One of the most important characteristics of any gasoline or diesel engine is its displacement. Since the appearance of the first internal combustion engines, this characteristic of the engine has been the primary indicator by which one or another power unit is distinguished. For this reason, the concept of “engine displacement” is constantly used in relation to various power plants. On many cars, the engine size is indicated in the form of a special nameplate next to the designation of the model itself. For example, BMW 740 means that it is the seventh series in the model range with an engine capacity of 4.0 liters.
The power characteristics, maximum vehicle speed, etc. greatly depend on the working volume of an atmospheric or turbocharged engine. Moreover, the division of cars into classes, the formation of taxation and the determination of the amount of payment of various fees also takes into account the type of engines and volumes that are installed by the manufacturer for different models/types of vehicles and other vehicles. It should be noted that many consumers are not always well aware of what engine displacement actually is. Next, we intend to talk about what makes up the working volume of an internal combustion engine, how to find out the engine size, etc.
What is engine displacement
An internal combustion heat engine is an impressive complex of various mechanisms, systems and additional attachments, forming a complex engineering solution. The general principle of operation of an internal combustion engine involves supplying fuel and air to a special closed chamber, where the resulting fuel-air mixture ignites. As a result of fuel combustion, energy is released, which pushes the piston located in the engine cylinder. The piston moves, the crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion, which allows the crankshaft to rotate. Next, the engine torque is transmitted to the transmission and then to the drive wheels of the car. This process is constantly repeated after starting the engine, that is, the engine is running all the time, provided that the components are supplied and the fuel mixture is efficiently burned in the working chamber. This chamber is called the combustion chamber. The volume of the combustion chamber (also known as the working volume) is the product of the cross-sectional area of the cylinder and the length of the piston stroke from BDC to TDC (top and bottom dead center of the piston stroke). The physical volume of the combustion chamber is the working volume of the engine in gasoline and diesel cars, motorcycles and other types of land, air or water transport, agricultural machinery, as well as other mechanisms and devices using internal combustion engines. Please note that if the engine has several cylinders, then the volume of the combustion chamber in each of them must be summed up with the others. In other words, the working volume of a multi-cylinder engine is the sum of the volume of the combustion chambers of all cylinders of such an engine. The total volume of all engine cylinders is usually expressed in liters. The working volume of the combustion chamber is indicated in cubic centimeters.
Briefly about compression
If everything is clear with the degree of compression, then let’s move on to the term compression. This concept refers to the maximum level of pressure that occurs in the combustion chamber at the moment before fuel combustion. If the degree of compression is a conditional value, then compression is an absolute value and is measured in atmospheres, kilograms per cubic centimeter (kg/cm2).
Compression is the pressure in the cylinder; the compression ratio is a dimensionless parameter that describes the geometric characteristics of the cylinder.
There is a close connection between these two concepts, but compression is affected not only by the compression level, but also by the tightness of the compression rings and valves, engine temperature, fuel combustion temperature and much more.
Classification of cars by engine size
As a rule, in the model range of each manufacturer there are more and less powerful cars that differ in size and weight. Small-sized cars, such as the Daewoo Matiz, are not equipped with large-volume engines, since an engine with a displacement of 1.0 is sufficient for this small and light car to achieve decent dynamic characteristics. Accordingly, Daewoo Matiz belongs to the class of minicars, and the heavy crossover BMW X5 with an engine capacity (in one of the modifications) of 4.6 liters belongs to the class of large cars. Between these “extremes” are small and medium-sized cars. By the way, in some cases there is no direct relationship between the working volume and its dimensions and weight. A good example is sports cars and supercars. The Lamborghini Gallardo engine capacity is 5 liters and weighs 1.5 tons. The recently published list of cars subject to the “luxury tax” does not include models with an engine capacity of less than three liters. Other parameters of the car also depend on the engine size. First of all, power. The more fuel is burned in one cycle in the engine cylinders, the more energy is released. The acceleration of the car and its maximum speed directly depend on the engine power. We should not forget about the existence of an inverse relationship: the larger the displacement, the higher the fuel consumption.
Tip 1: How to determine the power of a car
April 9, 2012 Author KakSimply! Car power is one of the main quantities that people look at when choosing an iron horse. The more power, the more expensive the car.
- How to find power Question “I disagree with the fine” - 2 answers Instructions 1 Take the documents for the car, which indicate the engine serial number. But the car power indicated in the documents does not always coincide with what it actually is. And in this case, you can try to calculate it yourself.
