Experts strongly recommend that you inspect the vehicle before driving. Such visual diagnostics help to identify various deviations in its operation, allowing them to be quickly eliminated. Particular attention must be paid to the indicators of the main systems, one of which is the operating temperature of the machine’s engine. It is displayed on the dashboard in the form of a small arrow display. Basically, motorists are faced with overheating of the power unit. Reverse deviations often occur when the driver notices that the engine temperature drops while driving.
Checking the Thermostat
- Start the cooled (cold) engine.
- Let it run for five minutes when the temperature on the instrument panel reaches the lower mark.
- It is necessary to check the hose that goes from the thermostat to the main radiator.
The arrow shows the hose that drains fluid from the radiator; the supply hose is located above and to the left. With the thermostat closed they should both be cold.
The hose must be cold. Liquid should not circulate through it. The disadvantage of this method is that the thermostat may jam during operation. That is, when the car warms up, the thermal element on the thermostat begins to work incorrectly, and the thermostat sticks in the middle position.
Alternative way
You can use “nano-cardboard”, which must be inserted between the radiator and the bumper. If during driving the temperature rises to operating parameters, this means that the coolant in the radiator is not blown by air flows. And if the thermostat was closed, then the cardboard would not be needed.
In this case, the thermostat needs to be replaced. If you often drive on the highway in sub-zero temperatures, then we can recommend the LUZAR thermostat. It opens completely at a temperature of 92°C.
Thermostat LUZAR 92 – the opening temperature is stamped on the cover of the device.
Principle of operation
Coolant enters the radiator through the thermostat. This is a large circle of fluid circulation. The thermostat usually opens at a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius. If the temperature has not reached this limit, then the liquid moves in a small circle. A thermostat malfunction is manifested by improper opening of the valves.
When the thermostat is closed, the engine overheats, and a constantly open one leads to low temperatures, since the liquid will only flow in a large circle.
Due to irregular changes of antifreeze or antifreeze, use of running water or mixing of coolants, various deposits in the form of scale may accumulate in the system. In this case, the thermostat will inevitably jam in one of its positions.
The main reasons for insufficient heating of the internal combustion engine
Thermostat stuck open
A common cause of insufficient engine temperature is a stuck thermostat.
One of the common causes of this problem is a stuck thermostat in the slightly open position. This may occur due to a foreign object getting under the valve: a piece of sealant, scale, scale. Also, the thermostat becomes unusable after a certain period of use. As a result, the coolant begins to circulate in a large circle rather than in a small one. The solution to this situation is to replace the jammed part. The next reason for the engine not warming up to operating temperature is the time of year.
Warming the engine in winter
The most unpleasant cause of low engine temperature is damage to the cylinder block gasket.
In winter, especially in severe frosts, the internal combustion engine may have insufficient temperature. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to perform additional insulation of the engine. The answer to the question is sometimes hidden in the discrepancy between the brand of coolant and the manufacturer’s recommendations. If this is the reason, then it is enough to change the fluid to the desired one. The most serious reason why the engine temperature does not rise above 80 degrees is a damaged cylinder head gasket. Because of this problem, exhaust gases begin to enter the cooling system, which leads to a violation of the temperature regime. Causes of gasket damage include engine overheating or a thermostat that is stuck in the closed position.
Let's sum it up
In this article, we examined one of the most common reasons why the engine does not warm up, may cool down while driving, the engine temperature does not rise above 70 degrees, etc. Let us add that in the latter case, on a car with an unknown history, it often turns out that the previous owner had previously installed a too “cold” thermostat. In parallel with this, other malfunctions of the cooling system may occur, as a result of which the internal combustion engine does not heat up.
It should also be noted that repairing the device is impractical given its relatively low cost. For this reason, instead of descaling the thermostat and trying to eliminate its jamming, it is better to immediately install a new element on the machine.
Sources
- https://autochainik.ru/dvigatel-ne-progrevaetsya.html
- https://avtodvigateli.com/neispravnosti/ne-progrevaetsya.html
- https://okeydrive.ru/pochemu-dvigatel-ne-progrevaetsya-do-rabochej-temperatury/
- https://KrutiMotor.ru/dvigatel-ne-nagrevaetsya/
- https://www.avtovzglyad.ru/sovety/ekspluataciya/2020-09-30-chto-delat-esli-dvigatel-perestal-progrevatsja-do-rabochih-temperatur/
[collapse]
What can be dangerous about a cold engine on the road?
First of all, an engine that has not been brought to operating temperature is dangerous for itself, although the full list of troubles also contains other problems:
- all the gaps between the parts have been changed, but the most critical will be the valves and the difference in diameters between the piston and the cylinder, the first threatens with shock loads and metal fatigue, and the second with the passage of gases, oil and the formation of hard, indelible deposits;
- any oil used, even the most expensive, has a viscosity dependence on temperature, and the engine is designed to give its maximum only at a certain value;
- On cold engine parts, fuel condenses and the oil film, which is already in short supply, is washed away, wear increases sharply;
- to obtain the required output, the driver has to increase the density of the mixture and its quantity, this negatively affects engine consumption and pollution;
- The heater hardly works, there is no comfort in the cabin, the windows freeze, safety deteriorates.
There are certain recommendations for warming up the engine before driving. They do not provide for achieving the nominal temperature, but are designed to ensure the serviceability of all systems.
If the engine is not in order, then the additional load will not speed up the process of entering the mode, but will cause wear and tear. Operating a car in this condition is dangerous and not economically justified.
How does the engine warm up?
