13.12.2019
| (Votes: 2, Rating: 5) |
Issues discussed in the material:
- How often to change the oil in the variator
- What oil to use for the variator
- How to partially change the oil in a variator
- How to completely change the oil in a variator
Modern models of cars and SUVs are increasingly equipped with CVTs instead of the more familiar automatic transmissions. It is not surprising that the owners of these cars are wondering how to properly maintain this type of gearbox. In our article we will focus on such an important task as a partial oil change in a variator. Does this procedure make practical sense and how to carry it out in this case? This will be discussed below.
When to change the oil in the variator
Replacing the lubricant in the variator is carried out in strict accordance with the regulations, which each automobile manufacturer has its own. On average, it is recommended to carry out maintenance at least once every 40 thousand kilometers.
The replacement interval is reduced if the vehicle is operated in unfavorable conditions:
- regular and prolonged towing of trailers or other vehicles;
- dynamic driving style with fast acceleration and braking;
- long periods of vehicle idle time in traffic jams at high air temperatures;
- frequent wheel slip and movement over rough terrain;
- operating the car in the mountains, driving on dusty and/or dirty roads.
If a check light lights up on the dashboard or a hum is heard while driving, there is vibration or an unpleasant burning smell appears - these are good reasons to check the level and condition of the oil in the CVT (continuously variable transmission).
Let's sum it up
So, despite the constant improvement in the design of automatic transmissions and CVTs, as well as lubricant production technologies, at increased loads on the gearbox, periodic replacement of the working fluid . To extend the service life and reduce the risk of unplanned expenses for expensive repairs, you must adhere to the recommendations of the car manufacturer both in choosing the fluid used and in observing the established service intervals. For CVTs, this is becoming more and more relevant every year, since according to forecasts in the near future, half of the cars produced will be equipped with this type of transmission.
How to check the condition of the oil in the variator
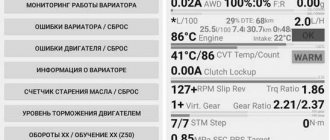
Before changing the transmission oil in the Jatco variator, the current condition of the fluid is assessed. This will give a final understanding of whether the time has come for automatic transmission service or not. There are two simple and proven ways to check the oil level in the box and assess the quality.
Drop test
Before the drop test, the engine is warmed up - the level and properties of the liquid are assessed when it is heated to 50-80 ° C. Then place the car on a flat horizontal surface and do not turn off the engine; it should be idling.
Take out the variator dipstick - it is located in the filler neck. This place can be found by the inscription "CVT" or "TRANSMISSION".
When you find the dipstick, start checking the oil:
- Press the dipstick lock to unlock it and remove it from the neck.
- Wipe the metal part dry with a rag.
- Immerse the dipstick back into the neck until it stops and hold for several seconds.
- Take out the part again and carefully inspect the oil trace on it.
In normal condition, the fluid on the dipstick reaches an average level between the maximum and minimum marks. As for quality, to evaluate it, drop a little lubricant onto a clean white napkin. If the liquid is cloudy, it means there is a high concentration of wear products.
Next, evaluate the smell of the oil: burnt indicates regular overheating of the liquid. This often happens due to incorrect operation of the cooling system or due to low pressure. For a more objective comparison, it is advisable to prepare a sample of pure oil.
Transmission fluid aging counter
Modern cars are equipped with an electronic CVT control unit, one of the functions of which is to calculate the remaining life of the transmission fluid. For this, a special mathematical algorithm is used: there is no doubt about the accuracy of the assessment of the “old age” of the oil.
Owners of Nissan and Toyota CVT cars have the opportunity to assess the condition of the lubricant using a meter. Limit recommendations vary from one automaker to another. For example, Toyota recommends changing the oil when the meter reaches 210 thousand units.
What to use for the variator
The choice of lubricant for CVT gearboxes is subject to increased requirements. Unlike engine oils, it is not recommended to use analogues or experiment with interchangeable compounds.
