The uninterrupted operation of the power unit depends on the serviceability of each individual element. If a characteristic metallic knock is noticed during its operation, this is usually caused by wear or rotation of the upper/lower sliding element. In this case, replacing the engine liner is carried out quickly in order to protect the engine from major repairs.
How to replace bearings without removing the engine?
To replace the liners successfully, it is not at all necessary to dismantle the motor. If you are assured that it is impossible to get to them without removing and pulling the engine out of the hood, urgently change the car service center. But be sure to take into account one condition - the crankshaft (CV) should not be worn out. Otherwise, you won’t be able to do without removing the engine and completely disassembling it!
Without dismantling the power unit, it is easier to change the connecting rod bearings; it is more difficult to change the main bearings. For the latter case, you need to loosen the fastenings and release the crankshaft by 10-15 cm. Although there is another method, adopted by our grandfathers from ship motorists. The main bearings are pushed out using a soft rivet or bolt, which is inserted into the desired lubrication passage and rotated clockwise. The main thing is that the size of the aluminum insert should be slightly smaller than the hole and not scratch the crankshaft.
After removing the half rings, it is imperative to evaluate their condition. If there are no visible scuffs or damage, you can get by with a simple replacement. However, if it is very worn, polishing the HF is mandatory. Therefore, you will have to remove it from the mounts, and to do this, pull out the motor.
More information about condition assessment:
- pits or pockets - fatigue wear;
- scratches and ingrained dirt - low-quality motor oil;
- worn surface - insufficient amount of lubricant;
- chamfers on the edge - taper of the necks.
Materials
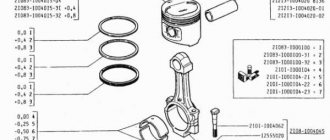
The liner is a steel strip with an anti-friction coating applied to it. Various alloys are used as this coating, based on copper, aluminum, and lead. Alloys based on aluminum and copper are equivalent in terms of load-bearing characteristics, but alloys of aluminum and tin will quickly break in to the shaft journal, are less susceptible to wear, wear out the journal less, and are less sensitive to oil quality.
In diesel engines, liners based on steel and aluminum are used. Alloys such as A020 and A06 are often used as antifriction materials. In carburetor gasoline power units, AMO1-20 alloys with an intermediate layer of pure aluminum are used. Heavy-duty KamAZ trucks use connecting rod bearings made of steel and bronze. BrS30 alloy will be used as an antifriction layer.
Parts made from durable materials additionally have a very thin layer of lead and tin. The layer, despite its thickness of only 0.02 millimeters, can significantly improve the adaptability of the liner to defects and deformations of the shaft journal and better absorb abrasive particles. The fatigue strength of the base antifriction coating increases.
Replacement procedure and marking of liners
Below are instructions for independent work. Replacing the engine liner will be faster and easier if you do it consistently.
- Place the car in a repair pit. Remove the power unit protective cover, if present. Place a jack under one of the drive wheels. Be sure to drain the engine oil.
- Remove exhaust pants and other components that interfere with work from below. Also unscrew the suspensions connecting the engine to the gearbox. Loosen the camshaft chain, remove the starter, and on some cars, the beam.
- Remove the oil pan bolts, nuts and studs.
- Rotate the wheel to move the connecting rods to the most convenient position for unscrewing the bolts. They are tightened with a force of approximately 3 kg, so you need to select the appropriate tool (usually a socket of the appropriate size with an extension). After tearing off the pins, you can continue to unscrew them by hand.
- Remove the half rings along with the connecting rod caps by pulling down. Be sure to check the condition of the internal surfaces of the half rings.
- Pull out the main bearings using a pusher - a bolt of a suitable size or rivet.
- Install a new set of half rings, tighten and reassemble everything in reverse order.
For quick installation of half rings, the connecting rod is completely raised up, moved to the side and lowered. Now nothing will interfere with the work, the sliding element can be inserted faster. Then the connecting rod is put in place.
It is important to tighten the fastener bolts tightly so that they do not loosen after the car has been driven for a long time and cause a malfunction, such as spinning. To do this, tightening is carried out at a specific moment:
The connecting rod bearings are marked with numbers directly on the head. After the initial grinding of the HF, bearings with a size of 0.25 mm are installed. After the second - 0.5 mm, and after the third - 0.75 mm. The latest size is 1 cm. There is no point in processing the crankshaft further.
To ensure that replacing the crankshaft liners without removing the crankshaft is successful, it is recommended to entrust the selection of parts to a specialist. It will correctly calculate the size and you won’t have to reinstall the parts again.
When is it necessary to replace crankshaft bearings?