Each serviceable unit has a different warm-up time. It is influenced by:
- degree of forcing;
- engine type: diesel or gasoline;
- cooling system condition;
- stove operation;
- quality of antifreeze or antifreeze;
- work load;
- outside air temperature;
- type and viscosity of engine oil.
The characteristics of the oil are rarely taken into account, but experts believe that this is necessary. Various friction reducing additives and the base stock, synthetic or semi-synthetic, affect the performance in the range of 5–7 degrees. Thus, the engine will heat up faster with thinner synthetic oil.
The engine temperature gauge does not rise often due to a malfunction of the thermostat. It is with this unit that the system check always begins if the engine takes a long time to warm up to operating temperature.
Which system is responsible for maintaining a constant engine temperature?
No vehicle is insured against breakdowns. Car components and assemblies consist of many small components, the functional life of which has significant limitations. If a car owner notices that the temperature of the internal combustion engine is dropping while driving, he needs to pay close attention to the integrity of the cooling system elements. This is where the causes of the problems lie.
The essence of the cooling system is the movement of a special liquid - antifreeze through two technological circles. One of them is small and does not provide for the passage of coolant through the cooling radiator located in the front part of the engine compartment. It is limited to circulation only along the “shirt”.
The passage of a large contour begins to occur when driving over medium and long distances. A special thermostatic valve is responsible for switching circles, opening the path for coolant into the radiator when it gets too hot. There the antifreeze cools down and returns to the system already cold.
Plug, fan, clogged radiator
These are fairly obvious and easily detectable faults. There may be air in the cooling system, which is noticeable if you notice periodic engine overheating. Getting rid of an air lock is simple - leave the car on a slope for several hours, opening the radiator cap. The air should come out on its own. A sensor in the cabin will tell you that the radiator fan is faulty - the engine temperature will rise sharply. If the fan belt is intact, then it is possible that the sensor itself is broken. Try disconnecting the sensor terminal and forcing the fan to work. You cannot operate the car without a sensor - this is a temporary solution until you change the part.
A clogged radiator is purged or cleaned with special liquids. This is a useful operation that should be performed regularly to get rid of dirt accumulation in the radiator. This type of service can only be performed in a workshop. Radiator clogging occurs much more often in cases where water is poured into the system instead of antifreeze. Sometimes adding household descaling products helps clean the radiator.
What to do when the engine suddenly heats up? Stop driving and stand on the side of the road. Turn on the stove at full power. If the temperature does not drop, turn off the car. Open the hood and wait 20-30 minutes. Do not try to open the cap when the radiator is boiling! Do not try to cool the engine by pouring water on it! When the engine has cooled down, carefully open the reservoir and add fluid. Disconnect the fan terminal so that it operates directly without a sensor. You need to continue driving very carefully, no higher than 50 km/h.
Ways to solve the problem
The cooling system of the internal combustion engine must have such power that on the hottest day, under particularly difficult driving conditions, when the engine produces maximum power and there is almost no oncoming air flowing through the radiator, the temperature gauge needle does not leave the normal zone.
This can only be achieved by using a thermostat - a device that regulates the flow of liquid through the radiator. Naturally, if the thermostat fails in the position of maximum cooling efficiency, the system will work at full capacity of all its capabilities, and it will not be possible to heat the engine to an acceptable temperature under any circumstances.
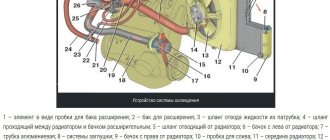
Checking the Thermostat
The simplest way to check the operation of the thermostat is to evaluate the temperature difference between the engine block and the radiator while the engine is warming up.
Until the temperature reaches the point where the thermostat valve begins to open, and this can be 60-90 degrees for different cars with possible deviations in both directions, the radiator should remain relatively cold. A slight heating is acceptable due to leaks associated with the organization of flow through the working element.
After opening, the radiator should quickly warm up, and its temperature will be almost equal to the cylinder head and block. A more accurate diagnosis can be made with a non-contact temperature meter. The shorter the opening stroke of the thermostat, the more the radiator is cooled when air flow is organized through it, for example, by forcibly turning on the fan.
This is how incomplete opening is calculated, but if the radiator and the block warm up synchronously from the very beginning, then the thermostat is faulty, and it no longer matters in what position its valves are stuck
Removing air from the internal combustion engine cooling system
Air in the cooling system almost always causes the opposite effect - overheating of the engine. But there are cars where air locks can cause incorrect readings from the sensor sending a signal to the dashboard. The driver will be misled by the low values of the displayed temperature, although in reality the engine is close to boiling.
Ultimately, everything will warm up and the sensor will record the critical temperature, but the moment will be missed and the engine will be damaged.
To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to take seriously the expulsion of air pockets from the system when replacing antifreeze or topping up to replace the lost one. Usually, the fastenings of the water hoses on the pipes at the highest points of the unit are loosened, after which the air escapes.
Some motors provide special fittings for venting the system. Their presence and location must be known to the driver.
Replacing the DTOZh temperature sensor
Like any measuring device, the coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH) may fail not completely, which would be instantly detected, but partially.
The indicator readings will suffer from serious errors; the driver will be concerned about the reduced temperature of an already hot engine.
The device must be checked using a known accurate thermometer. If fraud is detected, replacement will not cause any difficulties or high costs.
An inexpensive sensor can be easily unscrewed; with some skill, you can quickly insert a new one without losing a lot of fluid or significantly airing the system. But it is still necessary to make sure that there is no plug, as well as to replenish lost antifreeze.
Engine insulation
Most engines are not designed to operate at low temperatures without additional insulation. The instructions avoid this issue, so a driver who notices that a perfectly serviceable and tested engine still cannot warm up in the cold winter, makes sense to take up insulation.
