile refrigerant depends on its composition, describe how to measure this indicator and provide some recommendations for its adjustment.
Antifreeze density. How to check and what should it be? A few words about antifreeze
Not many people know, but antifreeze (and antifreeze) can be checked for density.
“For what,” you ask? YES it’s simple - it should be at a normal level, high enough to allow the coolant to work at low and sometimes critically low temperatures. After all, when you buy antifreeze, you don’t know its composition, but what if it’s just water that’s been tinted with regular dye! How to check this? Let's figure it out. As I already wrote above, antifreeze also has its own density, it characterizes exactly the right liquid for your car, it will not freeze, and most likely will not boil (more on this below), many of us do not check this parameter, but in vain! After all, low-quality fluid can cause destruction of the radiator, and in difficult cases the engine block will simply burst.
How is density formed? Indeed, you can - “what causes the density in the coolant, how is it formed there”?
Guys, it’s very simple - density indicates the presence of either acid or alcohol, sometimes salt or even sugar. That is, roughly speaking, it shows how many mass fractions of a particular substance are in distilled water.
Although the composition of antifreeze is not always just water and alcohol, it is usually:
Distilled water Special alcohols, usually propylene glycol or ethylene glycol Additives Dyes Fragrances and surfactants
How to check density? This is usually done with an ordinary hydrometer, a special device that resembles a pear on one side and a flask (with a spout) on the other. It has a special float (inside) with gradation, in fact this is the working mechanism. After you fill the flask with coolant, the float floats up; by a certain amount, if you look at the gradation on the flask, you can find out what your indicator is now.
The indicators are strictly tied to temperature, so it is not uncommon for floats to have a scale of grams per centimeter cubed on one side, and temperature characteristics on the other side. That is, you can immediately find out at what temperature your antifreeze or antifreeze will work
The verification process is very simple, literally anyone can do it, although some may still have questions, then watch this video.
Normal density of antifreeze Well, what have you decided, why measure it and how to do it. But what is a normal indicator is not clear.
Everything here is also simple, it depends only on one parameter, for example, on the freezing temperature, for antifreeze up to -25 it will be one, but up to -40 it will be different. Actually, this is logical because the concentration of active substances in the “strong” version will be greater.
Although it is also worth remembering that ethylene glycol itself, which is used in antifreeze, if not diluted with water, freezes at -13 degrees Celsius! It is important! That is why it cannot be used pure, but only in dilution.
Antifreeze density table
Fake antifreeze or antifreeze Lastly, I would like to say that guys are now on the market, there is a lot of fake coolant, instead of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol, acids and ordinary sugar or salt are used. Such a liquid, initially, will also not freeze at subzero temperatures, and the density indicator will be at the desired level.
BUT the whole problem is that after a short amount of time, the liquid will lose its properties, say, from heating and cooling! And after a month of operation, it will freeze at low temperatures. (Therefore, in a couple of weeks, after replacing the antifreeze, you need to measure the density again to make sure that it remains at the same level. If not (it has fallen critically)! Then such a liquid should be replaced) From experience I will say that now there are a lot of fakes based specifically on cheap acids.
I think the information was useful to you!
PSInformation taken from the website AUTOBLOG AUTOBLOG, link to the article avto-blogger.ru/ozh/plotnost-antifriza.html (read other articles is very interesting)!
Comments 7
The name antifreeze is for the first inhabitants. Commercial name taken from the State Standards Technical Department of Toxins. All these liquids are antifreeze, but they are made, bottled and sold in different ways. In fact, as far as I know, there are only two technologies: carboxyl and lobrid. Lobridna is divided into ethylene glycol G12++ and polypropylene glycol G13. Manufacturers have a lot of confusion in carboxylate technology, thus they have divided into immiscibility by colors, some of them are interrelated.
That's right, there's even a mixing chart,
The name antifreeze is for the first inhabitants. Commercial name taken from the State Standards Technical Department of Toxins. All these liquids are antifreeze, but they are made, bottled and sold in different ways. In fact, as far as I know, there are only two technologies: carboxyl and lobrid. Lobridna is divided into ethylene glycol G12++ and polypropylene glycol G13. Manufacturers have a lot of confusion in carboxylate technology, thus they have divided into immiscibility by colors, some of them are interrelated.
