Repairing, removing or replacing the catalyst is a procedure that owners of cars more than 5 years old often face.
- Diagnostics
- Common options for replacing a catalytic converter Repair and replacement of the Suzuki SX4 1.6L catalyst with a flame arrester. Video:
Purchase of catalysts: metal, ceramic, particulate filters - https://dragincat.ru/
Depending on the design of the exhaust system, the nature of the damage and the wishes of the car owner, the problem of a faulty catalytic converter can be solved in several ways. Read more about all aspects of repairing and replacing a faulty catalyst below.
There is a similar article on this topic - Pros and cons of replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester.
A Brief History of Catalytic Converters
The first standard regulating the amount of harmful emissions in exhaust gases appeared in 1988. Then it received the name EURO-0. This standard was almost never applied in practice. In fact, restrictions on the amount of emissions were only on paper.
In 1992, the EURO-1 standard was approved. And here, mainly for European countries, truly working restrictions have appeared for newly produced cars.
However, hazardous substance requirements have not become a big problem for automakers. And it was possible to achieve the required indicators by optimizing the operation of the power and ignition system. Even then, attempts were made to implant the first versions of neutralizers into the production systems. But there was no widespread use at that time.
After the introduction of the new EURO-2 environmental standard in 1995, achieving the required exhaust purity for some engines without the use of additional cleaning agents became problematic. For example, requirements only for the content of carbon monoxide in exhausts have increased 3 times.
Not all manufacturers decided to radically modify their engines.
And for them, the solution was found in the introduction of a special device into the exhaust system: a catalytic converter.
Today, the current standard in the EU and America is EURO-6. And to achieve the requirements of this environmental class, complex, multi-stage cleaning systems are used, which cannot be compared with the first versions of catalytic converters.
The principle of operation of the flame arrester
During operation, the flame arrester receives exhaust gases that enter the exhaust system, processes them and removes them. At the exit, the temperature of the gases becomes significantly lower, and their speed drops significantly.
In addition, the flame arrester breaks the primary flow of gases that come from the collector. This approach is used for the purpose of stable operation of the main resonator.
In addition, the flame arrester mixes all the unstable flows ufpjd from the cylinders into one stable flow. Thanks to the design of the body of the part itself, the flame arrester significantly reduces the level of noise that appears inside it due to the beating of gases.
Automotive catalyst device
To better understand how serious the consequences of operating a car with a broken catalytic converter can be, let's look at the design of the exhaust gas treatment system.
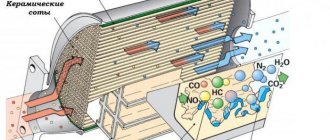
The catalytic converter consists of a base (metal or ceramic) coated with a coating of noble metals. The base is shaped like a cylinder or ellipsoid with through longitudinal channels.
The maximum cross-section of the channels, as a rule, does not exceed 1-2 mm. The entire surface of these channels is covered with a thin layer of noble metals and their alloys with some other chemical elements.
The base is placed in the exhaust tract closer to the engine. Typically, a small layer of elastic, heat-resistant material is placed between the metal body of the line and the base of the neutralizer. This protects the catalyst from mechanical damage.
The total area of all catalyst cells should ideally be equal to the diameter of the section of the exhaust tract in which it is installed. This solution prevents turbulence and pressure drops in the exhaust flow.
On engine versions with classes from EURO-3 and higher, a monitoring sensor is installed after the section of the line where the catalytic converter is located. It checks the efficiency of the cleaning system in real time.
In some car modifications, several catalysts are installed in the system. This depends on the type of engine, its power and the design decisions of the automaker.
For example, on V-shaped engines with separated exhaust lines, 2 or 4 catalysts are often installed.
Operating principle of the catalyst
The essence of how a catalytic converter works lies in its name. In the presence of high temperatures and noble metals such as platinum, rhodium and iridium, environmentally hazardous chemical compounds contained in exhaust gases are converted into harmless ones.