The problem can be divided into two. The first insulation reduces the flow of cold air through the engine compartment while driving, and the second prevents heat from quickly escaping after the engine is turned off while parked.
Both are produced as car accessories for a specific car model. The insulation covering the radiator can be with an adjustable curtain or in the form of blinds. There is even a tendency to resume their serial installation at the factory, as was common in the middle of the last century.
To preserve heat, “car blanket” type protection is used. They are located under the hood and reduce energy leakage. It is better not to make them yourself due to the risk of fire; modern engines contain parts with dangerously high operating temperatures.
Why is the engine cold?
In most cases, the culprit of this problem is the thermostat. It has a movable valve, with the help of which the flow of coolant is redirected. In the case when the valve “hangs” in the open position, the liquid moves in a large circle without having time to warm up to the desired state. You can verify this by checking the temperature of the supply pipes to the radiator. If it is approximately the same, then this is a sure sign of a jammed thermostat.
There are cases from the practice of repairmen when, when purchasing a used car, it was discovered that a “dummy” thermostat was installed. In such a device, a valve is pierced, and the liquid constantly moves in a large circle. In this case, there is only one way out, and that is to replace the thermostat with a new one.
The next obstacle to heating the coolant may be the presence of air in the system. A sure sign of such a problem may be antifreeze leaks. In this case, you need to tighten all the clamps of the connecting pipes and remove air from the system. Important! Do not forget to add antifreeze to the required level in the expansion tank.
Sometimes on a warm engine the gauge shows a low temperature. For early production cars this is not a problem. Modern cars are acutely sensitive to this problem. The engine control unit, receiving unreliable readings from the sensor in the cooling system, reacts incorrectly to its readings. The controller gives a signal to supply an over-enriched fuel mixture. This causes excessive fuel consumption and uneven engine operation.
Causes of malfunction
Arrow stuck on dashboard
It’s probably no secret to anyone that the arrows hanging on the dashboard are inextricably linked with the electrical circuits in the car. To troubleshoot the problem, the car enthusiast will need some knowledge of auto electrics, as well as design knowledge of the VAZ-2114.
As practice shows, most motorists, when such a breakdown occurs, turn to a car service center, but this problem can be eliminated on their own. But, first of all, it is necessary to find the immediate cause of the effect.
What are the options?
So, let's look at the possible options for the engine temperature indicator arrow to hang on the dashboard:
- The magnetic motor of the pointer drive is broken.
- Breaks and disturbances in the operation of the electrical circuits of the dashboard.
- Short circuit in the circuit board of the device itself.
- Freeze related to temperature sensor.
- Problems with the ECU.
Elimination methods
Once the root causes have been identified, you can move directly to methods to resolve the problem.
So, now that the motorist is fully armed, you can proceed directly to the diagnostic and repair process.
The magnetic motor of the arrow drive is broken
The process of repairing and disassembling the dashboard
The most common problem with the arrow hanging or not responding on the instrument panel is a breakdown of the drive motor. To diagnose this device, you need to use a multimeter to close the winding contacts to an electrical circuit or resistance.
To troubleshoot the problem, of course, it is recommended to contact an auto electrician, who will do everything quickly and efficiently, but if the car enthusiast has the necessary skills and abilities in repairing such equipment, then he will be able to independently replace the motor and solder the necessary contacts.
We recommend: Why and how does oil get into antifreeze?
Breaks and disturbances in the operation of the electrical circuits of the dashboard
Wiring related fault determination
Another common reason for a stuck sensor is a break in the electrical circuit from the coolant sensor to the dashboard. It is quite simple to identify this; you need to remove the ground wire from the sensor and connect it to any other “minus” so that the electrical circuit is closed.
If the wire is not broken, then the arrow will begin to move; if not, then according to the electrical diagram it is necessary to find the wire in which the break occurred and eliminate the fault. As practice shows, motorists do not change the wire, but simply connect and insulate the contacts at the break point.
Short circuit in the board of the device itself
Detection of short circuits on the instrument board
But, in this case, an indirect sign is that nearby signs also fail. So, the tachometer and other indicators may not show. Here, troubleshooting is to replace the instrument panel assembly.
Freeze due to temperature sensor
Temperature sensor location
A frozen temperature arrow on the instrument panel will be associated with a faulty temperature sensor. So, its diagnosis can be carried out by analogy with a wiring break, or checked using a tester. If, as a result of diagnostic operations, it turns out that the coolant sensor is faulty, it must be replaced.
Problems with the computer
The process of identifying ECU errors and eliminating them
In this case, using the appropriate cable, you need to connect to the “brains” of the car and see if there are any errors. If there are too many of them, then you need to reset them.
Of course, if this procedure does not help, then it is recommended to reset the software. It is recommended to trust this procedure to professionals who will not only fix the problem, but also set the motor to optimal operating mode.
Other reasons
A malfunctioning thermostat may not be the only reason why the engine does not reach operating temperature.
If the pipes were not tightened well during the previous repair, the car owner is faced with air leaks. Coolant begins to leak. If this is the problem, then you should tighten the clamps for a tighter fit of the tubes and add fluid to the required level in the expansion tank.
In this case, the car owner will see a low temperature on the dashboard, which is insufficient for operation. In fact, the engine will overheat and may even boil.
During the winter season, engine performance is also affected by the use of other systems. So, using a cabin heater can lead to the engine not heating up well, since the stove takes some of the heat onto itself. In this case, you will see how the arrow of the engine temperature indicator drops.
