Engine noise car can be caused by various reasons - a stretched alternator belt, a malfunction of the cooling system pump, problems with the ignition system and/or fuel supply system, timing and timing gear elements, faulty hydraulic compensators, and even the use of old or inappropriate motor oil. Moreover, the noise itself can occur in different operating modes of the engine - hot, cold, at idle, when accelerating the car, under load or during braking. A complete list of causes of various types of noise when the engine is running is collected in the article.
Some engine noise is clearly audible and does not require special diagnostics, but most often a stethoscope must be used. With its help, you need to go through the main possible sources that may produce extraneous clicking, knocking or rattling sounds. The table contains all the causes of noise in the engine no matter what mode of operation it occurs. Below, possible sources of occurrence will be discussed in more detail. You will find out why this happens and how you can remove or reduce the noise.
| Noise Conditions | Engine systems, possible causes of noise |
| Engine running, constant noise |
|
| On startup |
|
| When warming up |
|
| At idle |
|
| During acceleration (when pressing the gas) |
|
| Under load |
|
| After changing the oil |
|
| When turning the steering wheel |
|
Causes of noise in a gasoline engine
When starting a cold engine, its speed is about 1500...2000 rpm, and in this mode the operation will be noisier. As they warm up, they decrease to 800...1000 rpm. If there are no extraneous noises, you shouldn’t pay attention to it. But, when extraneous noise in the engine occurs in other situations, you need to look for the cause in the engine parts.
Noises from under the hood when the engine is running can be heard both for specific reasons and as a result of any malfunction of the system or part, which will entail a malfunction of the mechanisms.
Direct causes of engine noise
First, let's look at the direct causes of extraneous engine noise that can cause howling, rattling, clicking, knocking and other sounds.
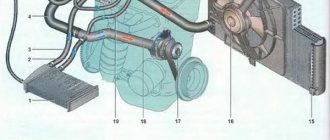
Generator belt
Loose alternator belt
A stretched or insufficiently tensioned alternator belt can make a loud noise similar to a whistle. As a rule, it does not sound all the time, but when the engine is started, mainly when it is cold, and also with a sharp increase in its speed. The alternator belt can “whistle” constantly only if it is very loose.
Coolant pump
The pump makes a thin squeaking sound when the engine is idling. If the pump impeller is worn out, the sound may be similar to a rumble. In this case, it will make noise in any engine operating mode. If the noise is in the front of the engine, then it may be coming from the pump.
Gas distribution mechanism
Noises from the elements of the gas distribution mechanism can usually be heard quite clearly. In this case, sounds come from the engine in the timing belt area and the cylinder head. The nature of the sounds will depend on the damaged parts.
Valve train chain
On cars that have a timing chain installed in the engine, a metallic clicking sound appears when the chain is stretched. Another option is wear or jamming of the hydraulic tensioner, wear of the damper or guide. And the sound becomes more frequent the higher the engine speed.
The chain must be replaced according to the regulations, even if it does not yet create clicking sounds. Usually the chain is changed every 200...250 thousand kilometers. There are engines that are replaced every 80...120 thousand kilometers. An example would be the 1.4 TFSI/TSI engine of the EA111 family from VAG. Along with the chain, its installation components also change - tensioners, dampers, guides.
Crankshaft
When the engine is running, extraneous noise may come from the crankshaft main bearings. The sounds are usually characterized by dull, metallic, repetitive impacts. They are heard best with a sharp increase in speed, both cold and hot. In addition to the main bearings, the same knocking noises will occur when there is scuffing on the surface of the crankshaft itself.
Crankshaft pulley damper
Collapsed crankshaft damper
The crankshaft pulley has a rubber damper inside. During operation, the damper may peel off, causing the pulley to become slightly deformed and begin to rub against the protection, which becomes the source of clanging sounds.
To fix this problem, you just need to replace the pulley with a new one. Most often, sounds from the pulley come from the bottom right in the engine compartment (although this depends on the specific engine). The described problem is typical for the following cars: Chevrolet Lacetti, Daewoo Lanos, some AUDI models and diesel BMWs that have a timing belt installed.
Connecting rod bearings
Damaged connecting rod bearings also result in harsh metallic sounds. Moreover, they will be quite loud and can be heard in all engine operating modes, but as the speed increases they will become louder.
valves
If the valves are worn and/or damaged when the engine is running, muffled clicking sounds will also appear. The sounds are best heard at high speeds and heavy load on the engine. The source of the sounds is the cylinder head.
Pistons
An easy way to detect piston or camshaft knock
Worn pistons begin to make increased noise over time. This is caused by deformation of both the pistons themselves and the cylinder walls. The nature of the sound is similar to normal engine operation, only with an increased sound level. The tone of the sound is similar to tapping on pottery. Sometimes clicking sounds may appear.
Piston knocking most often occurs when the engine is still cold and/or running at low speeds, and the gap size is about 0.3...0.4 mm. As the engine heats up, the sound disappears because the gaps between the parts decrease.
Main bearings
The main bearings make a low-pitched knocking sound. It comes from the bottom of the crankcase. The sound gets louder as the load on the engine increases and the rpm increases. The condition of the bearings can only be checked when dismantling them. Main bearings wear out as a result of normal wear and tear, as well as when the wrong or old oil is used, or when the engine is below the minimum amount.
Phase shifter
With significant wear, the phase shifters knock when they are hot, when the engine oil is in a liquid state. The sound of a faulty phase shifter has a clicking character, the clicks become more frequent as the speed increases. Phase regulators are usually installed in the timing belt area.
Hydraulic compensators
Most often, hydraulic compensators knock on engines with high mileage. The sound is similar to rattling. It is best heard when the engine is running cold. When it warms up, the sound partially or completely disappears. But it will depend on the reason. When hot, hydraulic compensators also often knock.
Fuel injectors
Worn fuel injectors make a clicking noise. This happens due to strong fuel pressure and rattling. The sound is rattling or clicking in nature and increases as engine speed increases.
Indirect causes of engine noise
Engine noise does not always arise from just one part; it can appear when a sensor, fuel, oil system, ignition system, or even a simply broken gasket fails.
Misfires
If a misfire occurs, repetitive noises will be heard from the engine. The sound in this case has a dull character, similar to that when the muffler burns out. It will come from the cylinders.
It is necessary to check the functionality and condition of the spark plugs, distributor, breakdown of the ignition coil, and also check the condition and insulation of high-voltage wires.
The engine is noisy after changing the oil and its level is low
If the engine starts to hum after changing the oil, this means that either the oil has the wrong viscosity, or it is of poor quality (most often a fake). Usually the sound is simply similar in nature to the sound made by the engine, but much stronger and more “growling”.
When the oil level is low, the rubbing pairs will work “dry” and hit each other. That is, the sounds will be clanging. The source of sound is the cylinder block, crankcase.
Poor quality fuel
When using low-quality gasoline, the overall engine noise usually increases. Moreover, this is typical in all modes of its operation. The noise does not have separate characteristics, it simply increases the noise level of the engine. Accordingly, to eliminate it, you just need to refuel with high-quality fuel with the octane number recommended by the car manufacturer. Indeed, if the fuel requirements do not meet, detonation can even occur, and this is much more dangerous.
When detonation occurs under the hood of a car, a metallic noise occurs in the engine. It is similar to when two metal parts collide at high speed. Increased engine noise in this case most often occurs when the engine is running under load and/or at high speeds. An additional sign of detonation is that the car loses power characteristics, and at idle speed it “chokes” and may stall altogether.
Cylinder head gasket
Broken cylinder head gasket
If the cylinder head gasket burns out, this also causes the engine to become noisier. Occurs due to a leak in the seal between the oil system and the cooling system. The source of the sound is the cylinder block. To eliminate the noise, you need to replace the gasket.
Process fluids getting into the oil
If antifreeze or fuel gets into the engine oil, this leads to a loss of its performance properties. The motor parts will hit each other with virtually no lubrication. Accordingly, the engine noise will increase. The very tone of the engine sound will not change, but the noise level will simply increase.