- How to determine the year of engine manufacture
We recommend reading: New Year holidays 2022 at Unicredit
Is it possible to increase the engine size?
This question is often asked by car owners who want to increase power. There is such a possibility, but it will not be possible to significantly increase the volume. The volume is increased during an engine overhaul, since to restore the shape of the cylinder walls they have to be bored on a special machine (unless, of course, liners are used in it). The cylinder walls are slowly but steadily ground down from constant friction, which leads to an increase in the volume of the combustion chamber, and boring only helps restore the damaged geometry and correct the discrepancy in the volume of different cylinders. In Japan, the class of small cars is “kei car” with an engine capacity of up to 660 cc. exempt from road tax The ability to increase volume is limited by the fact that manufacturers believe that major overhauls are only justified three times, after which the engine must be scrapped. After boring the block, each time you have to buy new pistons of larger diameter, which are called “repair”. There are only three calibers of repair pistons. In this regard, replacing the engine with the same one, but initially having a larger volume, is a much more promising activity in terms of increasing power.
Calculation methods and formulas
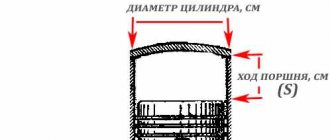
The volume is easy to calculate if the values of the piston radius (R) and piston stroke (H) are known. The values must be substituted into the formula (3.14 × R² × H). The result obtained is equal to the working volume of one cylinder; to find out the displacement of the engine, you need to multiply it by the number of cylinders.
Formula for calculation: Veng = ((3.14 × R² × H) × number of cylinders)/1000. Divide by 1000 to convert mm³ to cm³.
There are calculators on the Internet for calculating engine volume: just fill out the fields and click the “Calculate” button. You can measure the diameters of the cylinders with a micrometer and a bore gauge.
This is interesting: How to check ball joints on a Lada
OPTIMUM DISPLACEMENT
Almost all manufacturers offer several engines for the same car model, and choosing the optimal engine is not always easy. Conventionally, cars are divided into several classes:
- minicars, with an engine capacity of no more than 1100 cubic meters. cm;
- small-capacity, with a volume of 1200 - 1700 cubic meters. cm;
- mid-displacement, with a volume of 1800 - 3500 cubic meters. cm;
- large-capacity, with a volume of more than 3500 cubic meters. cm.
There is a gradation of power units by car class. For class B cars, engines from 1.0 to 1.6 liters are usually offered, C-class is equipped with engines with a volume of 1.4 to 2 liters, D-class - 1.6 - 2.5 liters, E-class - from 2 liters When choosing a suitable engine for himself, the future car owner must determine in what conditions the car will be primarily used. For driving in urban conditions, a motor with a smaller displacement (for example, 1.4 liters) is quite suitable if it has good traction at low speeds. If there is insufficient traction at the bottom, the engine will have to be constantly “twisted”, and you can forget about the promised eight liters of fuel per 100 km in the city.
It is also necessary to take into account that the switched on air conditioning system takes up a significant part of the power and increases fuel consumption. In this case, driving a car with a low-power engine becomes unpleasant, since the driver will constantly be forced to engage lower gears.
If the car will primarily be used on the highway, it is better to choose a larger engine.
- Firstly, the difference in consumption will not be so significant;
- secondly, under the hood of the car there will always be a reserve of power, which will allow the driver to overtake more confidently;
- In addition, turning on the air conditioning or climate control system has virtually no effect on the dynamics of the car.
Cylinder sections
When cutting a cylinder with a plane passing through both bases of the cylinder at an angle of 90 degrees, you will always get
.
When a cylinder is cut by a plane passing through both bases of the cylinder at an angle other than 90 degrees, the result is a figure
, but whose two sides will be curved lines.
If the secant surface runs parallel to the bases of the cylinder, then the section will be .
If the secant surface passes through the side surface, but is not parallel to the base of the cylinder, then the section results in .
If the secant surface passes through one base of the cylinder and the side surface, then the section will have a figure in the form.