Always choose the oil for your CVT that is specified in the manufacturer's recommendations.
Many are sure that there is no difference between oils for a CVT and a classic automatic transmission, that is, a torque converter. This is a misconception.
ATF and CVTF lubricants solve slightly different problems. Automatic transmission oils are aimed at ensuring hydraulic transformation of torque and providing lubrication for internal moving elements.
And oils for the variator lubricate and prevent the pulley from slipping. Because of this, the two types of lubricants differ significantly in composition and properties.
ATF and CVTF oils are completely incompatible with each other.
The only correct solution is to look at the instruction manual and find out which lubricant is suitable for the specific variator installed on the car.
Each auto company offering cars with CVT has its own recommended lubricants. Here are some examples:
- For Nissan vehicles, use CVT lubricants labeled NS1, NS2 and NS3.
- For these Japanese cars, the current version of the required oil is called Fluid J4. Although previously it was recommended to use Fluid J1. Oils are considered interchangeable.
- The Japanese company offers 2 types of lubricants for its machines. These are Fluid FE and Fluid TC. They have different markings and characteristics. They differ in additives. The FE version is more modern and can be used together with the conventionally outdated TC.
- HCF2 and HMMF lubricants are offered for these cars. But it is important to consider that they are not interchangeable.
- CVTs are also installed here, and they require G052 180A2 oil. The only regulated analogue is Febi 27975. The same lubricants are suitable for CVT on Volkswagen, Skoda and Seat cars.
- It is recommended to fill in different lubricants, depending on the model. CVT Lineatronic II composition is suitable for Lineatronic boxes. A special C30 fluid is supplied to the USA. ICVT FG lubricants are suitable for Subaru small cars.
- Elfmatic CVT oils are used here. An analogue is oil from Nissan NS2.
How to properly change the oil in a variator with your own hands
If, according to the regulations, the time has come to replace the CVT fluid, you can try to cope with the task yourself. There are two ways - partial and complete renewal of transmission oil.
It is impossible to carry out a complete replacement efficiently in a home garage, since this requires a special apparatus. It is only available at the service center.
The specialists at the CVT Repair Center No. 1 will help you cope with tasks of any complexity. Get additional information by calling: Moscow – 8 (495) 161-49-01, St. Petersburg – 8 (812) 223-49-01. We accept calls from any region.
Partial
Before moving on to a partial replacement of transmission oil, prepare fresh fluid in a sufficient volume. First read the vehicle's operating instructions, as the manufacturer specifies in it which lubricant should be filled in and in what quantity.
Prepare an empty container with a capacity of at least five liters - it is needed to collect waste liquid. Consumables will require a new pan gasket and an oil filter for the variator.
Before replacing the fluid, warm up the transmission - just drive the car about 10 kilometers. Then they park the car on a flat road and wait about an hour. This is necessary so that the oil flows back into the pan. After this, the procedure begins immediately:
- Place an empty container under the variator drain plug and unscrew it.
- Wait until all the transmission fluid has drained out.
- Unscrew all the bolts holding the pallet and carefully remove it.
- Rinse the tray and remove metal shavings deposited on the magnets.
- Disconnect the solenoids and dismantle the valve body, then wash it.
- Replace the fine paper filter (located behind the heat exchanger).
- Change the metal coarse filter (installed in the pan).
- Dry the hydraulic unit and pan, and then install them in place.
After completing the assembly of the variator, check that its pulley is completely aligned with the valve body pulley. To do this, switch the automatic transmission selector several times to different positions and make sure that all shifts work correctly without jamming or squeaking.
The final stage is filling the transmission with new oil through a special hole. When this is ready, check the fluid level using the dipstick. If necessary, add oil. After successful replacement, the aging counter is reset - a diagnostic tool is needed for this.
Despite the theoretical possibility of changing the fluid in a continuously variable transmission yourself, it is strongly recommended to entrust this task to experienced professionals from a service center.