It is important to understand that the metals themselves do not participate in the reactions. They only initiate and accelerate the decomposition of certain substances.
Exhaust gases from gasoline engines contain three main categories of harmful substances that are subject to mandatory control in accordance with EURO standards.
- Carbon monoxide. A dangerous chemical compound that has an extremely negative impact on human health. After passing through the catalyst, it is converted into safe carbon dioxide and water.
- Nitric oxide. A compound harmful to nature and the atmosphere. When passing through the catalyst, it decomposes into gaseous diatomic nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water.
- Hydrocarbons. Mostly falls in the form of solid precipitation. But they can also be gaseous. It all depends on the structure of the hydrocarbon. They are converted after passing through the neutralizer into carbon dioxide and water.
Currently, catalytic converters are a complex cleaning complex consisting of several sections. Each of the catalyst sections is responsible for its part of the chemical transformations. After cleaning, exhaust gases become tens of times less dangerous for the environment and human health compared to their original composition.
Removing the catalyst. Video:
Cleaning methods and products used
Car enthusiasts and service station technicians practice 3 methods of cleaning the catalyst from oil deposits and soot:
- Preventive cleaning with detergent is carried out at a mileage of 70–100 thousand km without removal from the car.
- Mechanical cleaning.
- Repeated washing.
The last 2 options involve dismantling and partial disassembling of the neutralizer.
For preventive maintenance of catalysts, special fluids such as Hi-Gear HG3270 are available for sale. The product is simply poured from the bottle into the fuel tank, and then the car is operated as before. The soot removed from the unit flies out along with the exhaust gases.
For mechanical cleaning, you need to have a compressor and prepare fine sandpaper. The method cannot be called successful, since only external contaminants are removed; part of the soot remains deep in the ceramic honeycomb.
Factors that reduce the life of the catalytic converter
The catalytic converter-neutralizer is usually calculated for 200-300 thousand kilometers. But this is under ideal conditions. In practice, this element fails much earlier. There are several reasons for early catalytic converter failure.
- Poor quality fuel. The problem of low-quality fuel is most significant for technological purification systems: EURO-5 and EURO-6. Today, downright bad fuel is becoming less and less common. But this factor is still relevant.
- Problems in the power supply, ignition and gas distribution systems. Untimely fuel injection, ignition malfunctions, and incorrect valve timing lead to an increase in temperature in the exhaust tract and accelerated destruction of the catalyst.
- General engine wear. Penetration of oil into the combustion chamber is considered especially unfavorable. Oil clogs the honeycomb and increases the temperature in the line. And this inevitably affects the durability of the neutralizer.
- Mechanical impact. Even a small blow to the housing in which the catalyst is placed can damage it.
In most cases, under the influence of the above factors, problems with the catalytic converter appear after 50-100 thousand kilometers.
Main breakdowns and signs of catalyst malfunctions
There are several known catalytic converter malfunctions. Let's first consider common breakdowns, then their manifestations. More than 95% of all problems with the catalyst are the following faults:
- decrease in operating efficiency due to clogging of honeycombs with soot and oily deposits or due to erosive destruction of active spraying;
- a drop in catalyst throughput, which is usually caused by melting of the base;
- mechanical destruction (cracks, chips, breaking into several parts).
There are also several signs of a broken catalytic converter.
- Error on the dashboard.
- Reduced power and acceleration of the car. The engine begins to “dull”, the car accelerates worse, and the maximum speed drops.
- Startup problems. The engine starts reluctantly, often stalls and is unstable at idle.
- The appearance of a pronounced smell of exhaust gases, more pungent than usual.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Slight increase in engine operating temperature.
Typically, all these manifestations are signs of a clogged catalyst. They most often appear in complexes, but there are also isolated manifestations. The first three signs appear more often than others and more clearly indicate problems with the catalyst.