Features of operation of large cars
Compared to small-displacement engines, large-displacement engines are characterized by smoother operation and less noticeable wear, since they are much less likely to have to operate at the power limit. An engine with a large combustion chamber produces its maximum capabilities only when it participates in racing, i.e. in sports competitions. When driving in normal mode, the engine retains a reserve of power, so it does not wear out. Fuel consumption, of course, remains higher than that of small-displacement engines, but it can be reduced by properly adjusting the gearbox. A powerful engine, which is rarely used in hard conditions, is capable of driving up to a million kilometers without the need for major repairs. Therefore, the costs incurred when purchasing a powerful large car are subsequently recouped by the long-term operation of the car.
Safety of operation of a powerful and voluminous power unit
The current trend towards reducing engine displacement is clear. The more cubic meters the power unit has in its volume, the more gasoline will have to be spent to ensure its operation. But fuel consumption is not the biggest expense for a car owner. After all, it is important that the engine does not require repair, and a large volume can really help with this.
When an engine has a small displacement, it has to work quite hard to achieve a certain acceleration or speed. With a large volume, the operation of the unit always remains soft and measured, parts are not overloaded, and engine wear does not occur too noticeably. In more detail, these factors are as follows:
- the voluminous power unit rarely operates at its maximum capabilities - only during sporty acceleration;
- operation of the piston system occurs gently, the speed increase is quite slow;
- the presence of a large power reserve allows the engine not to strain at high highway speeds;
- if the gearbox is properly configured, the unit does not consume so much fuel;
- Proper operation of the engine means that the power plant can travel more than 1 million kilometers without major overhauls.
These are the features today that large engines with good potential have. They provide not only high operational reliability, but are also the key to a safe trip for the driver, providing high power and power reserve under the driver’s right foot. Also, such units do not require regular repairs.
Of course, the more powerful and voluminous the engine is under the hood of your car, the more careful care it requires. Therefore, it is imperative to buy high-quality oil and replace it in a timely manner. This is where the operating costs for such an engine end. All that remains is to monitor the quality of the fuel and change the lubricant on time.
What does engine size affect?
Firstly, gasoline consumption. The larger the cylinder volume, the more fuel is needed to ignite it with maximum efficiency, and accordingly, consumption increases. However, this minus turns into an equally tangible plus. The larger the engine displacement, the greater the engine power, since more gasoline releases more energy.
Secondly, as already noted, the larger the volume, the greater the power, that is, a car with a larger engine will accelerate faster, be able to carry heavier loads and more passengers. Often, larger engines turn out to be much more economical: there is no need to press the gas pedal hard to accelerate the car. Fuel consumption does not increase, while small engines burn much more fuel under load. The larger the volume, the larger the engine itself, the larger the car. Let's put it this way: large volumes are used on higher-class cars, which is why the engine and all other systems are more expensive to maintain. The price for such a car is obviously higher. In order to understand which car is best for you, you should understand that micro and small cars are best suited for driving in large cities with traffic jams. Their consumption in city traffic will be minimal compared to other cars, but, in turn, such cars are not suitable for long journeys, since at speeds over 100 km/h they clearly do not have enough power. They will also not be able to transport a lot of cargo.
Cars with a volume of 1.8 to 3 liters are excellent for both city traffic and long trips; their power is enough for acceleration and driving at high speed, for transporting goods, and the gas mileage of such cars is not that great.
Cars equipped with engines of 3 liters or more are either SUVs or minibuses and minivans designed to carry more passengers or cargo.
Video
FAQ
How is engine displacement measured?
Engine displacement is measured in cubic centimeters
(cm3), but in documentation it is often written in liters (l.). 1000 cubic centimeters equals 1 liter. The most accurate unit for measuring volume is cubic centimeters, since when the volume of a car engine is indicated in liters, it is rounded to a whole number after the decimal point. For example, the volume is 2.4 liters. equal to 2429 cm3.
What is the formula for engine cylinder displacement?
The working volume of the engine cylinder is equal to the product of Pi (3.1415) by the square of the radius of the base and the height of the piston stroke in it. The formula itself for the volume of an internal combustion engine cylinder in cubic meters. centimeters looks like this: Vwork = π⋅r²⋅h/1000
How to measure car engine displacement?
Engine volume is the sum of the working volumes of all its cylinders; accordingly, you must first find out what the volume of one cylinder is, and then multiply by their number. The volume of a cylinder is calculated by multiplying the height by the square of the radius and the number “Pi”. But in order to measure exactly the working volume of a cylinder in an engine, you need to take the length of the piston stroke from BDC to TDC as the height, and the radius can also be measured with a ruler, having first found out the diameter of the cylinder. This measurement method is only possible when the head is removed or the parameters are known.