Full
A complete change of transmission oil in the variator is carried out using equipment that is at the disposal of the service center. The device supplies new fluid under pressure inside the automatic transmission, due to which the old oil, along with chips and deposits, is forced out of cavities and hard-to-reach places.
We invite you to watch a detailed video review of changing the oil in a variator.
CVT - design features
Instead of a three-dimensional set of shafts, gears and rocker arms, the variator consists of two pulleys with a variable gear ratio. By the way, compactness is the main virtue of this type of gearbox.
Scheme of operation of the variator
The operating principle is as follows: From the engine to the drive shaft (in other words, directly to the wheel hubs), torque is transmitted using a specially designed V-belt.
Some experts call this belt a chain drive. In part, they are right, since it is a set of metal links connected to each other in a special way.
The gear ratio (which changes the speed of rotation of the transmission shaft) varies due to synchronous changes in the diameters of the pulleys. The figure shows that by moving and spreading the “cheeks” of the pulleys, it is possible to regulate the speed of the wheels with high precision.
But to compress and hold these halves, transmission oil specially designed for CVTs is used.
The liquid is pumped into cylinders located on the same axis with the pulleys and compresses the halves with monstrous force. At the same time, the amount of oil in the second cylinder is reduced to just enough volume to ensure compression force and geometry.
In addition, this entire structure must be continuously lubricated at the points of contact between the belt (chain) and the pulley. At the same time, cooling is provided: the constant friction of metal on metal greatly heats the variator mechanism.
To be fair, one gear pair is still present. This is the reverse gear mechanism. No separate lubrication is required - the unit is “bathed” in the common transmission.
Which is better – complete or partial fluid replacement?
You cannot get by with only partial replacement of transmission oil over a long period of time. The fact is that when adding fluid, it is impossible to completely get rid of the chips that appear as a result of friction of the mechanisms inside the variator. Over time, it penetrates deeper into the design of the continuously variable transmission, eventually reaching the torque converter.
A complete oil change is something you shouldn't skimp on. You need to contact a car service, which takes time and money, but in the future, repairing the variator will cost more.
How does a continuously variable transmission work?
The variator is based on 2 expansion shafts and the drive element connecting them, that is, a belt or chain. Both shafts are connected to the gearbox oil system, through which the control unit regulates the compression ratio of each of them. The more strongly the drive shaft plates are compressed, the larger the diameter of rotation of the belt or chain on it, and therefore the smaller on the driven one. By changing the pressure in both shafts, the control unit changes the gear ratio within a wide range.
In addition, this type of transmission is equipped with:
- torque converter;
- planetary gearbox;
- friction clutch;
- an actuator (hydraulic unit) with hydraulic cylinders located inside the body, which makes it similar to traditional automatic transmissions, that is, hydraulic automatic transmissions and robotic transmissions (manual transmissions).
The torque converter acts as a clutch and converts the ratio of engine shaft speed to torque when the vehicle starts to move. The planetary gearbox switches the driving direction of the car (forward or backward). Frictions ensure the correct operation of the planetary gear, and on some transmissions they also serve as a clutch. The control unit located outside the transmission is the “brain” of the variator, performing the same functions as the ECU on a hydraulic automatic transmission, and the valve body cylinders, together with the oil pump, are the “arms” of this “brain”.
Difficulties and nuances of self-replacement
First of all, there is a risk of encountering a counterfeit when choosing gear oil. The market for consumables for cars is filled with counterfeit goods, and without proper experience and knowledge it is easy to buy counterfeit fluid. The consequences of its use are disastrous.
The second problem that many car owners face when trying to change the oil at home is the complexity of the process. You need a set of tools, an inspection hole, patience and free time, and even this does not guarantee success.
During maintenance, you can damage fragile mechanisms, forget parts during assembly, or make other serious mistakes.
About the filter
Some people noticed that I highlighted the word filter in the paragraph above. For what? I would like to draw your attention to them. This is another vital element (or rather elements) in the gearbox system. There are both two and one, the so-called coarse cleaning and fine cleaning.
A fine filter is a regular paper filter, somewhat similar to a car oil filter.