Engine sensors
Often, when an engine sensor fails, the engine loses power and becomes louder. The source of the sound is the motor itself. What needs to be done in this case is to check the ECU memory for error information using an electronic scanner. If any sensor breaks, it must be replaced.
Why does Hyundai accelerate poorly and roar?
Citizens who personally own cars with Hyundai engines note that after a certain time the power plant accelerates poorly and roars. Hyundai growls mainly when accelerating.
The engine exhibits a loss of thrust, adding an additional problem to the unpleasant sounds produced. And this happens, it would seem, at maximum speed. In this article we will try to explain the reasons for the negative behavior of the power plant.
Cause of the roar
It is not possible to immediately determine the reason why the motor behaves this way, since a set of faults can create them. A professional analysis of the shortcomings motivating the crackling sound in the power unit will reveal the origins of this behavior of the power unit.
The first thing you should pay attention to, if when accelerating a car it does not very quickly pick up cruising speed, is there high-quality fuel in the tank? When refueling your car, you should not skimp, but purchase fuel recommended by the manufacturer. To calm the soul, it is necessary to cleanse the food system of suspended matter.
If the cause is not eliminated when using the recommended fuel intended for this type of engine, there is a reason to pay attention to a malfunction in the ignition unit.
Bad fuel
Checking the quality of the poured fuel is carried out by the following steps:
- Remove the spark plugs and carry out a visual inspection;
- If carbon deposits of a specific color are detected, the car owner will receive an answer as to why the engine growls.
The appearance of soot on the spark plugs indicates the presence of more than the required amount of additives and additives in diesel or gasoline.
- If the skirt together with the electrode is covered with red carbon deposits, then there is only one conclusion - the reason is due to excessive additives;
- The black color of the soot coating indicates that the gasoline does not burn completely.
Ignition problem
The car may lose power when accelerating. The cause is a malfunction in the ignition system. Engine shortcomings are also noticeable at cruising speed of the vehicle. At a time when the car has gained high speed, hitches occur in the engine due to ignition failure. It cannot pick up speed further because it does not have the mobile reserve to bring the torque to peak levels.
A thorough inspection of the spark plugs should be carried out. Subject to disposal if they have been in use for a long time. Replace with new analogues. If after the manipulations the propulsion system growls, then the mechanic’s attention should be turned again to the operation of the fuel system. The unit plays a dominant role in ensuring the normal operation of the power unit.
Causes of noise on diesel engines
In diesel engines, many of the causes of knocking are similar to gasoline power units. However, they also have their own characteristics.
Diesel crankshaft
In a diesel engine, the crankshaft begins to knock when the engine wears out. This type of knock is called connecting rod knock. This is typical for all types of diesel engines, including turbocharged ones. The noise is metallic in nature and appears in all operating modes. It comes from the installation location of the crankshaft. The reason for the knocking is a large play in the connecting rod shaft.
Another reason for crankshaft knocking on a diesel engine lies in a loose connecting rod nut. This sound is not so sonorous, but more dull and reminiscent of the quiet clanging of metal parts. In this case, it is better to hear on a cold engine, when the engine oil has not yet sufficiently lubricated the engine bearing group. Then the sound may disappear altogether. The knocking noise increases with engine speed.
Camshaft
Most often, the diesel camshaft knocks when starting the engine and running it cold. It has a low frequency, and in terms of rhythm it is half as frequent as the knock of the crankshaft. Typically, the camshaft stops knocking as soon as engine oil reaches its bearings. This usually takes 2...4 seconds after starting the engine.
The reason for the knocking noise is the wear of the camshaft bearings. They wear out either due to natural causes or due to dirty oil.
High pressure fuel pump
With significant wear, the fuel injection pump may produce a significant noise. The sounds are similar to rattling or humming. Appears in all engine operating modes. The location of the fuel injection pump may differ for different car models, but in most cases it is located in the area of the cylinder block.