A faulty temperature sensor can cause the engine to feel like it takes a long time to warm up or may not heat up at all. In this case, the engine works properly. The sensor transmits temperature status data to the dashboard. If it does not work correctly, then the readings will be incorrect. Replacing this part will bring all indicators back to normal.
The problem with the sensor is quite serious on modern cars equipped with electronics. Here again you will have to deal with supplying an over-enriched mixture and replacing many other parts.
Checking the Thermostat
To diagnose the malfunction, you should contact a service specialist. However, you can check the thermostat yourself. The cold engine is allowed to idle for approximately 10 minutes. After this, you need to check the radiator pipes. If the thermostat is functioning properly, the hoses will not become hot. The temperature rises only at the moment when the coolant begins to circulate in a large circle.
The coolant enters the large circle only after reaching operating temperature. If the pipes begin to heat up before the specified point, you should immediately contact a technician for further diagnosis and troubleshooting. There are also more professional diagnostic methods using special sensors. Such a check can be carried out at a service station.
If the device does not open and close completely, partial overheating may occur or the temperature will rise, but very slowly. Also, the wedge can be observed only periodically.
Any specified defect requires careful examination and repair. If you do not have the necessary skills and minimal knowledge about the internal structure of a car, you should contact qualified car service specialists.
To remove the thermostat, you must first get rid of the liquid in the system
It is important to wait until the entire system has cooled down before replacing the part. Removing the thermostat is quite simple; to do this, just unscrew the three bolts located on the cover and remove it together with the thermostat
Taking into account all the design features of this model, it can be replaced with an identical or suitable analogue. Well-known brands produce units that can be interchanged, so there are no difficulties with selection. In any case, all manipulations must be carried out by a person who knows exactly what needs to be done, takes into account the make, year of manufacture, and mileage of the car.
It is very important to consider that the cost of this part is quite low, so it would be more appropriate to replace it than to repair it. Thus, you can get rid of problems with low engine temperature for the entire winter season
Since when replacing the thermostat you will have to drain the fluid, it is worth checking the engine for performance before the start of the winter season. Many car owners pour antifreeze into the system and then face the need to replace the unit, therefore paying twice for the coolant.
Thermostat
The main task of the thermostat is to direct coolant through two cooling circuits depending on its temperature. When the engine is cold, the thermostat is closed, but when it warms up it opens, releasing coolant through a large circuit.
If the thermostat is stuck open, the coolant warms up very slowly and the engine temperature gauge shows insufficient heating. It can become jammed as a result of a foreign object getting under the valve. This could be a piece of scale, sealant, or scale. Also, the reason for its failure may be simple wear and tear. In any case, this part must be replaced.
The engine temperature arrow jumps, floats or jumps: causes and main malfunctions
So, normally the needle should rise to a certain value after the internal combustion engine has completely warmed up and not deviate from its occupied position. Note that during driving, small deviations are quite acceptable, and often to a lesser extent.
This phenomenon usually occurs in the cold season, often when driving on the highway. This is explained by the fact that in cold weather the engine is intensively cooled at high speed by counter flows of cold air.
Also, the heater takes away some of the heat from the engine in winter. As a result, the arrow may “fall” a little (by 2-3 mm from normal values). If you reduce the speed or allow the car to run at idle for several minutes, then the temperature gauge will rise to normal.
First, in order to understand why the engine temperature gauge needle jumps, it should be taken into account that changing readings on the indicator do not always mean that in reality such significant changes in the temperature of the internal combustion engine occur.
In other words, a change in readings within the average range of 75-95 degrees does not reflect the actual picture, since heated coolant (antifreeze, antifreeze) cannot heat up and cool down so quickly. It turns out that the indicator does not display the actual engine temperature.
Otherwise, a smooth change in readings can be taken as the norm, making allowances for the conventional error of the dial or digital indicator itself. Moreover, if temperature fluctuations do not exceed acceptable limits, it is likely that this is the operating temperature of the engine.
A cause for concern is chaotic, usually sharp fluctuations of the needle, and the amplitude of such fluctuations is quite large. In this situation, it is necessary to determine whether there really is a violation of the thermal balance, whether the indicator itself is working normally, and also for what reasons the malfunction occurred.
So, let's go. If the system is sealed and the coolant level in the expansion tank is normal, then the most frequently failing element, on which the engine temperature directly depends, is the cooling system thermostat. Moreover, this device often fails even on completely new cars with minimal mileage. So it’s better to start checking with the thermostat.
In practice, this manifests itself as follows: when the driver first warms up the engine, the temperature needle rises to operating temperatures, then the thermostat opens. Next, the coolant flows in a large circle, the engine temperature decreases, but then the thermostat jams and does not close completely.
Naturally, the liquid continues to flow partially or completely through the radiator (in a large circle). As a result, the engine begins to cool down and the temperature gauge drops. Then the thermostat will either close, after which the coolant will heat up to operating temperatures, or it will remain stuck in the jammed position and the engine will not warm up completely.
In this case, often after stopping the engine and the pressure in the cooling system drops, the needle will first rise to normal temperatures as it warms up, but then after the thermostat opens, everything will repeat again. There are also cases when the thermostat may not jam constantly, but every once in a while, and may not allow coolant access to a large circle.
In this case, the engine will overheat. It happens that the operation of the thermostat is disrupted both in opening and closing, that is, it is appropriate to talk about a combination of problems. One way or another, you need to make sure that the thermostat is working properly and normally.
Now let's look at a situation where the engine temperature needle is jumping, but the thermostat and other elements of the cooling system are fine. In this case, the problem may be in the coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH). It turns out that if the temperature needle jumps, the culprit is often an incorrect signal from the temperature sensor.