Coarse cleaning is metal, usually in a flat housing.
For the sake of fairness, I want to point out once again - there is also one in “metal”, everything there is combined, both “rough” and “fine”.
They are needed to catch chips, dirt, burnt marks, etc. formed during work, there is no escape from this.
That is, to summarize - the oil (liquid) is cleaned and cooled during operation, this is important to understand.
Changing the oil in a variator at a car service center
The optimal solution to the issue of changing the oil in a continuously variable transmission is a visit to Jatco service. Since 2008, experienced craftsmen have been servicing Japanese CVTs around the clock. In addition, we maintain a low cost for changing transmission oil in a variator and provide a tow truck service to the service center completely free of charge.
You can diagnose and fix problems of any complexity at the CVT Repair Center No. 1. Get additional information by calling: Moscow – 8 (495) 161-49-01, St. Petersburg – 8 (812) 223-49-01. We accept calls from any region.
We invite you to contact the service right now, get a free consultation and find out how much a partial and complete oil change costs for the CVT model in your car.
Hardware oil change
Hardware oil change is a modern technology for servicing a variator using pumping equipment. But this method has its pros and cons.
Pros:
efficient pumping out of most metal shavings and deposits;
there is no need to disassemble the pan and hydraulic unit, which speeds up the procedure;
relatively low cost due to ease of operation;
there is no need for special tools, or a pit or overpass.
The downside is that during the procedure it is not possible to visually check the condition of the variator mechanisms from the inside, since this requires disassembling the unit. But on the other hand, if necessary, such a check will still be carried out.
As for the cost of hardware oil change, it is calculated on the spot. The price of the service is calculated in the presence of the car owner, so everything is fair.
Checking the fluid level
Since CVT malfunctions are sometimes associated with low oil levels and not with its quality, it is recommended to periodically check the amount of lubricant. This is done within the framework of each maintenance and in the intervals between them.
In most cases, you can follow the same instructions on how to properly check the lubricating oil level in the variator yourself. To do this you need:
- place the car on a level surface;
- warm up the engine;
- squeezing the brake, switch the selector to each of the available positions;
- hold in each position for 10 seconds;
- switch to parking mode;
- open the hood, wipe the outside of the dipstick;
- pull out the dipstick, removing any remaining oil from it;
- return it to its place, hold it for 5 seconds and pull it out again;
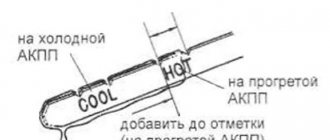
- look at the probe marks (checking the hot level, hot);
- put the dipstick in place.
Based on the marks, you can find out how much lubricant is currently in the CVT and whether the current level corresponds to the required volume of lubricant.
Do I need to change the filter when changing the oil?
CVTs from the manufacturer Jatco are factory equipped with two filters:
- Disposable fine cleaning cartridge. Absent on some modifications, including the F1CJA and W1CJA versions. This element must be changed at every oil change. Its cost cannot be called high.
- Metal coarse filter. This part must be replaced every time the transmission fluid is changed. Otherwise, you can save money, but before that you need to clean the filter from metal shavings.
Reuse of the coarse filter is not allowed if its lattice part is clogged with resinous glue, which is used in the construction of friction linings.
We invite you to watch a video review of changing the oil and filters in the CVT of a 2012 Nissan Qashqai.
What spoils oil
The main sources of ATP contamination are clutches and shafts with a belt or chain. Every time you start moving, the clutches experience increased loads, which is why part of the lining coating turns into dust and gets into the oil. The higher the load during start, the more the friction layer is destroyed and the more dust gets into the fuel fluid.
Oil for variator in cars
The shafts and belt or chain are in constant mesh, so their surface wears down over time, turning into fine steel dust. Under sudden or high loads, the belt or chain slips a little, causing metal shavings to appear. In addition, all rubbing parts become very hot, which leads to oxidation of the fuel fluid and the formation of soot, which also ends up in the oil.