The last three are complementary and, together with others, increase the likelihood that the problem really lies in the exhaust gas cleaning system.
Diagnostics
Checking the condition of the catalytic converter is possible without the use of specialized tools used at service stations. However, the result is not 100% reliable. If the efficiency of the catalyst is difficult to assess without testing for CO-CH at a service station, its throughput can also be measured in a garage.
How to check the catalyst for clogging without removing it? The simplest and most reliable method of self-diagnosis is to measure the so-called back pressure. This phenomenon occurs in the exhaust tract when the catalyst is clogged and exhaust gases cannot move freely along the highway.
To check, you will need a regular pressure gauge and a hose for it with an adapter for the thread of the oxygen sensor installed in front of the catalyst. Unscrew the sensor, connect the pressure gauge, start the engine and give 3-4 thousand revolutions. The pressure should not rise above 0.3-0.4 kg/cm3.
For cars with EURO-4 standards and higher, you can check the pressure after the catalyst by unscrewing the control sensor. The difference in readings before and after the neutralizer should not exceed 20-30%.
Together with other symptoms of a clogged catalyst described in the previous paragraph, this method provides almost one hundred percent reliability of the test results.
Gentle methods
There are the mildest ways to clean the catalyst using modern automotive chemistry. In addition, the dismantled device can be cleaned by prolonged soaking and subsequent removal of contaminants mechanically.
Additives
Modern specialized stores offer a wide selection of special products that are intended for washing and restoring the neutralizer. They are very easy to use. To do this, you need to pour the contents of the bottle into the fuel tank of the car.
But it should be remembered that it is impossible to clean a heavily contaminated catalyst only by chemical means. It is advisable to use these additives for preventive purposes, with low levels of contamination or wear. Regular use of such products can increase the life of the device.
Soaking and removing deposits
It is better to dismantle a heavily contaminated neutralizer and try to clean it using special chemicals, ethanol, or carburetor fluid.
This can be done by following the following algorithm:
- dismantle the exhaust manifold with pre-catalyst by unscrewing two nuts;
- carefully check the integrity of all cells;
- If there is no mechanical damage, start washing.
It should be taken into account that in case of subsidence or burnout, the catalyst must be replaced.
Flushing using carburetor fluid is required according to the following scheme:
- first prepare a plastic container of sufficient depth for vertical immersion of the neutralizer;
- water the honeycombs of the device generously;
- wrap the part with dampened rags and place inside the container;
- after 20-30 minutes, rinse the honeycombs under hot water pressure;
- dry and blow out the catalyst with compressed air;
- repeat this procedure again.
If this procedure does not bring the expected results, then you can try kerosene.
DIY catalyst repair
A severely clogged, melted, cracked or cracked catalytic converter cannot be repaired. It is possible to repair only a catalyst that is not very clogged, in which the cross-section of the passage channels is reduced due to blockages, or plaque has formed on the end surface of the base.
A relatively effective solution is cleaning. How to clean the catalyst? Depending on the degree and nature of the contamination, two methods are practiced: mechanical or chemical cleaning.
1. Mechanical cleaning is rarely used. It consists of cutting out a section of the exhaust system with an installed catalyst, carefully disassembling it, removing and mechanically removing deposits from the end surface of the base.
It requires a careful and scrupulous approach and is not always an effective measure. Often it is either impossible to clean the catalyst at all, or during the cleaning process it is damaged to an unusable state.
2. Chemical cleaning of the catalyst is a more common method. It is important to understand that the chemical method is rather a preventive measure. If the catalyst is clogged to the point of almost complete clogging, then no amount of chemicals will help.
There are two fundamentally different methods. One involves adding a special reagent to the fuel, which gradually removes contamination from the surface of the honeycomb. The method is effective as a preventive measure, nothing more.
I often use a special catalyst cleaner. This is a special chemical composition in which the base is immersed for some time. To use this method, the neutralizer must be dismantled. In not very advanced cases, a chemical catalyst cleaner copes with the task quite effectively.
Common Catalytic Converter Replacement Options
In the overwhelming majority of cases in Russia and post-Soviet countries, a failed catalyst is not restored, but removed. The usual removal and installation of the hollow pipe in its place (or simply cutting the base out of the body) is not the most effective solution.
The parameters laid down by the system design are violated. This leads to an increase in the temperature of individual elements of the exhaust tract and increased exhaust sound.
The following solutions are considered more effective, which are practiced much more often than the banal removal of the catalytic converter:
- Replacement with original catalytic converter. An expensive and not always justified measure. An indisputable plus is that the proper operation of the exhaust gas cleaning system is guaranteed.
- Installation of a universal catalyst. It will cost less than replacing the original. Today there are quite a lot of replacements for original catalysts on the market. It makes sense to consider only universal catalysts from the middle and higher price segments. As practice has shown, cheap options are unable to effectively clean exhaust. This results in an error on the dashboard.
- Installing a flame arrester or stronger instead of a catalyst. The optimal solution, which is practiced today more often than all others combined. Firstly, the microclimate in the exhaust system is maintained. Secondly, the flame arrester not only cools the exhaust and reduces the thermal load on subsequent elements of the system, but also dampens sound vibrations. That is, the machine starts to run quieter.
If you replace the catalyst with a flame arrester or stronger, the purification of exhaust gases will stop. This will cause the ECU to constantly display the error on the dashboard: “Ineffective catalyst operation.” On some car models, this error automatically affects the engine operating mode.
To bypass this control system, a special device, the so-called snag, is installed on the second catalyst sensor. There are several types of deceptions.
1. A simple mechanical snag. It is made in the form of an adapter with a calibrated hole (less gases pass to the sensor and creates the illusion of the cleaning system working) or in the form of an insert between the lambda probe and the exhaust tract with a small piece of catalyst placed inside.
Locally purifies gases entering the sensor. Which is also perceived as normal operation of the system. Such sensors are suitable for almost all EURO-3 and some EURO-4 systems.
2. Electronic catalyst blende. It is implanted into the electrical circuit of the oxygen control sensor. Consists of a capacitor and resistor.
Modifies the electrical signal sent to the ECU, thereby creating the illusion that the catalyst is working properly. Used on engines operating according to EURO-4. Sometimes it works on some engines with the EURO-5 environmental class.
3. Electronic modulator. Complex device. Installed in the open circuit between the lambda probes and the ECU. An advanced version of the usual electronic decoy. Works where simple devices based on a resistor and capacitor cannot cope.
Generates the signal expected from the oxygen control sensor based on the readings of the system sensor, which is placed in front of the catalyst.
ECU firmware is also practiced. This measure allows you to forget about the catalyst error forever without using tricks.
However, such a decision often has a negative impact on engine performance. Not all freely available firmwares work correctly.
Repair and replacement of the Suzuki SX4 1.6l catalyst with a flame arrester. Video:
Is it worth replacing: the pros and cons of the solution
As mentioned above, the issue is controversial. And he is surrounded by a huge number of the most controversial rumors and speculations circulating in the car enthusiast community. Here are the most popular ones:
- after installing a flame arrester, the service life of the muffler is significantly reduced;
- the car becomes noisier;
- the car engine wears out much faster;
- It will be impossible to drive a car with a fire extinguisher installed, since the driver and passengers risk getting burned right in the cabin;
- a car with a flame arrester causes more harm to the environment;
These are all subjective judgments of individuals. Perhaps only the last point is fair: the flame arrester is really not able to clean exhaust gases the way a catalyst does. The conclusion is simple: for the vast majority of drivers in our country, the decisive issue is price. If a car service center offers you to pay about a third of the cost of your car for a new catalyst, then the issue in favor of installing a flame arrester can be considered resolved. The low cost of the flame arrester is the only, but very serious plus that can outweigh all the myths associated with this device.