This means that you need to check the specified sensor
It is important to take into account that many cars may have 2, 3 or even 4 such sensors. These sensors are also located in different places depending on the design of a particular internal combustion engine
At this time, the assistant must monitor whether the temperature indicator on the instrument panel in the car interior fluctuates. Often, poor contact causes the temperature needle to fluctuate, while the cooling system works normally.
The engine does not reach operating temperature
You can monitor the temperature readings of the power unit directly from inside the car. The dashboard of all modern cars has a small information field, usually round or semicircular in shape, showing the driver the coolant temperature readings. This is the device that gives an idea of the temperature conditions in which the engine is operating at a given time.
If the temperature gauge does not reach 90 degrees during a long trip, you should seriously think about finding the cause of the deviation from the normal operation of the power unit. It is not recommended to delay its diagnosis, because prolonged operation of the motor in this mode will lead to wear of its internal components.
The fact is that the electronic control unit, which is popularly called the “brains” of the car, recognizes an engine that has not reached the nominal temperature as cold, and therefore the fuel system injects an over-enriched mixture.
Working in this mode leads to heavy carbon deposits on the spark plugs and, accordingly, on the internal elements of the engine, which in the future will lead to the need for a major engine overhaul.
Does the heater affect the engine temperature gauge?
The inclusion and constant operation of the cabin heater has no less a strong impact than malfunctions or frost. It is especially noticeable on small cars and models equipped with medium-sized engines. The situation is also typical for diesel engines, which not only do not warm up well at idle, but also cool down quickly when driving with insufficient intensity.
The car heater has a special radiator, which is included in the general operating circuit of the cooling system. When the driver turns on the interior heating, antifreeze passes through it, giving off some of the heat. The amount that will be given depends on the set temperature of the heater and its operating mode. The higher these indicators are, the more the interior of the car will heat up.
If the engine operates at low speeds, and is also used in winter, there may simply not be enough heat to fully warm up the coolant. In such a situation, the engine will not reach its operating temperature.
Causes and consequences of overheating
The engine gets very hot. Absolutely all car owners are facing or will face this problem. You can forget about it in winter, but you will definitely remember about it as soon as the ambient temperature approaches 30-35°C. And this happens in almost any region, at least for a few weeks, no matter how “northern” it is considered.
But first you need to figure out why the power unit of your car is heating up. The reasons for this can be very different. For example, a likely cause is failure (or severe wear) of the rotating impeller blades of a water pump. Your pump cannot create a constant movement of coolant in the system. When the engine is idling for a long time, for example, the car is stopped in a traffic jam, the antifreeze remains in the block and begins to boil. And all that can be done to prevent the engine from heating up is to purchase a new water pump. Below we will look at some more common causes of overheating.
Tips for improving engine warm-up
In order for the car to be operated in optimal operating mode of the power unit, several rules must be followed:
- The car owner must monitor the quality of the cooling system. Periodic diagnostics require not only the thermostat and fan, but also the antifreeze itself. It is necessary to maintain its regulated quantity, avoiding minimum values. Air pockets must be removed from the system and any leaks must be eliminated. The coolant also needs timely replacement. The amount of its functional resource is determined individually for each individual model.
- Traveling in the cold season should be carried out in medium speed mode, at the level of 3000-3500. It is recommended to use a lower gear more often, especially when driving on the highway.
- An excellent solution would be to insulate the engine compartment. Even the presence of ordinary cardboard inserted in front of the cooling radiator can improve the situation. If the owner covers the engine compartment with porous materials or felt, the engine will warm up noticeably faster, and its natural cooling will no longer have a significant effect on operation.
The thermostat is broken
A thermostat is a special component in a car that regulates the temperature in the cooling system. It closes and opens the valve that directs the flow through the so-called “small” or “large” (through the radiator) cooling circle. The thermostat is an important part, and if it malfunctions, it will cause serious overheating of the engine.
In the old days, drivers, owners of Soviet cars in the southern regions of the country, simply pulled out the thermostat for summer time and operated the car without it. You can check the operation of the thermostat by touch by touching the upper pipe leading to the cooling radiator. If the engine is cold when the engine is running, it means the fluid is not reaching the radiator. Thermostats are tested using a container of boiling water. The device in it should work - open slightly for a few seconds. If this does not happen, the part is faulty and must be replaced.
The temperature needle drops. Why?
The most common problems are when the temperature of the unit increases uncontrollably, reaching critical values. The cause of overheating is a jammed thermostat, which does not allow the coolant to pass through the radiator. The heated antifreeze continues to circulate in a small circle until it boils.
The opposite situation often occurs when the engine temperature gauge drops while driving. Why? The point, again, is the quality of operation of the mentioned valve. If the thermostat cannot close all the way, allowing the fluid to continuously circulate in a large circle, the engine will not warm up to its operating temperature.
Sometimes the thermostat gets stuck after the engine has warmed up. When this happens, the driver may notice that the engine temperature drops while driving, although it should be maintained at a consistently even, operating level.
Sometimes the temperature regime changes abruptly, sometimes increases, sometimes decreases sharply. This means that the valve periodically jams, and the driver will notice a situation where the temperature arrow periodically drops.
The engine temperature arrow does not rise, the engine temperature fluctuates, the engine cools down while driving
The time it takes for the engine to warm up to operating temperature may vary for each serviceable unit. This happens because the heating and its intensity depend on a number of conditions. The warm-up speed can be affected by the power of the engine, its type (gasoline/diesel), the general condition of the cooling system, the quality of the fill, the outside temperature, the degree of load when driving, the intensity of the heater in the cabin, and so on.
Let us add that many experts agree that different types of motor oils and their viscosity can also affect the overall heating of the engine, although only slightly. The operating temperature of the oil in a conventional engine is around 100-150 degrees, not exceeding the maximum threshold of about 200 degrees (all indicators are averaged). In parallel with this, the maximum oil temperature in the engine is determined by the flash point of the oil, its coking, etc.
It may seem that the temperature range will be the same for different oils, but this is not the case. Special additive packages that reduce friction losses and the base itself () affect the degree of oil heating. In other words, low-viscosity oils cool rubbing couples better, but the lubricant itself heats up more. It turns out that with different engine oils, the temperature in the crankcase of the same engine can differ by 5-7 degrees. If we take into account these features, then we can assume that with “liquid” synthetics, the engine will not only be easier to start in winter, but will also warm up faster.
So, let's return to the cooling system. A cold engine and a non-working stove in most cases are the consequences of malfunctions. If you notice that the power unit takes a very long time to heat up and the engine does not warm up to operating temperature, then you should start checking with this device.
The thermostat allows heated coolant to enter the radiator. This circulation through the radiator is called a large circle. The thermostat opens strictly at a certain temperature on different internal combustion engines (on average about 90 degrees Celsius), that is, up to the specified value, the liquid circulates only in a small circle. Problems begin when the thermostat stops opening or closing in a timely manner. If it does not open, then the engine overheats. If the thermostat is open all the time, the antifreeze will constantly circulate only in a large circle, and the engine will not warm up to operating temperature.
The temperature of the Kalina 8 valve engine does not rise
- To the beginning of the forum
- Forum Rules
- Old design
- FAQ
- Search
- Users
A friend of mine has a Kalina, 1.6 engine. for some reason the temperature does not rise above 85-90. The thermostat was changed, there seem to be no bubbles, the radiator is covered - no use.
This is the factory thermostat. It’s the same for me.
Added after 1 minute 2 seconds:
With my original thermostat, the temperature on the dashboard was always well below 90. I replaced the thermostat, and now the temperature is not much below 90.
For the winter I bought a ween insert and sharpened it.
This is a thermocouple in the thermostat. Opening temperature 85 degrees. Where does it come from?
I waited for the temperature to reach 87 degrees. I pulled it out and cooled it down. In theory, if you cool it down, it should again be 7mm? Or am I not getting it?
It turned out that the temperature along the highway was about 92
But I can’t heat it above 82-84. It also happens 81-80. This is with a tightly sealed radiator. And I checked the lower pipe today - it was cold. And I removed the cardboards - it didn’t help.
Added after 1 minute 41 seconds:
I measured its temperature and just cut it a couple of mm.
Information on icons and features
You can not
start topicsYou
cannot
reply to messagesYou
cannot
edit your messagesYou
cannot
delete your messagesYou
cannot
vote in pollsYou
can
attach filesYou
can
download files
Source
Engine temperature sensor
Another important aspect. This sensor often fails and, as a result, the engine temperature gauge does not rise. This can happen during severe shaking, after an accident or off-road driving without preparation. As a result, the wire leading to the temperature sensor may be damaged and the engine temperature indicator will provide incorrect information.
It is quite simple to understand that the temperature gauge needle will not deviate when the engine is fully warmed up. It is quite easy to change. It is enough to unscrew the old one, install the new one and connect the wire to it. If the temperature sensor fails, if you are not careful, it can lead to serious engine damage. It can simply overheat, which can easily result in deformation of the cylinder head. This is an expensive and time-consuming repair.
Engine overheating: main signs and causes
Let's start with the signs. First of all, this is the engine temperature indicator on the dashboard in the red zone. Also, on some models, a warning light may simply light up, indicating overheating.
Another sign of engine overheating is a decrease in engine power, loss of traction and detonation knocks when you sharply press the gas pedal or simply when accelerating. The reason is that the combustion process in the cylinders is disrupted due to an increase in temperature (explosions of the working mixture instead of combustion).
Let's move on
It is important to understand that the normal operating temperature of the engine is 85-95 degrees Celsius. Also acceptable is the engine temperature up to 100 degrees or even 105, especially if such an increase is short-term (up to 5 minutes)
Drivers often encounter this situation when sitting in a traffic jam in the heat.
Causes of engine overheating
Overheating can be caused by many reasons, all of them are related to a malfunction of the cooling system, or the quality of the coolant, as well as contamination of the cooling system jacket, which impairs the fluid throughput
It is important to use high-quality spare parts, otherwise the reasons below will happen suddenly. Let's consider each of the reasons
Low coolant level
The most common problem is a lack of coolant in the system. Coolant, in the form of antifreeze or antifreeze, constantly circulates through the system, removing heat from heated engine parts. If the coolant level is insufficient, the heat will not be removed sufficiently, which means an increase in temperature will be inevitable.
_
If it is not possible to add coolant, then turn on the heater to reduce the likelihood of overheating. As a last resort, add regular or distilled water, after which the cooling system must be flushed and then filled with fresh antifreeze. At temperatures above 90 degrees, you should immediately stop the car, turn off the ignition, and allow the engine to cool.
Electric cooling fan failed
The electric fan forces cool air onto the radiator, which is especially necessary when driving at low speeds when there is insufficient air flow. The fan can be installed either in front or behind the radiator. If the temperature arrow starts to rise, stop the car and check the fan for serviceability. Reasons for fan failure:
- electric motor failed
- connector oxidized
- fan relay burnt out
- The internal combustion engine temperature sensor has failed.
To check the fan, remove the connectors from it and connect the wires directly to the battery, which will allow you to determine the cause of the failure.
Thermostat malfunction
The thermostat is one of the main elements of the cooling system. The cooling system has two circuits: small and large. A small circuit means that fluid circulates only through the engine. In a large circuit, fluid circulates throughout the system. The thermostat helps you quickly reach and maintain operating temperature. Thanks to the sensitive element, which opens the valve at 90 degrees, the liquid enters a large circle, and vice versa. The thermostat is considered faulty in two cases:
- operating temperature of the coolant is not reached
- the power unit tends to overheat.
The thermostat can be located directly in the cylinder block, in a separate housing, or as one unit with a temperature sensor and pump.
Broken cooling fan belt
On vehicles with a longitudinally mounted engine, the fan can be driven by a drive belt from the crankshaft pulley. In this case, the fan works forcibly. The service life of the drive belt is from 30 to 120 thousand km. Typically, several units are driven by one belt. When a belt breaks, the internal combustion engine immediately tends to overheat, especially when the speed decreases. If you have a domestic car with a belt-driven fan, it is recommended to install an additional electric fan to avoid unpleasant incidents.
Dirty radiator
Once every 80-100 thousand kilometers it is necessary to flush the radiator along with the entire cooling system. The radiator becomes clogged for the following reasons:
- untimely replacement of antifreeze
- use of low-quality liquid
- application in water system
- application of cooling system sealant.
To wash the radiator, you should use special compounds that are added to old antifreeze; the engine runs on this “mixture” for 10-15 minutes, after which you need to remove water from the system. It is advisable to remove the radiator and wash it with water under pressure, inside and out.
Signs of engine overheating
There is a gauge on the dashboard that displays the engine temperature. However, the driver often does not pay attention to it while driving, and may miss the moment the temperature in the engine rises. Therefore, every driver needs to know and recognize the first signs of engine overheating. Let's look at each one separately.
Recommended article: The operating principle of the internal combustion engine is used in modern cars
One of the external signs can be identified in cold weather. When the heater is running, warm air stops flowing into the car interior. The reason for this is a decrease in the coolant level.
ATTENTION! The supply of warm air stops before the coolant boils. The first signs are detonation, which appears when the combustion mode of a flammable liquid fails due to a temperature jump in the combustion chamber
Characteristic knocking noises appear in the engine due to heating of the coolant
The first signs are detonation, which appears when the combustion mode of a flammable liquid fails due to a temperature jump in the combustion chamber. Characteristic knocking noises appear in the engine due to heating of the coolant.
Periodic knocking in the engine and a decrease in its power indicate overheating. It is necessary to stop and allow the engine to cool.
Cold radiator
The other day I noticed that the coolant level in the reservoir was below minimum. Added more. A few days later I decided to check it in the garage (after some driving and proper warming up). I discovered that the ext. the tank is cold. I touched the radiator - it was also cold. The pipe that goes up from the thermostat is hot, and the pipe that goes down is cold. Before shutting down the engine, the fans worked like propellers. Moreover, after some time (after it was turned off), the radiator began to slowly warm up from the edges towards the center. What do you think? Thermostat? This warming just confused me. Or is this normal at T = -15C? If it’s a thermostat, what would be suitable or is it better to look for the original? Why is further driving scary (without fanaticism)? Pace. on the instrument panel - normal, heats up quickly, the stove is steaming.
Causes of diesel engine overheating
Diesel can overheat for various reasons. The cooling system is responsible for maintaining the operating temperature of the diesel engine within strictly limited limits. To monitor and detect rapid increases or decreases in engine temperature, there is a separate indicator on the dashboard of most cars.
As practice shows, it is not always possible to timely identify deviations from the norm while driving. You should also take into account possible malfunctions of the diesel engine temperature sensor or the indicator on the instrument panel. Direct and indirect signs of diesel engine overheating can include:
- constant operation of the cooling system fan at maximum rotation speed in idle mode (if there is an electric drive);
- increased noise and vibration levels during internal combustion engine operation, loss of power, detonation knocks;
- the appearance of white steam from the engine compartment, which became noticeable while driving;
Low coolant level and leakage
One of the most common causes of overheating is a lack of coolant in the diesel engine cooling system. The coolant tends to evaporate over time, since the constituent component is distilled water. In this case, it is necessary to add water or dilute the antifreeze/antifreeze concentrate with water in the required proportion, and only then pour the resulting mixture into the expansion tank.
Carefully! It is strictly forbidden to check the level and add coolant to the expansion tank until the engine has cooled. Increased pressure is created in the cooling system, as a result of which liquid can splash out of the filler neck and cause serious burns. It is also prohibited to pour liquid into a hot engine, so as not to damage the engine due to the temperature difference between the heated power unit and fresh cooling liquid. If an intense drop in level is noticed after adding coolant, then you should visually inspect the pipes and connections, the radiator, the expansion tank itself, as well as the location of the water pump (pump) of the cooling system for cracks or other damage, as well as leaks
It is also forbidden to pour liquid into a hot engine, so as not to damage the engine due to the temperature difference between the heated power unit and fresh cooling fluid. If an intense drop in level is noticed after adding coolant, then you should visually inspect the pipes and connections, the radiator, the expansion tank itself, as well as the location of the water pump (pump) of the cooling system for cracks or other damage, as well as leaks.
Another reason for a drop in coolant level may be cracks in the cylinder block or cylinder head, as well as damage to the head gasket. If these damages affect the channels through which coolant circulates (engine cooling jacket), then some of the liquid from the cooling system may enter the cylinders of the diesel engine, as well as the lubrication system of the diesel internal combustion engine.
Radiator and thermostat
If the coolant level is normal, but the engine temperature is noticeably higher than permissible, then overheating of the diesel engine may also be associated with a decrease in the efficiency of cooling the liquid in the radiator. Contaminated radiator honeycombs do not allow this element of the cooling system to perform heat exchange normally. In this case, the radiator must be thoroughly washed.
A diesel engine can also overheat due to thermostat malfunctions, namely when the diesel engine thermostat is stuck opening. A constantly closed thermostat does not open as the engine temperature increases, forcing the fluid to move only along a small circuit (small circle). This means that the coolant does not pass in a large circle (through the radiator) for cooling.
Other faults
A critical increase in diesel engine temperature may be caused by a malfunction of the cooling system fan or diesel engine temperature sensor. Another reason for diesel overheating is severe contamination of the internal channels of the cooling system, which prevents the normal circulation of coolant.
It is also worth noting the incorrect adjustment of the fuel injection advance angle. For this reason, the temperature of the exhaust gases increases significantly, as a result of which the overall temperature of the diesel engine increases, especially under load. The pump deserves special attention. Destruction of the water pump blades and other breakdowns reduce the efficiency of coolant circulation through the system and cause diesel overheating.
Faulty sensors
The engine temperature shown on the dashboard is data from a sensor installed on the engine. The sensor from which the readings are transmitted to the computer determines the temperature of the antifreeze in the thermostat. To control the engine, data from the coolant temperature sensor (coolant temperature sensor), a sensor next to the thermostat, is used.
If the VAZ 2114 does not heat up and there is a possibility that the sensors are faulty, it is better to contact a car service center to have their operation checked by a qualified technician.
What to do first
In order not to get buried in the abundance of reasons, it is necessary to act from simple to complex. Leave the frightening thoughts of a broken cylinder head gasket and take a trifling attitude, as if the electric damper actuator has failed. Actually, that's where we'll start.
Check the operation of the climate control shutters
Turn the knob or rocker of the climate system and evaluate the temperature of the incoming air. For example, with “blue all the way” the air should be noticeably cold, and with the maximum red settings it should be warmer.
Immobilized valves will not be able to mix flows according to the specified °C value. Therefore, at any position of the regulator, air will blow at the same temperature. The dampers stop as a result of damaged fasteners or a failed servomotor.
Is the antifreeze level in the expansion tank stable?
Lift the hood, find the “extender” and the boundary marks on it. When cold, the antifreeze level should be between the MIN and MAX marks. If the tank is constantly emptying, look for leaks. You can look at where the coolant goes using the Lada Vesta as an example.
Heater radiators of some cars, for example Lada Kalina, are very sensitive to the amount of antifreeze in the expansion tank. At the slightest leak, the engine heats up, and the stove is cold or barely warm. And in general, when liquid flows out, air comes in and thus the system becomes airy.
Inspect the heater radiator for unobstructed circulation
Find two pipes going to the heater heat exchanger near the engine shield and touch them. The radiator assembly is embedded in a small circle in parallel, which means that the hoses should warm up immediately after starting the engine. It is better to carry out work when the engine is warmed up.
How to remove an air lock without draining the coolant
It happens that if there is air in a small circuit, the temperature sensor on the dashboard behaves strangely: the needle sometimes jumps. For example, it was at 60°C and instantly became 90-100°C, then returned back. This is explained by the fact that the air heats up noticeably faster than the liquid and to higher temperatures. As a rule, the needle twitches when the system is seriously aired.
The fact is that a small traffic jam does not always go around the entire small circle. Air accumulates at the highest point of the circuit - the radiator of the car furnace, causing the circulation of coolant in it to slow down. At the same time, there are no sudden temperature changes in the motor jacket. Even without observing extraneous symptoms, assume that the engine is overheating and the cabin heater is blowing cold air due to air accumulation. Try to etch it out, because you don’t need to disassemble anything:
- Raise the front end on a lift or drive up a hill.
- Allow air to escape through the highest point in the system. Why unscrew the cap of the expansion tank if it is a circulation tank (there is no plug on the engine radiator), or the cover of the engine heat exchanger. On front-wheel drive Ladas, the highest point is the throttle heating hose, disconnect it.
- Warm up the engine to operating temperature at idle speed.
- Increase the speed to 2,500-2,700 units.
How to easily remove a dirt plug from a furnace heat exchanger
When one side of the heater radiator is cold and the other is hot + no antifreeze is coming out, feel free to flush the heater radiator installation. There is no need to remove anything except the pipes. The only equipment that will be useful is a submersible pump from a country well, a deep basin, long hoses and one of the means for flushing the car engine cooling system.
Find out where the heat exchanger has the inlet and outlet and start cleaning:
- Disconnect the standard tubes. When dismantling the pipes, 1-1.5 liters will drain. coolant. A 2-3 liter coolant canister is quite enough to replenish reserves. There is no need to drain all the antifreeze from the system.
- Connect the hoses leading to the pump and basin: supply to the radiator outlet, drain to the inlet.
- Fill the container with cleaning agent.
- Turn on the pump for 10-15 seconds.
- Reconnect the hoses: supply - to the inlet of the heat exchanger, drain - to the outlet.
- Turn on the pump for 15-20 minutes.
- The flushing composition will circulate in a circular manner: from the basin and back into it.
- A short supply of fluid in the opposite direction quickly flushes out the dirt plug at the radiator inlet.
- Check whether antifreeze flows from the radiator steam pipes into the tank (relevant for circulation “expanders”).