The HF engine experiences heavy loads. Just look at the vibration on the axis, which invariably occurs during the operation of the crankshaft. It is clear that the sliding bearings also suffer, because they take the blow first.
- Physical wear is the main reason when an engine liner needs to be replaced. The surfaces of parts wear out, backlash and vibration increase. Naturally, in such conditions the engine is in danger of knocking.
- Rotation is the second reason. More details about this are written below.
Thus, replacement of liners is required in several cases. Problems can be judged by various signs. For example, by the absence or presence of abrasive inside the lubricant. Also, a symptom of half-ring wear is low interference when installing the connecting rod cap.
Regarding factors that lead to wear or turning:
- dirty or too viscous lubricant - impurities and abrasive particles reduce the properties of the lubricant, and in general its cleanliness is one of the key rules of prevention;
- constant overload of the internal combustion engine - you cannot drive for a long time at high speeds, from time to time you need to pause, slowing down to 80-90 km/h;
- incorrect installation of half rings during a previous repair - as a rule, this occurs due to weak tension (insufficient clamping torque), so tightening must be carried out using a torque wrench.
Geometry
Naturally, the sizes of connecting rod bearings are different for different internal combustion engines. The most basic parameter is the oil gap. It is equal to the difference between the inner diameter of the liner and the diameter of the shaft. Another important indicator is the size of the oil gap. If the gap is very large, then the oil flow increases, which reduces the heating of the bearing. But oil also causes uneven load distribution, which increases the likelihood of bearing failure due to fatigue. A large gap will result in operating noise and vibration. A small gap will cause the engine oil to overheat and reduce viscosity.
The landing tension is needed to ensure a reliable fit of the VAZ connecting rod bearing in its socket. Reliably and firmly seated bearings are in even contact with the surface of the seat - this will prevent the possibility of bearings moving during operation. Effective heat dissipation is also ensured.
Rotated liners: what does this mean and why do they rotate?
Rotating the engine bearings is a change in their position relative to the crankshaft journal or block. As mentioned above, this is caused by the colossal loads to which the parts are subjected. Shifting the bearings from their place immediately negatively affects the flow of oil. His pressure worsens, starvation begins and the power unit is destroyed. And all because the half rings are equipped with holes that must clearly coincide with the channels for the passage of lubricant.
The main reasons for cranking
There are several known reasons that cause elements to rotate:
- banal wear - the end parts of the sliding bearings wear out (support collars, stops, antennae), which are no longer able to hold the parts in one place;
- weak, incorrect fixation of the covers - the half-rings must be tightened with a certain torque specified in the passport data.
And of course, this arises due to a violation of the design operating conditions of the plain bearings themselves. In other words, due to a large and uneven load. This happens especially often with half rings with weak tension.
Rotating sliding parts can cause big troubles and therefore requires urgent intervention. The most dangerous is the shift of the main bearings. In this case, the power unit will definitely need an expensive overhaul.
It is noteworthy that when the connecting rod half ring rotates, it is simply updated. However, it is wrong to do so - because the resource of the mating connecting rod-pin pair in this case is reduced by almost 70%. Therefore, it is necessary to replace the connecting rod itself, in which a broken lock can often be found. And the most optimal method of repair is considered to be boring the crankshaft and replacing the complete liners, along with the connecting rods.
Causes of wear
As mentioned above, when the engine is running, each main liner of the engine is constantly exposed to a frictional force, tending to displace it from its original location. In the original state of a working engine, the strength of the parts is calculated with a margin in order to withstand such loads. For power units up to 200 hp. With. The stress on the liner ranges from 0.1 to 1 kgf. The magnitude of its force is proportional to the load at a constant coefficient of friction.
In addition, the main liners are protected by the fact that they operate in liquid friction mode. This is ensured by the use of oil, which creates a film between the shaft journal and the working surface of the liner. In this way, the parts in question are protected from direct contact and a minimum friction force is achieved. The formation of an oil film is determined by the speed of mutual movement of the rubbing parts. As it increases, the hydrodynamic friction regime increases. This term refers to an increase in the efficiency of pulling the film into the gap and an increase in its thickness as a result. However, as the speed of the parts increases, the amount of heat generated during friction also increases, and, consequently, the oil temperature increases. This leads to its liquefaction, resulting in a decrease in film thickness. Therefore, for optimal operation it is necessary to achieve a balance between the considered processes.
If the integrity of the oil film is damaged, the friction coefficient increases. As a result, the cranking torque generated by the crankshaft increases even under constant load.
However, sometimes the opposite situation occurs when increased loads for some reason lead to a decrease in the thickness of the oil film. Also, as a result of this, the temperature increases, especially in the friction zone. As a result, the lubricant dilutes, further reducing the thickness.