Injection pumps can have many breakdowns - wear of plunger pairs, wear of bearings and other parts, problems with the advance valve. The injection pump may even hum due to the fact that there is water in the diesel fuel! You need to check the high pressure pump at a special stand in a car service center.
Soundproofing of the engine compartment
The owner of the Lada Vesta decided to completely soundproof the engine compartment:
As a result, he writes:
The noise from the engine has decreased so much that all its derivatives are not audible at all! The only noise left is a VAZ family trait - a howl from the rollers in the range of 1500 - 2200. Please don’t tell me tales about the howl of the gearbox at these speeds! This howl most likely comes from the timing belt tensioner; if you overtighten it, the howl turns into a trolleybus howl.
Measurement results:
How to eliminate engine noise
To get rid of engine noise, you need to understand the reason why it arose. First of all, you need to check the level of oil in the crankcase, antifreeze in the cooling system and other process fluids. The second simple step is to check for errors in the ECU memory. If the appropriate repairs do not help, then it is necessary to diagnose the noise using the signs described above. In some cases, the problem can be eliminated or temporarily removed using special additives, but remember that they do not “cure”, but only mask the noise.
Additives for reducing engine noise
Atomex F8 Complex Formula
Manufacturers of modern auto chemicals offer car enthusiasts additives that reduce engine noise. Typically, this is done by anti-friction additives or additives that reduce oil consumption.
There are also additives that improve the quality characteristics of the fuel. Examples are Atomex F8 Complex Formula or Jet100 Euro 4 Petrol. They protect the fuel system and reduce engine noise if low-quality gasoline has been filled.
However, before using the additive, you must understand that the corresponding product does not eliminate the cause of the breakdown, but only masks its symptoms. Therefore, it is recommended to use additives exclusively for preventive purposes.
Refueling with low-quality fuel
Many systems and devices of the power unit can contribute to the fact that a gasoline engine operates like a diesel engine. However, there is one external reason that contributes to the appearance of unusual sounds. This is low-quality fuel.
The main property of gasoline, which characterizes its resistance to detonation (explosive pre-ignition), is the octane number. If the engine is designed for AI-95 gasoline, and at the gas station you were filled with low-octane fuel, troubles are inevitable.
- Under certain loads, fuel detonation occurs, accompanied by detonation knocks reminiscent of the ringing of piston pins and, remotely, the sound of a running diesel engine.
- To increase the octane number, octane-increasing additives are added to low-grade gasoline, which are deposited in the nozzles of the working injectors on an injection engine. The supply of fuel to different cylinders becomes uneven, which leads to harsh engine operation. In advanced cases, the injectors become completely clogged, as a result of which the engine begins to “trouble.”
- The additives contained in “bodied” gasoline cover the electrodes of the spark plugs with a layer of red soot, and due to misfires, the engine again “troubles.”
Tip: try to refuel at chain gas stations located in large populated areas or along busy highways. If you run out of fuel, fill up the minimum amount of gasoline at the first gas station you come across in order to get to the nearest verified gas station.
Timing faults
Breakdowns or wear of timing parts (gas distribution mechanism) can also be involved in the appearance of extraneous sounds under the hood of a gasoline engine. The most common faults:
- Valves are knocking. This disadvantage is inherent in older gasoline engines, which required periodic valve adjustment, even during the first annual maintenance. Knocking can be caused by unqualified repairs (poor fit of the valve plates to the seats), as well as deformation due to overheating of parts.
- Hydraulic valve compensators are knocking. Modern valve mechanisms equipped with automatic adjustment are more durable, however, even in this case, the hydraulic compensators wear out sooner or later, after which they should be replaced.
- The timing chain drive is loose or worn. In this case, the dangling chain touches the guard cover, which causes a rattling knock.
- The timing belt jumped several teeth, causing the valve timing to be disrupted. The engine runs harshly, untimely combustion of fuel causes a characteristic diesel sound.
- The bearing beds of the camshaft are worn out, which causes noticeable knocking noises, especially when the engine is not warmed up, when the gaps in the bearings have not yet been cleared.