You have the wrong ideas about antifreeze, everything is confused! I recommend an article from professionals: peakauto.ru/blog/ekspertn…riza-iat-oat-hoat-lobrid/
What's wrong? I’m not defending a scientific dissertation, but I described it briefly! As for the G12++ and G13 technology, both lobrides are divided into ethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol and are miscible. Everything else is based on carboxylate technology, a hybrid or something else with the presence of alkalis! So what's wrong there?
You see, you need to understand the issue, otherwise you will mislead others. G12++ and G13 are not a technology, but a brand of VW antifreeze. G12++ is manufactured using lobrid technology. G13 is not a lobride. There is no polypropylene glycol in both, in G12++ - ethylene glycol, in G13 - ethylene glycol + glycerin. You write “only two technologies” - there are many technologies, but indeed, there are two types of additives: mineral or otherwise called inorganic additives, the second - carboxylate or otherwise called organic. A number of statements that you write, unfortunately, I cannot understand the idea, it is very vague and certainly far from the truth.
G13 and G12++ are both lobrid! I knew this personally back in 2012, when I was faced with the lack of OE packaging G12++ and which was a lobride from off. source! Both have glycol and can be mixed. Ethylene glycol + glycerin = polypropylene glycol! Let it be known to you! G13 is more economical. G13 (G12++) - index, belong to the WV concern on a special order from BASF - a giant in the production of masterbatches, and other companies buy masterbatches from it. I won’t explain anything more, here - From the source: In 2005, a new antifreeze was developed and began to be introduced that meets the requirements of the VW TL 774-G (G12++) specification. This antifreeze has taken an intermediate position between the hybrid and carboxylate types, and is most often referred to as lobrid. The additive package of this antifreeze consists mainly of carboxylates with the addition of a small amount (no more than 10%) of inorganic components, which leads to improved technical characteristics compared to hybrid antifreeze. The inorganic components, by analogy with hybrids, are silicates (European producers) or phosphates (Asian producers).
Antifreeze of this type does not yet have a generally accepted name, and developers call it differently - Lobrid (Arteco company) or, for example, SOAT (BASF company). You can also find its designations as Si-OAT, P-OAT, Lobrid coolants. In addition to the Volkswagen group, such antifreezes are used on new car models by the PSA group (Peugeot-Citroen), the Hyundai-KIA concern, and the Mitsubishi company (some modifications since the 2011 model year).
There are still few representatives of Lodrid type antifreezes - these are Glysantin G40 from the German company BASF, Freecor DSC (specification PSA B71 5110) and Freecor QRC (specification VW TL 774-G) from the Belgian company Arteco, Crown LLC A-110 from the Korean company Kukdong.
In 2008, a new specification VW TL 774-J (G 13) also appeared for Lodrid antifreezes, in which the base component ethylene glycol is partially replaced by glycerol (up to 20% by volume). Glycerin has similar properties to ethylene glycol, but is less harmful to the environment. At the same time, its production requires less energy resources. That is, the use of glycerin is largely due to increasing environmental requirements. It is possible to assume that logical questions may follow about the effect of glycerin on the crystallization temperature of the finished antifreeze. In fact, a small (up to 20%) amount of this component has little effect on the freezing point of antifreeze, so the temperature characteristics remain the same as those of conventional lobride antifreeze. According to available information, such antifreezes are currently used only on VW group vehicles.
Why did I write that G13 is not a lobride - because strictly speaking, it is an antifreeze unlike anything else, with glycerin. Well, ok, based on the composition of the additives it can be called a lobride - because. despite the carboxylate package, it also contains silicates (looked at the VW specification). In general, the source you quoted is much closer to the truth. And what they wrote “on their own” is complete nonsense. Although there are mistakes in the source, for example, “There are still few representatives of Lodrid type antifreezes...” - maybe once there were a few, but now there are many more than those listed. “by special order from BASF” - where does the information come from that antifreeze for VW is produced by BASF? According to my data - not only BASF (in different periods of time).
Source
Battery hydrometer
Car hydrometer In addition to universal instruments for measuring the density of electrolyte, special hydrometers are also produced.
In addition to the digital designation of the scale, color markings are also made on the devices: green zone - everything is normal, red - low density, etc. Having determined the density in this way, the car owner already knows what he needs to do - either add water or acid.
Electrolyte measurements are slightly complicated by its poor transparency. It is better to take measurements by first lowering your gaze below the surface of the liquid, and then slowly raising your eyes until the scale and the upper boundary of the substance become one line.
Checking battery electrolyte density at home
Measuring density is a fairly simple process and does not require special skills. The sequence of actions when measuring the density of a liquid with a car hydrometer with a bulb:
- the battery is removed from the car and brought indoors (leave for 5–6 hours so that the electrolyte warms up to room temperature, approximately 20 °C);
- the plugs are unscrewed from the battery;
- the hydrometer pipette is immersed in the first battery jar and the electrolyte is collected using a bulb;
- only after the hydrometer has completely stopped in the flask should the test result be recorded;
- then all battery banks are checked in the same sequence;
- Based on the measurement results, a decision is made to add water or acid.
During work, it is important to remember that the electrolyte is a solution of sulfuric acid, so safety rules must be followed. Use gloves and be careful not to get it on exposed skin, clothing, or especially your eyes.
How to use a hydrometer with sticks
In addition to the devices mentioned, stick hydrometers are also quite common. They work according to the following principle: the flask is filled with electrolyte, and depending on its density, a float of a certain color floats to the surface. The correspondence between the colors of the sticks and the density is indicated on the body of the device.
To take readings correctly, you should not rush when working with such a device. After taking a sample of electrolyte from the battery, you need to wait 10 - 15 seconds. When taking measurements at the density edge, the indicator may appear with a slight delay.
What is antifreeze density and how to check it yourself
In the process of servicing cars, owners have to periodically change some consumables, as well as check their current condition. This makes it clear whether it is time to drain this or that liquid, or whether it can still serve normally for some time.
Antifreeze can easily be considered one of the most important fluids in a car. It is also coolant or simply coolant.
In addition to draining and replacing antifreeze, motorists often check the density. Not everyone understands why to do this and how to perform such a procedure.
Let's consider the main parameters by which antifreeze can be distinguished from antifreeze:
Not many drivers know that antifreeze is a name developed by Soviet scientists, and the name antifreeze refers to the globally accepted name for liquids for cooling car systems.
All antifreezes are divided into mineral, organic and lobrid. Domestic antifreeze can be classified as mineral - class G 11. Imported liquids are coolers of classes G 12, G 12 +, G 12 ++ and G 13, i.e. consist of components of organic and lobride origin.
Antifreeze is used in cars exclusively of domestic production, antifreeze is used in both imported and domestic cars.
In order to measure the density of antifreeze, you cannot use a device that is designed to measure the density of antifreeze.
For coolers, there are parameters according to which they differ - these are boiling and freezing temperatures, lubricating and anti-corrosion properties.
Antifreeze is mainly blue, and antifreeze has a relatively wide range of colors - it can be green, purple, red, orange, pink and other colors.
According to the above parameters, we can summarize that it is possible to distinguish antifreeze from antifreeze only by the number of additives, additives and dyes contained in them, which primarily affect their properties.
Why do you need to check density?
In itself, checking the density of the antifreeze used to cool the engine is not difficult. Even a beginner can handle it.
Another question is why do this at all.
Coolant density is a characteristic that reflects the percentage of alcohol (ethylene glycol) in the working fluid. And density directly affects the temperature at which the process of crystallization, that is, freezing, begins.
In this case, antifreeze and antifreeze can be considered identical liquids.
You need to understand how density affects the freezing point of the coolant. For ordinary distilled water, the density is 1. In this case, it will freeze at 0 degrees Celsius. This is a well-known fact.
In the case of antifreeze, the principle does not work in which an increase in the amount of ethylene glycol in the coolant increases the freezing point.
That is, the lowest possible freezing threshold is achieved only through certain proportions. As the percentage of ethylene glycol in antifreeze increases, the resulting mixture will freeze at a lower temperature.
This is why density testing is carried out. Moreover, it is recommended to check the liquid already used in the cooling system, as well as the one purchased in the store. This will make it clear what condition the coolant is in the car, or what will be replaced, and how suitable this antifreeze is.
Basically, the problem of insufficient density is solved. Although it is possible that the test may show that the recommended ratio of water and alcohol is exceeded. Both situations are undesirable, since they lead to possible freezing of the coolant during severe frosts.
General information about antifreeze
During summer operation, the most economical method of cooling the engine is water. At low atmospheric temperatures, in order to avoid defrosting of the unit, alcohol-containing water-soluble mixtures are used - antifreeze.
The most common types of antifreeze compounds are chemical compounds of ethylene glycols with distilled water. Ethylene glycols are transparent yellow liquids, boil at a temperature of - plus 197°C, crystallize at minus 70°C, and the density of the substances is 1.112 g/cm3.
By changing the volumetric ratio of liquid and alcohol, you can lower or increase the density value, and therefore control the physical properties of coolers.
Our industry produces two brands of low-freezing liquids based on glycols – OZh-40 and OZh-65, with a crystallization threshold of 40 and – 65°C, respectively. To easily recognize the type of antifreeze, the reagents are painted in different colors: grade 40 is blue, grade 65 is red.
The density of the solution is not the only indicator of the quality of the liquid. In factory conditions, the acceptance of antifreeze compositions is carried out according to a number of characteristics:
- Homogeneity of mixtures.
- The ratio of the volume of active components (alcohol, water, additives).
- Upper and lower temperature limits for changes in the aggregative state of the solution (boiling, crystallization).
- Compatibility of the chemical properties of coolants with the physical and chemical characteristics of engine materials in contact with the liquid. (copper, brass, rubber, etc.).
Antifreeze must meet the following performance requirements:
- maximum thermal conductivity;
- optimal viscosity – 1 mm2/s;
- freezing temperature not lower than 65°C;
- liquid boiling – no higher than 120°C;
- high physical stability.
Of all the listed properties, only two parameters are available to the average consumer - measuring the density of the solution and assessing the appearance of the liquid.
Verification methods
There are several options for checking the density of antifreeze with your own hands. Moreover, such procedures are easy to perform at home or in the garage.
Before measuring the current density of antifreeze, you should decide on the method used. Each of them requires the presence of certain devices.
To check the current density of antifreeze at home, you can use:
With such measurements of the density of antifreeze, the motorist will find out the current state of the liquid and decide on further actions with it.
Hydrometer
The easiest way to check the current density of filled or purchased antifreeze is with a hydrometer.
This is an affordable measuring device that clearly reflects the density values of automotive antifreeze. You can purchase it at any auto parts store. The purchase will cost an extremely modest amount.
Now briefly about how you can measure the density of antifreeze using a conventional hydrometer:
It is on the scale that it is easy to determine the current density relevant for antifreeze.
For the result to be accurate, measurements must be taken at an ambient temperature of 15–20 degrees Celsius.
If it is cold or hot, then the data will be incorrect.
Refractometer
There is another option for measuring the density of antifreeze using a special refractometer.
It perfectly displays the density of both green antifreeze and red, for example. Color does not play a special role here, since this does not affect the density of antifreeze.
A refractometer is much more expensive than a hydrometer, but the data accuracy is higher.
To check the current density of antifreeze, the following manipulations should be performed with the coolant and the measuring device:
Using the device is extremely simple. Plus, the measurement accuracy is noticeably higher. The only problem is that not every car enthusiast is ready to spend that kind of money.
Folk way
In some cases, the density parameters of antifreeze are checked using a simple folk method.
Actually there are 2 options here:
The experiment is extremely simple. The idea is to take a small amount of coolant, pour it into a container and expose it to low temperatures. If it's outdoors, just use an outdoor thermometer to accurately know the current temperature. The freezers of modern household appliances have a regulator.
Thus, it will be possible to understand at what temperature the composition crystallizes and how many degrees below zero it can withstand.
Normal indicators
It is very important to know about the normal density of antifreeze in order to build on these values and draw conclusions based on the measurement results.
Experiments show that the current density of antifreeze will change depending on the temperature. The only question is what indicator is considered the norm.
To determine the proper level, a special table will help. It reflects the density of antifreeze, such as G11 or G12, for example.
But if the concentration is higher or lower than normal, then there is a possibility of freezing already at 10–20 degrees Celsius below zero.
The most convenient way is to use an information table. By comparing the parameters obtained as a result of testing with the data from the table, you can understand at what temperature the coolant used will freeze.
How to spot fake antifreeze
When purchasing, it is almost impossible to determine the “wrong” antifreeze, even with the help of a hydrometer.
Recently, scammers have been actively using acids, sugar, and salt to dilute with water and create “antifreeze,” instead of the necessary ethylene glycol. Accordingly, when measuring such mixtures with a hydrometer, their density will be at the correct level. The problem is that counterfeit antifreeze, unlike real antifreeze, loses its properties faster during operation. That is, it is enough for it to work in the coolant cycle for several weeks - constantly heating and cooling - and it will become unusable.
To ensure the quality of antifreeze, you must first check it with a hydrometer. If the indicator is normal, the liquid can be poured into the car and driven for a week. After a week, you need to take the liquid from the radiator with a hydrometer for density analysis:
- If the indicator has not changed, everything is fine;
- If the change is insignificant, repeat the check in a week;
- If it has changed significantly, you need to drain the antifreeze and add new one.
Operating a car with counterfeit coolant will quickly lead to engine failure.
( 443 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)
Related Posts
Express oil change in a car engine
Raptor paint for car body protection
Density adjustment
Based on the table above, it becomes clear that the increased density indicator needs to be reduced, and the decreased one needs to be raised.
At the same time, practice shows that most often it is necessary to improve the characteristics.
To make the adjustment, you need to arm yourself with a hydrometer, ethylene glycol concentrate and data on the volume of the cooling system.
For clarity, it is worth considering the adjustment using a specific example. The conditions are as follows:
That is, the task is to increase the density in 7 liters of liquid to 1.06.
At 1.05 the percentage of ethylene glycol is about 35%. And this is 2.5 liters of the total volume of the system. And for the density to rise to 1.06, the proportion of ethylene glycol must be 45%. That is 3.1 liters of volume. Everything else will come from distilled water. In this case, you need to add 600 ml of concentrate, since 3.1-2.5 = 0.6 l.
To adjust you need:
Now the engine needs to be allowed to run so that the liquid begins to circulate through the system and can be completely mixed.
How much does a 5 liter plastic bottle weigh?
Do you know how much one plastic bottle weighs on average? Let's take one of the most popular containers - 1.5 liters. Its weight will be 41 grams.
Interesting materials:
How to insulate a bathhouse from the inside with your own? How to insulate a door in a private house? How to clarify SNILS? How is the shift schedule approved? How to notify a tenant of termination of a lease? How to notify about a residence permit? How to increase the net assets of an enterprise? How to increase FPS in Pubg Mobile? How to enlarge a T-shirt? How to increase the volume through the Samsung engineering menu?
Authentication
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to identify counterfeit antifreeze when purchasing. To do this, you can only submit samples for analysis, spending a lot of time and money.
But there is a much simpler verification option.
Fake and low-quality antifreeze quickly loses its characteristics.
This is due to the fact that in order to reduce the cost of production, scammers replace ethylene glycol with sugar, salt, acid, etc. That is, when checked with a hydrometer, the density parameters will be normal. But in practice, such a liquid will freeze even in slight frost.
To check the quality of the coolant, you need to make an initial control measurement. If it is normal, the composition is poured into the cooling system. During the week you can drive a car. Then, after a week, the coolant is taken from the car and the density is checked again:
If you continue to operate a car with low-quality fluid, this will negatively affect the condition of the engine. Antifreeze can damage the internal combustion engine and cause a number of unpleasant and expensive malfunctions.
Source
How not to buy a fake
High-quality antifreeze has the required amount of special additives and density specified at the factory. All this provides reliable protection for the car engine from sudden temperature changes.
Even at low values exceeding the recommended values, the solution, in case of freezing, will turn into a plastic jelly-like mass and will not damage the structural elements of the motor.
If, instead of a conditioned liquid, a counterfeit is poured into the cooling system, then when the temperature drops below 0°C, such a mixture will expand and increase in volume. Having reached a critical threshold, frozen antifreeze will tear the cooling jacket, radiator and engine water pump.
When purchasing, you can check the quality of the coolant using a mobile hydrometer (flask with a bulb) or litmus paper. When immersed in liquid, it should change its neutral color to the color of the purchased antifreeze.
A more complex test method will be more convenient to carry out at home. It is intended to test a solution for the presence of sulfuric or perchloric acid in its composition.
Antifreeze is poured into a separate capacious container. Add a small amount of soda to it. If the coolant is normal, then no reaction will follow, but if the liquid begins to foam and hiss, this is an irrefutable fact of the presence of acidic reagents in the mixture.
When choosing antifreeze, it is recommended to buy only from trusted places and purchase coolant brands from well-known manufacturers.
Source
Density of antifreeze. How to measure and what does it affect?
Most car enthusiasts do not take the liquid poured into the car radiator seriously. But this is not just water, it has technical characteristics. For example, the density of antifreeze can tell about its quality and ability to perform its task.
To begin with, let’s resolve the well-known debate: “antifreeze or antifreeze?” In fact, this is nothing more than a play on words. The concept of “antifreeze” is a generally accepted transliteration of the Latin “antifreeze” (translated as non-freezing).
This group includes any coolant that can remain liquid at sub-zero temperatures. And “Tosol” is a domestic development with its own name. TOS is a technology of organic synthesis, the ending “ol” indicates the content of alcohols in it (these liquids also have the ending “ol”).
Should you mix antifreeze with water?
It is not worth purposefully diluting antifreeze with water to save money. If it’s a pity to throw out a properly working composition, but its level is not high enough, then it makes sense to add filtered or distilled water to maintain the volume. For example, if about 200 ml is missing from the standard level. But is it possible to dilute antifreeze with water, if we are talking about large volumes of the missing composition? Theoretically, it is possible, however, as in the case of combining two antifreezes, the risk of changing performance properties increases. The use of water is preferable in the sense that it does not lead to extreme modifications of the antifreeze with the precipitation of certain components. However, with large mixing proportions, it may well weaken the anti-corrosion properties and reduce the temperature resistance limits by 15-20%.
What are antifreezes and antifreezes made of?
Like motor oils, coolant is created from a base. In this case it is water. Only not simple, but distilled and thoroughly purified. Natural salts that are present in water cause deposits in engine cooling jackets and also contribute to corrosion.
The main task of this component is to lower the freezing level of antifreeze. Depending on the concentration, the mixture can remain liquid in the range from - 5 °C to - 90 °C.
What is it for? When freezing, any liquid expands. If ice forms in the engine cooling system, it will simply burst from the inside. At the very least, the cooling radiator will crack.
In addition, a number of additives are added to the coolant:
The ratio of water, antifreeze components, and, to a lesser extent, additives determines the density of antifreeze and antifreeze.
How to use an optical refractometer?
The sequence of actions performed depends on the type of refractometer. With an analog refractometer, the sample is placed on a lid and prism and then held up to the light to view a scale that is located inside the housing.
Digital refractometers require that a drop of the test solution be placed in a special well. This well is illuminated by a light source, usually an LED, and the measuring device interprets the light transmittance into a refractive index or whatever unit of measurement the device is programmed to read.
To obtain the result, it is enough to place 2...4 drops of the test liquid in the prism or well and secure the lid - this will increase the accuracy of the measurement, since the liquid will be more evenly distributed over the prism. Then (for an optical device) you should point the prism section of the refractometer at the light source and focus the eyepiece until the scale is clearly visible.
The scale is read at the point where the dark and light areas meet. For a digital refractometer, the desired result is displayed after a few seconds on the display screen.
The reference temperature for measurements is considered to be 200C, although automatic compensation is designed for the range 0...300C. The length of the refractometer does not exceed 160…200 mm. It should be kept dry and clean.
An antifreeze refractometer is suitable for determining the concentration of lubricating oils if their refractive indices are within the technological range of this device. To do this, first prepare a Brix diagram and convert the obtained values into an indicator of the density of the measured medium.
What does density affect?
The density of antifreeze itself is not a factor that determines any unique properties. Rather, it is a status indicator. Simply by mixing the base with additives, a certain specific gravity of antifreeze and antifreeze is formed.
In relation to the density of pure water equal to unity, a certain coefficient appears. It shows the mass fraction of additional substances dissolved in distilled water.
Determining the quality of antifreeze without special tools - video
Too high an indicator leads to thickening of the “anti-freeze”. This is an additional load on the pump impeller. In addition, too viscous antifreeze does not circulate as effectively through the channels of the cooling jacket, reducing the efficiency of heat transfer. Undesirable deposits appear in the small cells of the radiator.
If the density of antifreeze tends to unity, this indicates a critically low concentration of additives. This is not bad for cooling; clean water has the best thermal conductivity.
It clearly shows how nonlinearly (and at first glance illogically) the freezing temperature changes depending on the mass fraction of additives.
What is a hydrometer
First, what is the density of an electrolyte - this is the specific gravity of the acid in distilled water in relation to the total volume of the entire solution. In other words, the acidity of the mixture.
The density of any liquid is measured by an instrument called a hydrometer, which works on the principles of Archimedes' law. The density of the acid solution in the battery is determined by the depth of the device’s immersion, that is, by the volume of liquid that it was able to displace with its own weight.
There are different types of hydrometers, depending on the liquid being measured, one or another model is used. We are more interested in measuring the density of battery electrolyte or, more simply, a car hydrometer.
How to measure coolant density?
First, let's figure out why the density changes.
If you do not monitor this process, you can either overheat the engine with too thick coolant, or on the contrary: in cold weather, crystallization will occur, and the radiator will leak due to expansion. In the most advanced cases, the cylinder head may crack.
Therefore, it is necessary to check the density of the antifreeze at least 2 times a year (when the seasons change) in the same way as the density of the electrolyte in the battery. For this you need a regular hydrometer.
The indicators are measured at an antifreeze temperature of about +20°C. This has nothing to do with regional operating conditions; manufacturers simply adopted such a standard for uniformity of measurements.
When checking, you will need to drain some of the liquid from the expansion tank (you can bring the container into the room to create temperature conditions). If the outside temperature allows, measurements are taken directly in the tank.
After measurement, if the density does not meet the established standards, the concentration should be changed. To do this, it is not necessary to drain all the antifreeze and dilute it again.
Knowing the volume of coolant in the system, you can simply add concentrate or distilled water to the expander tank (depending on the hydrometer readings). Of course, you must first select excess liquid.
We measure the density of antifreeze directly from the car’s tank - video
Then you should start the engine (for mixing) and measure the density again.
How to measure with a hydrometer
It is necessary to squeeze the bulb well, and then immerse the pipette in the liquid. Slowly release the bulb, thereby filling the flask with the hydrometer located in it with the substance to be measured. There should be no air bubbles left in the flask; if there are any, twist the device a little. Holding the device in a vertical position, wait until the hydrometer inside has completely stopped. The coincidence of the liquid level and the mark on the hydrometer scale will indicate the density value.
Important! To obtain accurate readings, the hydrometer should not come into contact with the body of the flask.
For greater accuracy, measurements should be taken at a liquid temperature close to 20 °C. Otherwise, the resulting value must be adjusted in accordance with the table.
Temperature correction table
| Temperature of the substance being measured, oC | — 20 | — 10 | + 10 | + 20 | + 30 | + 40 |
| Amendment | ||||||
| Antifreeze, oC | + 27 | + 21 | + 12 | + 5 | — 7 | — 12 |
| Electrolyte, g/cm3 | — 0.035 | — 0.025 | — 0.014 | — 0.007 | +0.007 | +0.014 |
Properties of antifreeze that are important during their operation
They are as follows:
- Operation over a long period of time. Without replacing the coolant, antifreeze systems can be safely used for a long time. This also achieves an increase in the service life of the entire heating or ventilation system as a whole.
- Antifreezes are resistant to corrosion. It is thanks to the presence of special additives in antifreeze that rust does not form inside heating systems. This helps to increase the efficiency of heating the room, and at the same time significantly reduces energy costs.
- Cavitation resistance. In ordinary water, if the pressure in the system decreases, bubbles will inevitably appear. This is not the case with antifreeze. Thus, they also protect systems from water hammer and vibrations.
In the production of antifreeze, additives are necessarily used. Not using these components in propylene glycol or ethylene glycol would be unjustified from an economic point of view.