These processes can be interconnected and manifest together. That is, one of them may be a consequence of the other.
Therefore, the cranking torque is significantly influenced by the viscosity of the oil. The relationship between these factors is directly proportional, that is, the higher it is, the greater the friction force. In addition, with high viscosity, the oil wedge increases. However, if the viscosity is excessive, the oil does not flow into the friction zone in sufficient volumes, as a result of which the thickness of the oil wedge decreases. As a result, the effect of oil viscosity on bearing rotation cannot be determined unambiguously. Therefore, another property of this material is taken into account: lubricity, which is understood as the strength of its adhesion to the working surface.
The friction coefficient is determined by the roughness and accuracy of the geometry of the contacting surfaces, as well as the presence of foreign particles in the lubricant. In the case of the presence of particles in the lubricant or surface irregularities, the film is disrupted, as a result of which a semi-dry friction mode appears in some areas. Moreover, these factors manifest themselves most intensively at the beginning of the vehicle’s operation, when parts are running in, so rubbing parts are especially sensitive to overloads during this period.
In addition, the crankshaft main bearings rotate due to insufficient force holding them in place. It may be due to improper installation or be a consequence of wear as a result of the influence of the turning torque.
The difference between main bearings and connecting rod bearings
The radical semirings sit in the lower cavity of the BC. They are also located in separate beds, like the connecting rod ones. Their purpose is to facilitate smooth rotation of the crankshaft and serve as supports for it when the latter is installed in the BC of the power unit. They are in direct contact with the root journals. On 4-cylinder engines, 5 main plain bearings are usually used. They are equipped with grooves and holes for better lubricant supply.
The connecting rod bearings are installed at the very bottom of the pan. They are pressed into the connecting rod (head) caps. Mounted on connecting rod journals. Compared to radical half rings, they have a simpler design.
Specialists and experienced drivers are able to distinguish wear of main and connecting rod bearings by sound:
- the main ones knock dully, a metallic clang is heard - usually during sharp acceleration or at idle;
- connecting rod ones are almost the same, but the sound is much sharper, and the frequency of the noise increases with increasing speed.
Selection of crankshaft liners
In most cases, the selection is entrusted to a specialist. But after studying the information in detail, you will be able to do this on your own. In addition to the fact that it is necessary to combine spare parts with the car model, the general condition of the vehicle is also taken into account.
Selection of main liners
Some useful recommendations for selecting a new HF when replacing the crankshaft liners:
- it is better to buy basic elements of the same color as the standard ones (used, old);
- Be sure to check the markings directly on the shaft.
A special identification color selection card is issued for main bearings. For example, for a 4-cylinder engine, the markings applied to the BC and the CV assembly are used. If marked C3, then you can install yellow and green elements. More details about the colors in the picture below.
And this is an identification card for 6-cylinder engines.
Selection of connecting rod bearings
And here, if the HF is new, the plain bearings are selected according to the diagram. If the color code is lost, you need to look at the markings on the connecting rod caps.
Below is an identification card for selecting connecting rod half rings for four-cylinder power units.
And this is the color map for 6-cylinder units.
The choice of bearings also depends on the antifriction coating. As a rule, it consists of several layers:
- biometallic with a steel base (1-4 mm) - lead, copper, zinc, tin, silicon and aluminum;
- trimetallic - lead, tin, copper.
Use the correct engine oil that meets all the requirements and approvals of the engine manufacturer. It is also necessary to update the filter promptly to prevent abrasive particles from entering the lubricant. It is also not recommended to overload the engine. All this will extend the service life of the liners by almost 2-3 times.
Performance characteristics of motor 21083
VAZ-2101-2107 crankshaft support half-ring repair kit
In theory, the technical characteristics of the ICE 2108 should have satisfied the travel modes of the three-door hatchback VAZ 2108. In practice, tuning was required to increase power, and a little later, a reduction in volume to 1.1 liters for supplies of the Eight for export to countries with special performance requirements ICE.
Moreover, the model 2108 was designed by the Germans from the Porsche concern for a 5-speed manual transmission; the budget of the manufacturer AvtoVAZ was not enough for a larger budget, so the engine was boosted by domestic designers, the result was the 21083 engine with a volume of 1.5 liters, and then the 21081 with a volume of 1.1 liters.
For the latter option, a special input manifold was created, just like for an export-spec engine. The intake manifold from 2108 was mounted on modification 21083, which was initially incorrect, since the needs for the quality of the fuel mixture for the formed engine were not met. The manual included the same requirements regarding what kind of oil to pour, and the regulations for replacing coolants remained the same.
At the output, the engine characteristics were as follows: